Abstract
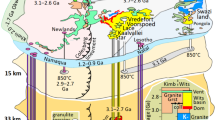
The high-Mg mafic dykes from the Singhbhum Granitoid Complex in East India have geochemical characteristics [e.g., enrichment of the large ion lithophile elements and light rare earth elements (LREEs) relative to high field strength elements (HFSEs): high-MgO (>8 %), high-SiO2 (≥52 %), low-TiO2 (≤0.5 %), and high CaO/Al2O3 (≥0.58)] similar to those found in boninitic/noritic rocks. Their high percentage of orthopyroxene as a mafic mineral and of plagioclase as a felsic mineral, and normative hypersthene content greater than diopside content are also indications of their boninitic/noritic affinity. On a triangular diagram of MgO-CaO-Al2O3 and on binary diagrams of Ti/V vs Ti/Sc and TiO2 vs Zr, these samples show geochemical similarities with Phanerozoic boninites and Paleoproterozoic high-Mg norites. On major and trace element variation diagrams, these dykes show a normal crystallization trend and their Nb/La (<0.5) and Nb/Ce (<0.21) values lower than average bulk crust (0.69 and 0.33, respectively) suggest no crustal contamination. Their low values of Rb/Sr (0.11–0.41) and Rb/Ba (0.10–0.27) also suggest little or no effect of post magmatic processes. Their TiO2 (0.27–0.50), Al2O3 /TiO2 (19.30–42.48), CaO/TiO2 (12.96–32.52), and Ti/V (12–18) values indicate derivation from a depleted mantle source under oxidizing conditions such as a mantle wedge. Ni vs Zr modeling shows that the studied high-Mg dykes were generated by 25–30 % melting of a refractory mantle source. Enrichment of Rb, Th, U, Pb, Sr, and LREEs, and depletion of HFSEs—especially Nb, P, Ti, Zr—on primitive mantle—and chondrite-normalized spider diagrams, respectively, are clear signals that the slab-derived component played an important role in the formation of melts for these rocks in a supra-subduction zone setting.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahijado A, Casillas R, Hernandez-Pacheco A (2001) The dyke swarms of the Amanay Massif Fuerteventura, Canary Islands (Spain). J Asian Earth Sci 19:333–345
Ahmad T, Tarney J (1991) Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Garhwal volcanics: implications for evolution of the north Indian lithosphere. Precambrian Res 50:69–88
Ahmad T, Tarney J (1994) Geochemistry and petrogenesis of late Archean Aravalli volcanics, basement enclaves and granitoids, Rajasthan. Precambrian Res 65:1–23
Alvi SH, Raza M (1991) Nature and Magma type of Jagannathpur volcanics, Singhbhum, Eastern India. J Geol Soc India 38:524–531
Alvi SH, Raza M (1992) Discovery of Proterozoic boninite from Jaganathpur volcanic suite, Singhbhum craton, Eastern India. Curr Sci 62(8):573–574
Arculus RJ (1994) Aspects of magma genesis in arcs. Lithos 33:189–208
Arndt NT, Brögmann GE, Lenhert K, Chappel BW, Chauvel C (1987) Geochemistry, petrogenesis and tectonic environment of Circum-Sperior Belt basalts, Canada. In: Pharaoh TC, Beckinsdale RD, Rickard D (eds) Geochemistry and mineralisation of proterozoic volcanic suites. Blackwell, London
Balaram V, Gnaneshwara Rao T (2003) Rapid determination of REEs and other trace elements in geological samples by microwave acid digestion and ICP-MS. Atomic Spectr 24:206–212
Banerjee PK (1982) Stratigraphy, petrology and geochemistry of some Precambrian basic volcanic and associated rocks of Singhbhum district, Bihar and Mayurbhanj and Koenjhar districts, Orissa. Mem Geol Surv India 111:58
Bose MK (2000) Mafic–ultramafic magmatism in the eastern Indian craton-a review. Mem Geol Surv India 55:227–258
Bose MK (2009) Precambrian mafic magmatism in the Singhbhum Craton, Eastern India. J Geol Soc India 73:13–35
Bryan SE, Ernst RE (2008) Revised definition of Large Igneous Provinces (LIPs). Earth Sci Rev 86:175–202
Cameron WE, McCulloch MT, Walker DA (1983) Boninite petrogenesis: chemical and Nd-Sr isotopic constraints. Earth Planet Sci Lett 65:75–89
Condie KC, Sinha AK (1996) Rare earth and other trace element mobility during mylonitization: a comparison of the Brevard and Hope Valley shear zones in the Appalachian Mountains, USA. J Metamorph Geol 14:213–226
Crawford AJ (1989) Boninites and related rocks. Unwin Hyman, London, p 465
Dawoud M, Eliwa HA, Traversa G, Attia MS, Itaya T (2006) Geochemistry, mineral chemistry and petrogenesis of a Neoproterozoic dyke swarm in the north Eastern Desert, Egypt. Geol Mag 143:115–135
De Paolo DJ (1981) Trace element and isotopic effects of combined wallrock assimilation and fractional crystallization. Earth Planet Sci Lett 53:189–202
Dunn JA (1929) Geology of North Singhbhum including parts of Ranchi and Mayurbhanj districts. Mem Geol Surv India 54(2):1–166
Dunn JA (1940) The stratigraphy of South Singhbhum. Mem Geol Surv India 63(3):303–369
Farahat ES (2006) The Neoproterozoic Kolet Um Kharit bimodal metavolcanic rocks, south Eastern Desert, Egypt: a case of enrichment from plume interaction. Int J Earth Sci 95:275–287
Hall RP, Hughes DJ (1987) Norite dykes of southern Greenland, early proterozoic boninitic magmatism. Contrib Miner Petrol 97:169–182
Hall RP, Hughes DJ (1990a) Norite magmatism. In: Hall RP, Hughes DJ (eds) Early Precambrian basic magmatism. Blackie, Glasgow, pp 83–110
Hall RP, Hughes DJ (1990b) Precambrian mafic dykes of southern Greenland. In: Parker AJ, Rickwood DH, Tucker DH (eds) Mafic dykes and emplacement mechanisms. A. A. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 481–495
Hawkesworth CJ, Gallagher K, Hergt JM, McDermott F (1993) Mantle and slab contributions in arc magmas. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 21:175–204
Kuehner SM (1989) Petrology and geochemistry of early proterozoic high-Mg dykes from the Vestfold Hills, Antarctica. In: Crawford AJ (ed) Boninites and related rocks. Unwin Hyman, London, pp 208–231
Lafleche MR, Dupuy C, Bougault H (1992) Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Archean volcanic rocks of the southern Abitibi Belt, Quebec. Precambrian Res 57:207–241
Le Bas MJ (2000) IUGS reclassification of the high-Mg and picritic volcanic rocks. J Petrol 41:1467–1470
Le Cheminant AN, Heaman LM (1989) Mackenzie igneous events, Canada: middle proterozoic hotspot magmatism associated with ocean opening. Earth Planet Sci Lett 96:38–48
Le Maitre RW, Bateman P, Dudek A, Keller J, Lameyre J, Le Bas MJ, Sabine PA, Schmid R, Sorensen H, Streckeisen A, Woolley AR, Zanettin B (1989) A classification of igneous rocks and glossary of terms: recommendations of the International Union of Geological Sciences Subcommission on the systematics of igneous rocks. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford
Mahadevan TM (2002) Geology of Bihar and Jharkhand. In: Text book series. Geological Society of India, Bangalore
Mallick AK, Sarkar A (1994) Geochronology and geochemistry of mafic dikes from Precambrians of Keonjhar, Orissa. Indian Miner 48:3–24
Mandal N, Mitra AK, Misra S, Chakraborty C (2006) Is the outcrop topology of dolerite dykes of Precambrian Singhbhum craton fractal. J Earth Sci Syst 115:643–660
Mir AR, Alvi SH, Balaram V (2010) Geochemistry of mafic dikes in the Singhbhum Orissa craton: implications for subduction-related metasomatism of the mantle beneath the eastern Indian craton. Int Geol Rev 52(1):79–94
Mir AR, Alvi SH, Balaram V (2011) Geochemistry of the mafic dykes in parts of the Singhbhum Granitoid complex: petrogenesis and tectonic setting. Arabian J Geosci 4:933–943
Moorbath S, Taylor RN, Jones NW (1986) Dating the oldest terrestrial rocks—facts and fiction. Chem Geol 57:63–86
Mukhopadhyay J, Ghosh G, Nandi AK, Chaudhuri AK (2006) Depositional setting of the Kolhan Group: its implications for the development of a Meso to Neoproterozoic deep-water basin on the South Indian craton. S Afr J Geol 109:183–192
Naqvi SM (2005) Geology and evolution of the Indian plate. Capital Publishing Company, New Delhi
Neogi S, Miura H, Hariya Y (1996) Geochemistry of the Dongargarh volcanic rocks, Central India: implications for the Precambrian mantle. Precambrian Res 76:77–91
Nielsen SG, Joel AB, Krogstad EJ (2002) Petrogenesis of an early Archaean (3.4 Ga) norite dyke, Isua, West Greenland: evidence for early Archaean crustal recycling. Precambrian Res 118:133–148
Pearce JA, Cann JR (1973) Tectonic setting of basic volcanic rocks determined using trace element analysis. Earth Planet Sci Lett 19:290–300
Pearce JA, Parkinson IJ (1993) Trace element models for mantle melting: application to volcanic arc petrogenesis. In: Prichard HM, Alabaster T, Harris NBW, Neary CR (eds) Magmatic processes and plate tectonics. Spec Publ Geol Soc Lond. 76:373–403
Piercey SJ, Murphy DC, Mortensen JK, Paradis S (2001) Boninite magmatism in a continental margin setting, Yukon-Tanana terrane, southeastern Yukon, Canada. Geology 29:731–734
Poidevin JL (1994) Boninite-like rocks from the Paleoproterozoic greenstone belt of Bogoin, Central African Republic: geochemistry and petrogenesis. Precambrian Res 68:97–113
Rajamani V, Shivkumar K, Hanson GN, Shirey SB (1985) Geochemistry and petrogenesis of amphibolites, Kolar schist belt, South India: evidence for komatiitic magma derived by low percentage of melting of the mantle. J Petrol 26:92–123
Raza M, Alvi SH, Abu-hamatteh ZSH (1995) Geochemistry and tectonic significance of Ongarbira volcanics, Singhbhum craton, Eastern India. J Geol Soc India 45:643–652
Robinson PT, Zhou M, Hu X, Reynold P, Bai W, Yang J (1999) Geochemical constrains on the origin of the Hegenshan ophiolite, Inner Mongolia, China. J Asian Earth Sci 17:423–442
Rogers JJW, Santosh M (2003) Supercontinents in earth history. Gondwana Res 6:357–368
Rollinson HR, Tarney J (2005) Adakites—the key to understanding LILE depletion in granulites. Lithos 79:61–81
Saha AK (1994) Crustal evolution of Singhbhum- North Orissa, Eastern India. Mem Geol Surv India 27:341
Sahu NK, Mukherjee MM (2001) Spinifex textured komatiite from Badampahar-Gorumahisani Schist belt, Mayurbhanj Dist., Orissa. J Geol Soc India 57:29–534
Salavati M, Kananian A, Noghreyan M (2013) Geochemical characteristics of mafic and ultramafic plutonic rocks in southern Caspian Sea Ophiolite (Eastern Guilan). Arabian J Geosci 6:4851–4858
Sarkar AN, Chakraborti DK (1982) One orogenic belt or two? A structural reinterpretation supported by Landsat data products of the Precambrian metamorphics of Singhbhum, eastern India. Photogrammatria 37:185–201
Sengupta S, Acharyya SK, Deshmeth JB (1997) Geochemistry of Archaean volcanic rocks from Iron Ore Supergroup, Singhbhum eastern India. Proc Indian Acad Sci (Earth Planet Sci) 106:327–342
Sharma M, Basu AR, Ray SL (1994) Sm-Nd isotopic and geochemical study of the Archaean Tonalite-Amphibolite association from the eastern Indian craton. Cont Mineral Petrol 117:45–55
Sheraton JW, Thompson JW, Collerson KD (1987) Mafic dyke swarms of Antarctica. In: Halls HC, Fahrig WF (eds) Mafic dyke swarms. Spec Pap Geol Assoc Can. 34:419–432
Shervais JW (1982) Ti-V plots and the petrogenesis of modern and ophiolitic lavas. Earth Planet Sci Lett 59:101–118
Smithies RH (2002) Archaean boninite-like rocks in an intracratonic setting. Earth Planet Sci Lett 197:19–34
Sobolev AV, Danyushevsky LV (1994) Petrology and geochemistry of boninites from the north termination of the Tonga trench: constraints on the generation conditions of primary high-Ca boninite magmas. J Petrol 35:1183–1211
Srivastava RK (2006) Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Neoarchaean high-Mg low-Ti mafic igneous rocks in an intracratonic setting, Central India craton: evidence for boninite magmatism. Geochem J 40:15–31
Srivastava RK (2008) Global intracratonic boninite-norite magmatism during the Neoarchean–Paleoproterozoic: evidence from the Central Indian Bastar craton. Int Geol Rev 50:61–74
Srivastava RK, Singh RK (2003) Geochemistry of high-Mg mafic dykes from the Bastar craton: evidence of late Archaean boninite-like rocks in an intracratonic setting. Curr Sci 85:808–812
Srivastava RK, Sivaji Ch, Chalapathi Rao NV (2008) Indian Dykes: Geochemistry Geophysics and Geochronology. Narosa Publishing House Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi
Subba Rao DV, Khan MWY, Sridhar DN, Naga Raju K (2007) A New find of within basin younger dolerite dykes with continental flood basalt affinity from the meso-neoproterozoic Chattisgarh Basin, Bastar craton, Central India. J Geol Soc India 69:80–84
Subba Rao DV, Balaram V, Naga Raju K, Sridhar DN (2008) Paleoproterozoic boninite-like rocks in an intercratonic setting from Northern Bastar craton, Central India. J Geol Soc India 72:373–380
Sun SS, Mc Donough WF (1989) Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD, Norry MJ (eds) Magmatism in the ocean basins. Spec Publ Geol Soc Lond. 42:313–345
Sun SS, Nesbitt RW (1978) Geochemical regularities and genetic significance of ophiolitic basalts. Geology 28:689–693
Sun SS, Nesbitt RW, McCulloch MT (1989) Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Archaean and early proterozoic siliceous high-magnesian basalts. In: Crawford AJ (ed) Boninites and related rocks. Unwin Hyman, London
Tarney J (1992) Geochemistry and significance of mafic dyke swarms in the proterozoic. In: Condie KC (ed) Proterozoic crustal evolution. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Tarney J, Jones CE (1994) Trace element geochemistry of orogenic igneous rocks and crustal growth models. J Geol Soc Lond 151:855–868
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1981) The composition and evolution of the continental crust: rare earth element evidence from sedimentary rocks. Phil Trans Royal Soc Lond 300:381–399
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1985) The continental crust: its composition and evolution. Blackwell, Oxford
Taylor RN, Nesbit R, Vidal P, Harmon RS, Auvray B, Croudace IW (1994) Mineralogy, chemistry, and genesis of the boninite series volcanics, Chichijima, Bonin Islands, Japan. J Petrol 35:577–617
Toplis MJ, Corgne A (2002) An experimental study of element partitioning between magnetite, clinopyroxene and iron-bearing silicate liquids with particular emphasis on vanadium. Cont Mineral Petrol 144:22–37
Wallin ET, Metcalf V (1998) Supra-subduction zone ophiolites formed in an extensional forearc: trinity Terrae, Kalmath Mountains, California. J Geol 106:591–608
Weaver BL, Tarney J (1983) Chemistry of the sub continental mantle inferences from Archean and Proterozoic dykes and continental flood basalts. In: Hawkesworth CJ, Norry MJ (eds) Continental Basalt and mental xenoliths. Shiva, Nantwich, pp 209–229
Wilson M (1989) Igneous petrogenesis. Unwin Hyman Ltd., London
Winchester JA, Floyd PA (1977) Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements. Chem Geol 20:325–343
Acknowledgments
Authors are sincerely thankful to the Director, NGRI, for providing permission to analyze these samples. First author pays sincere thanks to Prof. Shakil Ahmad Romshoo, Head, Department of Earth Sciences, University of Kashmir, Srinagar for providing various facilities and genuine time to time guidance to complete this article. Constructive comments and valuable suggestions from anonymous reviewers are duly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mir, A.R., Alvi, S.H. & Balaram, V. Boninitic geochemical characteristics of high-Mg mafic dykes from the Singhbhum Granitoid Complex, Eastern India. Chin. J. Geochem. 34, 241–251 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-015-0044-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-015-0044-8