Abstract
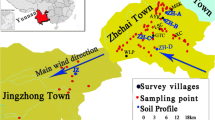
To assess the potential ecological and health risks of trace elements (Hg, Cd, As, Mn, Sb, Pb, Cu, Ni, Cr, and Zn), a total of 138 soil samples from rice paddies were collected during the rice harvest season in the Wanshan mining area, Guizhou Province, Southwest China. Factors of the pollution load index (PLI), geo-accumulation index (I-Geo), enrichment factor (EF), and risk index (RI) were determined. High concentrations of Hg, Sb, As, Zn, Cd, Cu, and Mn were observed in the soils. The PLI, I-Geo, and EF results all showed high levels of contamination by Hg and Sb and moderate levels of contamination by As, Pb, Zn, Cu, Cd, and Mn. There was no significant contamination from Ni and Cr. The RI was very high, with Hg as the dominant pollutant, as expected, indicating that the historical large-scale Hg mining, as well as artisanal mining, has had a significant impact on the Wanshan area. Moreover, coal combustion, manganese factories, and the use of agrochemicals by the local population could also have an impact on the soil through the introduction of heavy metal loads. To address the current state of contamination, pollutant remediation and the regulation control of the anthropogenic activities in Wanshan are urgently needed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham GMS, Parker RJ (2008) Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki estuary, Auckland, New Zealand. Environ Monit Assess 136(1–3):227–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9678-2
Adedosu HO, Adewuyi GO, Adie GU (2013) Assessment of heavy metals in soil, leachate and underground water samples collected from the vicinity of olusosun landfill in Ojota, Lagos, Nigeria. Transnatl J Sci Technol 3(6):73–86
Al-Anbari R, Abdul Hameed MJ, Obaidy A, Fatima HAA (2015) Pollution loads and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the urban soil affected by various anthropogenic activities. Int J Adv Res 2:104–110
Begum K, Mohiuddin KM, Zakir HM, Moshfiqur Rahman M, Nazmul Hasan M (2014) Heavy metal pollution and major nutrient elements assessment in the soils of Bogra City in Bangladesh. Can Chem Trans 3:316–326
Chakravarty M, Patgiri AD (2009) Metal pollution assessment in sediments of the Dikrong River, N.E India. J Hum Ecol 27:63–67
Chen H, Teng Y, Lu S, Wang Y, Wang J (2015) Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci Total Environ 512–513:143–153
Clarkson TW (1998) Human toxicology of mercury. J Trace Elem Exp Med 11:303–317. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1520-670X(1998)11:2/3%3c303:AID-JTRA18%3e3.0.CO;2-V
Dai Z, Feng X, Fu X, Li P (2012) Spatial distribution of mercury deposition fluxes in Wanshan Hg mining area, Guizhou, China. Atmos Chem Phys 12(2):5739–5769. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-12-6207-2012
Dai Z, Feng X, Zhang C, Wang J, Jiang T, Xiao H, Li Y, Wang X, Qiu G (2013) Assessing anthropogenic sources of mercury in soil in Wanshan Hg mining area, Guizhou, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(11):7560–7569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1616-y
Díez MM, Simón F, Martín C, Dorronsoro I, García CAM, Van G (2009) Ambient trace element background concentrations in soils and their use in risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 407:4622–4632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.05.012
Fagbote EO, Olanipekun EO (2010) Evaluation of the status of heavy metal pollution of soil and plant (Chromolaena odorata) of Agbabu Bitumen Deposit Area, Nigeria. Am Eurasian J Sci Res 4:241–248
Fan Y, Zhu T, Li M, He J, Huang R (2017) Heavy metal contamination in soil and brown rice and human health risk assessment near three mining areas in Central China. J Healthc Eng 2017:9, Article ID 4124302 https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4124302
Feng X (2005) Mercury pollution in China—An overview. In: Pirrone N, Mahaffey KR (eds) Dynamics of mercury pollution on regional and global scales. Springer, Boston, pp 657–678. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-387-24494-8_27
Feng X, Qiu G (2008) Mercury pollution in Guizhou, Southwestern China—an overview. Sci Total Environ 400:227–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.05.040
Feng X, Qiu G, Wang S, Shang L (2003) Distribution and speciation of mercury in surface waters in mercury mining areas in Wanshan, Southwestern China. J Phys IV Fr 107:455–458. https://doi.org/10.1051/jp4:20030339
Feng X, Li P, Qiu G, Wang SF, Li GH, Shang LH, Meng B, Jiang H, Bai W, Li ZG, Fu XW (2008) Human exposure to methylmercury through rice intake in mercury mining areas, Guizhou Province, China. Environ Sci Technol 42:326–332. https://doi.org/10.1021/es071948x
Gong Q, Deng J, Xiang Y, Wang Q, Yang L (2008) Calculating pollution indices by heavy metals in ecological geochemistry assessment and a case study in parks of Beijing. J China Univ Geosci 19:230–241
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
He S (1998) Geochemical background of supergene sediments in Guizhou. Guizhou Geology 15:149–156
Hernandez L, Probst A, Probst JL, Ulrich E (2003) Heavy metal distribution in some French forest soils: evidence for atmosphere contamination. Sci Total Environ 312:195–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(03)00223-7
Hu Y, Liu X, Bai J, Shi K, Zeng EY, Cheng H (2013) Assessing heavy metal pollution in the surface soils of a region that had undergone three decades of intense industrialization and urbanization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:6150–6159
Inengite AK, Abasi CY, Walter C (2015) Application of pollution indices for the assessment of heavy metal pollution in flood impacted soil. Int Res J Pure Appl Chem 8:175–189
Li P, Feng X, Shang L, Qiu G, Meng B, Liang P, Zhang H (2008) Mercury pollution from artisanal mercury mining in Tongren, Guizhou, China. Appl Geochem 23:2055–2064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.04.020
Li P, Feng X, Qiu G, Shang L, Wang S (2012) Mercury pollution in Wuchuan mercury mining area, Guizhou, Southwestern China: the impacts from large scale and artisanal mercury mining. Environ Int 42:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2011.04.008
Li P, Zhang J, Wang J, Li Z (2015) Heavy metal (loid) pollution in mine wastes of a Carlin-type gold mine in Southwestern Guizhou, China and its environmental impacts. Chin J Geochem 34(3):311–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-015-0055-5
Lin Y, Larssen T, Vogt RD, Feng X, Zhang H (2011a) Modelling transport and transformation of mercury fractions in heavily contaminated mountain streams by coupling a GIS-based hydrological model with a mercury chemistry model. Sci Total Environ 409:4596–4605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.07.033
Lin Y, Larssen T, Vogt RD, Feng X, Zhang H (2011b) Transport and fate of mercury under different hydrologie regimes in polluted stream in mining area. J Environ Sci 23(5):757–764. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1001-0742(10)60473-1
Lindqvist O, Johansson K, Bringmark L, Timm B, Aastrup M, Andersson A, Meili M (1991) Mercury in the Swedish environment—recent research on causes, consequences and corrective methods. Water Air Soil Pollut 55(1–2):xi–261. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00542429
Liu JY (1998) The influence of environmental pollution on eco-agriculture systems in Guizhou Province. Guizhou Environ Prot Sci Technol 4:40–44 (in Chinese)
Müller G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine river. J Geol 2:108–118
Ololade IA (2014) An assessment of heavy-metal contamination in soils within auto-mechanic workshops using enrichment and contamination factors with geoaccumulation indexes. J Environ Prot 5:970–982
Omatoso OA, Ojo OJ (2015) Assessment of some heavy metals contamination in the soil of river Niger floodplain at Jebba, central Nigeria. Water Util J 9:71–80
Qiu G, Feng X, Wang S, Shang L (2005) Mercury and methylmercury in riparian soil, sediments, mine-waste calcines, and moss from abandoned Hg mines in east Guizhou province, Southwestern China. Appl Geochem 20:627–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.09.006
Qiu G, Feng X, Wang S, Xiao T (2006) Mercury contaminations from historic mining to water, soil and vegetation in Lanmuchang, Guizhou, Southwestern China. Sci Total Environ 368:56–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.09.030
Qiu G, Feng X, Wang S, Fu X, Shang L (2009) Mercury distribution and speciation in water and fish from abandoned Hg mines in Wanshan, Guizhou Province, China. Sci Total Environ 407:5162–5168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.06.007
Romić M, Romić D (2003) Heavy metal distribution in agricultural topsoils in urban area. Environ Geol 43:795–805. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-002-0694-9
Schroeder WH, Munthe J (1998) Atmospheric mercury—an overview. Atmos Environ 32(5):809–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(97)00293-8
SEPAC (State Environmental Protection Administration of China) (1995) Chinese environmental quality standard for soils (GB 15618-1995)
Shotyk W, Blaser P, Grunig A, Cheburkin AK (2000) A new approach for quantifying cumulative, anthropogenic, atmospheric lead deposition using peat cores from bogs: Pb in eight swiss peat bog profiles. Sci Total Environ 249:281–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00523-9
Søvika ML, Larssen T, Vogt RD, Wibetoe G, Feng X (2011) Potentially harmful elements in rice paddy fields in mercury hot spots in Guizhou, China. Appl Geochem 26:167–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.11.015
Sutherland RA (2000) Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ Geol 39:611–627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050473
Tomlinson DL, Wilson JG, Harris CR, Jeffrey DW (1980) Problems in assessment of heavy metals levels in estuaries and formation of pollution index. Helgol Mar Res 33(1):566–575. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02414780
Wu Y, Wang S, Streets D, Hao J, Chan M, Jiang J (2006) Trends in anthropogenic mercury emissions in China from 1995 to 2003. Environ Sci Technol 40:5312–5318. https://doi.org/10.1021/es060406x
Xu X, Liu N, Landis MS, Feng X, Qiu G (2016) Characteristics and distributions of atmospheric mercury emitted from anthropogenic sources in Guiyang, Southwestern China. Acta Geochim 35(3):240–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-016-0111-9
Xu X, Meng B, Zhang C, Feng X, Gu C, Guo J, Bishop K, Xu Z, Zhang S, Qiu G (2017) The local impact of a coal-fired power plant on inorganic mercury and methyl-mercury distribution in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Pollut 223:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.11.042
Xu X, Gu C, Feng X, Qiu G, Shang L, Xu Z, Lu Q, Xiao D, Wang H, Lin Y, Larssen T (2019) Weir building: a potential cost-effective method for reducing mercury leaching from abandoned mining tailings. Sci Total Environ 651:171–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.150
Zhang L, Ye X, Feng H, King Y, Ouyang T, Yu X, Liang R, Gao C, Chen W (2007) Heavy metal contamination in Western Xiamen Bay sediments and its vicinity, China. Mar Pollut Bull 54:974–982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2007.02.010
Zhang H, Feng X, Larrsen T, Shang L, Vogt RD, Rotherberg SE, Li P, Zhang H, Lin Y (2010) Fractionation, distribution and transport of mercury in rivers and tributaries around Wanshan Hg mining district, Guizhou Province, Southwestern China, part 1-total mercury. Appl Geochem 25:633–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.01.006
Zhou H, Guo X (2015) Soil heavy metal pollution evaluation around mine area with traditional and ecological assessment methods. J Geosci Environ Prot 3:28–33. https://doi.org/10.4236/gep.2015.310005
Acknowledgements
Financial support was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41573135) and the Opening Fund of the State Key Laboratory of Environmental Geochemistry (SKLEG No.2019716).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adlane, B., Xu, Z., Xu, X. et al. Evaluation of the potential risks of heavy metal contamination in rice paddy soils around an abandoned Hg mine area in Southwest China. Acta Geochim 39, 85–95 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-019-00364-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-019-00364-8