Abstract
This study focuses on the mineralogy and bulk chemical composition of 19 sediment samples, collected from the Sanaga River bed, between Nanga-Eboko and the Atlantic Ocean in Cameroon, to infer provenance, weathering, and tectonic setting. The textural analysis revealed that these sediments are mainly coarse-grained sands. X-ray diffraction and heavy mineral analyses show that these sands are made of quartz, microcline, plagioclase, muscovite, ilmenite, anatase, magnetite, opaques, and epidote. The Index of Chemical Variability values (1.07–2.68) indicates that the sands are immature. The Chemical Index of Alteration (53–66 %), Plagioclase Index of Alteration (PIA; 57–75 %), and Mafic Index of Alteration (54–67 %) values revealed a moderate intensity of weathering for these sediments. According to the compositional maturity diagram, the sands are mainly litharenites. The studied sands show enrichment in light rare earth elements relative to heavy rare earth elements and a negative anomaly in Eu (Eu/Eu* = 0.32–0.83). These sands were derived from felsic metamorphic rocks dated Meso to Neoproterozoic from the Pan-African (700–1000 Ma) domain of south Cameroon. Th/U ratios (mean = 5.40; n = 19) reveal that these sands originating from felsic source rocks and are low to moderately recycled. On the tectonic discrimination diagrams, all the samples are plotted in the rift and passive margin domains, which is consistent with the tectonic history of Pan African in southern Cameroon.

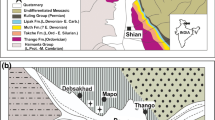
(after Tchakounté et al. 2017)


(after Rudnick and Gao 2003)

(after Herron 1988)

(after Rudnick and Gao 2003)









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability material
All data are available upon request.
References
AFNOR (1998) NF P 94–068 Sols: reconnaissance et essai. Mesure de la capacité d’absorption de bleu de méthylène d’un sol ou d’un matériau rocheux. AFNOR, Paris
Anaya-Gregorio A, Armstrong-Altrin JS, Machain-Castillo ML, Montiel-Garcia PC, Ramos Vazquez MA (2018) Textural and geochemical characteristics of Late Pleistocene to Holocene fine-grained deep-sea sediment cores (GM6 and GM7), recovered from southwestern Gulf of Mexico. J Palaeogeogr 7(3):253–271
Armstrong-Altrin JS (2009) Provenance of sands from Cazones, Acapulco, and Bahía Kino beaches. Rev Mex Cien Geol 26(3):764–782
Armstrong-Altrin JS, Ramasamy N, Balaram V, Olmedo NP (2015) Petrography and geochemistry of sands from the Chachalacas and Veracruz beach areas, western Gulf of Mexico: constraints on provenance and tectonic setting. J S Am Earth Sci 64:199–216
Armstrong-Altrin JS, Lee YI, Kasper-Zubillaga JJ, Trejo-Ramírez E (2017) Mineralogy and geochemistry of sands along the Manzanillo and El Carrizal beach areas, southern Mexico: implications for palaeoweathering, provenance, and tectonic setting. Geol J 52(4):559–582
Armstrong-Altrin JS, Ramos-Vázquez MA, Zavala-León AC, Montiel-García PC (2018) Provenance discrimination between Atasta and Alvarado beach sands, western Gulf of Mexico, Mexico: constraints from detrital zircon chemistry and U-Pb geochronology. Geol J 53:2824–2848
Babechuk MG, Widdowson M, Kamber BS (2014) Quantifying chemical weathering intensity and trace element release from two contrasting basalt profiles, Deccan Traps, India. Chem Geol 363:56–75
Bah MLM, Hiroaki I (2016) Geochemical classification and determination of maturity source weathering in Beach Sands of Eastern San’ in Coast, Tango Peninsula, and Wakasa Bay, Japan. Earth Sci Res 5:542–550
Bhaskar JS, Satya RG, Borthakur R, Indu BR, Rashmi RB (2015) Spectroscopic characterization and quantitative estimation of natural weathering of silicates in sediments of Dikrong River, India. J Modern Phys 6:1631–1641
Bhuiyan MAH, Rahman MJJ, Dampare SB, Suzuki S (2011) Provenance, tectonics and source weathering of modern fluvial sediments of the Brahmaputra-Jamuna River, Bangladesh: inference from geochemistry. J Geochem Explor 111:113–137
Bock B, McLennan SM, Hanson GN (1998) Geochemistry and provenance of the Middle Ordovician Austin Glen Member (Normanskill Formation) and the Taconian Orogeny in New England. Sedimentology 45:635–655
Cox RN, Lowe DR, Cullers RL (1995) The influence of sediment recycling and basement composition on evolution of Mudrock chemistry in the South-Western United States. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59(14):2919–2940
Cullers RL (2000) The geochemistry of shales, siltstones and sandstones of Pennsylvanian-Permian age, Colorado, USA: implications for provenance and metamorphic studies. Lithos 51:18–1203
Cullers RL (2002) Implications of elemental concentrations for provenance, redox conditions, and metamorphic studies of shales and limestones near Pueblo, CO, USA. Chem Geol 191:305–327
Cullers RL, Basu A, Suttner L (1988) Geochemical signature of provenance in sand-size material in soils and stream sediments near the Tobacco Root batholith, Montana, USA. Chem Geol 70:335–348
Djomeni AL, Ntamak-Nida MJ, Mvondo Owono F, Fowe Kwetche AL, Iboum Kissaaka JB, Mooh-Enougui E (2011) Soft-sediment deformation structures in Mid-Cretaceous to Mid-Tertiary deposits, Centre East of the Douala sub-basin, Cameroon: preliminary results of the tectonic control. Syllabus Rev 2(3):92–105
Duplaix S (1958) Détermination microscopique des minéraux des sables, 2ème édition révisée, Librairie polytechnique ch. Béranger, Paris et Liège
Dzana JG, Ndam Ngoupayou JR, Tchawa P (2010) The Sanaga discharge at the Edea catchment outlet (Cameroon): an example of hydrologic responses of a tropical rainfed river system to changes in precipitation and groundwater inputs and to flow regulation. River Res Appl 3:100. https://doi.org/10.1002/rra.1392
Etemad-Saeed N, Hosseini-Barzi M, Adabi MH, Sadeghi A, Houshmandzadeh A (2015) Provenance of Neoproterozoic sedimentary basement of northern Iran, Kahar Formation. J Afr Earth Sci 111:54–75
Fedo CM, Nesbitt HW, Young GM (1995) Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary soils and paleosols, with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance. Geology 23:921–924
Garzanti E, Resentini A (2016) Provenance control on chemical indices of weathering (Taiwan river sands). Sediment Geol 336:81–95
Garzanti E, Andò S, France-Lanord C, Galy V, Censi P, Vignola P (2011) Mineralogical and chemical variability of fluvial sediments. 2. Suspended-load silt (Ganga-Brahmaputra, Bangladesh). Earth Planet Sci Lett 302:107–120
Guo Y, Yang S, Su N, Li C, Yin P, Wang Z (2018) Revisiting the effects of 28 hydrodynamic sorting and sedimentary recycling on chemical weathering indices. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 227:48–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2018.02.015
Hernández-Hinojosa V, Montiel-García PC, Armstrong-Altrin JS, Nagarajan R, Kasper-Zubillaga JJ (2018) Textural and geochemical characteristics of beach sands along the Western Gulf Of Mexico, Mexico. Carpath J Earth Environ 13(1):161–174. https://doi.org/10.26471/cjees/2018/013/015
Herron MM (1988) Geochemical classification of terrigenous sands and shales from core or log data. J Sediment Petrol 58:820–829
Madhavaraju J, Saucedo-Samaniego JC, Loser H, Espinoza-Maldonado IG, Solari L, Monreal R, Grijalva-Noriega FJ, Jaques-Ayala C (2018) Detrital zircon record of Mesozoic volcanic arcs in the Lower Cretaceous Mural Limestone, North western Mexico. Geol J. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.3315
Maharana C, Srivastava D, Tripathi JK (2018) Geochemistry of sediments of the Peninsular rivers of the Ganga basin and its implication to weathering, sedimentary processes and provenance. Chem Geol 483:1–20
Mbale NE, Sababa E, Bayiga C, Ekoa BZA, Ndjigui P-D (2019) Mineralogical and geochemical characterization of the unconsolidated sands from the Mefou River terrace Yaoundé area, Southern Cameroun. J Afr Earth Sci 159:1–14
McDonough WF, Sun S-S (1995) Composition of the earth. Chem Geol 120:223–253
McLennan SM, Hemming SR, McDaniel DK, Hanson GN (1993) Geochemical approaches to sedimentation provenance and tectonics. Geol Soc Am Spec Pap 284:21–40
Messanga PA, Efon B, Ntamack D, Tatietse TT (2019) Multicriterial analysis and choice of hydrological models in tropical zone: application to the Sanaga Watershed in Cameroon. Int J Civil Eng Technol 10:505–520
Moussango IAP, Mvondo Owono F, Njom BSP, Mbog Bassong JP, Nlomngan Sep, Owona S, Ekodeck GE (2018) Sanaga fault: evidence of Neotectonics and Landscape Evolution in Edéa Region (Cameroon, Centre-Africa). J Geogr Geol 10(3):57–79. https://doi.org/10.5539/jgg.v10n3p57
Nagarajan R, Armstrong-Altrin JS, Kessler FL, Jong J (2017) Petrological and geochemical constraints on provenance, paleo-weathering and tectonic setting of clastic sediments from the Neogene Lambir and Sibuti Formations, northwest Borneo. In: Mazumder R (ed) Sediment provenance. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 123–153
Ndam Ngoupayou JR, Dzana JG, Kpoumie A, Tanwi Ghogomu R, Fouepe Takounjou A, Braun JJ, Ekodeck GE (2016) Present-day sediment dynamics of the Sanaga catchment (Cameroon): from the total suspended sediment (TSS) to erosion balance. Hydrol Sci J. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2014.968572
Ndjigui P-D, Beauvais A, Fadil-Djenabou S, Ambrosi JP (2014) Origin and evolution of Ngaye River alluvial sediments, Northern Cameroon: geochemical constraints. J Afr Earth Sci 100:164–178
Ndjigui P-D, Ebah Abeng SA, Ekomane E, Nzeukou NA, Ngo Mandeng FS, Lindjeck MM (2015) Mineralogy and geochemistry of pseudogley soils and recent alluvial clastic sediments in the Ngog-Lituba region, Southern Cameroon: an implication to their genesis. J Afr Earth Sci 108:1–14
Ndjigui P-D, Onana VL, Sababa E, Bayiga EC (2018) Mineralogy and geochemistry of the Lokoundje alluvial clays from the Kribi deposits, Cameroonian Atlantic coast: Implications for their origin and depositional environment. J Afr Earth Sci 143:102–117
Ndjigui P-D, Bayiga EC, Onana VL, Djenabou-Fadil S, Ngono GSA (2019) Mineralogy and geochemistry of recent alluvial sediments from the Ngaye River water shed, northern Cameroon: implications for the surface processes and Au-PGE distribution. J Afr Earth Sci 150:136–157
Ndome EPE, Onana VL, Boubakar L, Kamgang KBV, Ekodeck GE (2014) Relationships between major and trace elements during weathering processes in a sedimentary context: implications for the nature of source rocks in Douala, Littoral Cameroon. Chem Erde-Geochem 74:765–781
Ndougsa-Mbarga T, Gouet DH, Bisso V, Meying A, Manguele-Dicoum E (2012) Imaging the subsurface in the Cameroon centre region using the audio-magnetotellurics (AMT) soundings for the monitoring of the Monatélé-Sa’a Earthquake Area. J Earth Sci Geotechn Eng 3(4):107–123
Nesbitt HW, Young GM (1982) Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature 299:715–717
Nesbitt HW, Young GM (1984) Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic-rocks based on thermodynamic and kinetic considerations. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48(7):1523–1534
Ngapna MN, Owona S, Owono FM, Mpesse JE, Youmen D, Lissom J, Ondoa JM, Ekodeck GE (2018) Tectonics, lithology and climate controls of morphometric parameters of the Edea-Eseka region (SW Cameroon, Central Africa): implications on equatorial rivers and landforms. J Afr Earth Sci 138:219–232
Ngon Ngon GF, Etame J, Ntamak-Nida MJ, Mbesse CO, Mbai JS, Bayiga EC, Gerard M (2016) Geochemical and palaeoenvironmental characteristics of Missole I iron duricrusts of the Douala sub-basin (Western Cameroon). CR Geosci 348(2):127–137
Ngueutchoua G, Ekoa BAZ, Eyong TJ, Demanou DZ, Baba DH, Tchami NF (2019) Geochemistry of cretaceous fine-grained siliciclastic rocks from Upper Mundeck and Logbadjeck Formations, Douala sub-basin, SW Cameroon: implications for weathering intensity, provenance, paleoclimate, redox condition, and tectonic setting. J Afr Earth Sci 152:215–236
Nyeck B, Ngimbous RV, Ndjigui PD (2019) Petrology of saprolitedeveloped on gneisses in the Matomb region, South Cameroon. J Afr Earth Sci 150:107–122
Nzeukou NA, Fagel N, Njoya A, Beyala Kamgang V, Eko Medjo R, Melo Chinje U (2013) Mineralogy and physico-chemical properties of alluvial clays from Sanaga valley (Center Cameroon): suitability for ceramic application. Appl Clay Sci 83–84:238–243
Parfenoff A, Pomerol C, Tourenq J (1970) Les minéraux en grains méthodes d’études et détermination. Masson et Cie, Paris
Purevjav N, Roser B (2013) Geochemistry of Silurian- Carboniferous sedimentary rocks of the Ulaanbaatar terrane, Hangay-Hentey belt, central Mongolia Provenance, paleoweathering, tectonic setting, and relationship with the neighboring Tsetserleg terrane. Chem Erde-Geochem 73:481–493
Ramos-Vázquez MA, Armstrong-Altrin JS, Machain-Castillo ML, Gío-Argáez FR (2018) Foraminiferal assemblages, 14C ages, and compositional variations in two sediment cores in the western Gulf of Mexico. J S Am Earth Sci 88:480–496
Ramoz-Vásquez MA, Armstrong-Altrin JS (2019) Sediment chemistry and detrital zircon record in the Bosque and Paseo del Mar coastal areas from the southwestern Gulf of Mexico. Mar Petrol Geol 110:650–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.07.032
Regard V, Carretier S, Boeglin J-L, Ngoupayou J-RN, Dzana J-G, Bedimo J-P, Riotte J, Braun J-J (2016) Denudation rates on cratonic landscapes: comparison between suspended and dissolved fluxes, and 10Be analysis in the Nyong and Sanaga River basins, south Cameroon. Earth Surf Process Landf 41:1671–1683
Rivera-Gómez MA, Armstrong-Altrin JS, Verma SP, Díaz-González L (2020) APMdisc: an online computer program for the geochemical discrimination of siliciclastic sediments from active and passive margins. Turk J Earth Sci 29:550–578. https://doi.org/10.3906/yer-1908-15
Roddaz M, Viers J, Brusset S, Baby P, Boucayrand C, Hérail G (2006) Controls on weathering and provenance in the Amazonian foreland bassin: insights from major and trace element geochemistry of Neogene Amazonian sediments. Chem Geol 226:31–65
Rosales-Hoz L, Machain-Castillo ML, Carranza-Edwards A (2017) Geochemistry of deep-sea sediments in two cores retrieved at the mouth of the Coatzacoalcos River delta, western Gulf of Mexico. Mexico Arab J Geosci 10(6):148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2934-z
Roser BP, Korsch RJ (1988) Provenance signatures of sandstone-mudstone suites determined using discrimination function analysis of major-element data. Chem Geol 67:119–139
Rudnick RL, Gao S (2003) The composition of the continental crust. In: Rudnick RL (ed) The crust. Elsevier-Pergamon, Oxford, pp 1–64
Sangen M, Eisenberg J, Kankeu B, Runge J, Tchindjang M (2010) Preliminary results on palaeoenvironmental research carried out in the framework of the second phase of the resako-project in the upper catchments areas of the Nyong and Sanaga Rivers in Cameroon. Palaeoecol Afr 30:165–188
Schneider S, Hornung J, Hinderer M, Garzanti E (2015) Petrography and geochemistry of modern river sediments in an equatorial environment (Rwenzori Mountains and Albertine rift, Uganda)—implications for weathering and provenance. Sediment Geol 336:106–119
Silva MMVG, Cabral Pinto MMS, Carvalho PCS (2016) Major, trace and REE geochemistry of recent sediments from lower Catumbela River (Angola). J Afr Earth Sci 115:203–217
Tawfik HA, Salah MK, Maejima W, Armstrong-Altrin JS, Abdel-Hameed A-MT, El Ghandour MM (2017) Petrography and geochemistry of the Lower Miocene Moghra sandstones, Qattara Depression, north Western Desert, Egypt. Geol J. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.3025
Taylor S, McLennan S (1985) The continental crust: its composition and evolution. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford, p 312
Tchakounté J, Eglinger A, Toteu SF, Zeh A, Nkoumbou C, Mvondo Ondoa J, Penaye J, de Wit M, Barbey P (2017) The Adamawa-Yadé domain, a piece of Archaen crust in the Neoproterozoic Central African Orogenic belt (Bafia area, Cameroon). Precambrian Res 299:210–229
Tchameni R, Pouclet A, Penaye J, Ganwa AA, Toteu SF (2006) Petrography and geochemistry of the Ngaoundéré Pan-African granitoids in Central North Cameroon: implications for their sources and geological setting. J Afr Earth Sci 44:511–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2005.11.017
Velmurugan K, Madhavaraju J, Balaram V, Ramasamy S, Ramachandran A, Ramirez-Montoya E, Saucedo-Sama-Niego JC (2019) Provenance and tectonic setting of the clastic rocks of the Kerur Formation, Badami Group, Mohare area, Karnataka, India. In: Mondal MEA (ed) Precambrian crustal evolution of India: geological evolution of the precambrian indian shield, 1st edn. Society of earth scientist series. Springer, Berlin, pp 239–269
Verma SP, Armstrong-Altrin JS (2013) New multi-dimensional diagrams for tectonic discrimination of siliciclastic sediments and their application to Precambrian basins. Chem Geol 355:117–133
Verma SP, Armstrong-Altrin JS (2016) Geochemical discrimination of siliciclastic sediments from active and passive margin settings. Sediment Geol 332:1–12
von Eynatten H, Tolosana-Delgado R, KariusV Bachmann K, Caracciolo L (2016) Sediment generation in humid Mediterranean setting: grain-size and source-rock control on sediment geochemistry and mineralogy (Sila Massif, Calabria). Sediment Geol 336:68–80
Wentworth CK (1922) A scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediments. J Geol 30(5):377–392
Yvon J, Garin P, Delon JF, Cases JM (1982) Valorisation des argiles kaolinitiques des Charentes dans le caoutchouc naturel. Bull Minér 105:535–541
Acknowledgements
We express our gratitude to the GeoLabs (Sudbury-Canada) for mineralogical and geochemical analyses. We also thank anonymous reviewers who have greatly improved the quality of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nanga Bineli, M.T., Onana, V.L., Noa Tang, S. et al. Mineralogy and geochemistry of sands of the lower course of the Sanaga River, Cameroon: implications for weathering, provenance, and tectonic setting. Acta Geochim 40, 348–365 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-020-00437-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-020-00437-z