Abstract
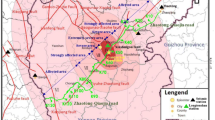
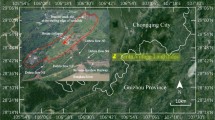
Information about the long-term spatiotemporal evolution of landslides can improve our understanding of the landslide development process and can help prevent landslide disasters. This paper describes the Xiaozhuang landslide triggered by a historical earthquake and rainfall in Tianshui, Northwest China. The landslide is dominated by rotational-sliding movement. Several new failures and many fissures formed in the landslide area as a result of the 2013 Ms 6.6 Minxian earthquake and rainfall. Accordingly, field investigations, borehole drilling, geotechnical laboratory tests, and numerical calculations were conducted to study the mechanism of the landslide and to forecast its stability. A triaxial creep test of the slip soil indicates that the axial deformation of the mudstone increases with increasing water content. Numerical simulations suggest that failure is prone to occur within the deep part of the landslide under earthquake conditions. If the input seismic acceleration exceeds 0.2 g, the landslide will become unstable. Furthermore, the horizontal peak ground acceleration near the surface of the landslide is greater than that at depth. During a strong earthquake, the unstable regions are primarily located in the middle of the landslide and at its crest. When the rainfall intensity rate is 200 mm/d, the factor of safety is 1.319 and a dangerous zone appears in the lower and middle parts of the landslide.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borja RI, White JA, Liu XY, et al. (2012) Factor of safety in a partially saturated slope inferred from hydro-mechanical continuum modeling. Int J Numer Anal Meth Geomech 36: 236–248. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.1021
Borrelli L, Gullà G (2017) Tectonic constraints on a deep-seated rock slide in weathered crystalline rocks. Geomorphology 290: 288–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.04.025
Derbyshire E (2001) Geological hazards in loess terrain, with particular reference to the loess regions of China. Earth Sci Rev 54: 231–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0012-8252(01)00050-2.
Gasmo JM, Rahardjo H, Leong EC (2000). Infiltration effects on stability of a residual soil slope. Comput Geotech 26: 145–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0266-352X(99)00035-X.
Gullà G (2014) Field monitoring in sample sites: hydrological response of slopes with reference to widespread landslide events. Prog Earth Planet Sci 9: 44–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeps.2014.06.008.
Genuchten VTM (1980) A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44(5): 892–898. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050002x
GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. (2010) Seepage modeling with SEEP/W 2007. Calgary, Alberta, Canada.
Jiang F, Chen X, Zhan Y, et al. (2016) Shifting correlation between earthquakes and electromagnetic signals: A case study of the 2013 Minxian-Zhangxian ML, 6.5 (MW, 6.1) earthquake in Gansu, China. Pure Appl Geophys 173(1): 269–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-015-1055-4
Kuhlemeyer RL, Lysmer J (1973) Finite element method accuracy for wave propagation problems. J Soil Mech Found Div 99(SM5): 421–427. https://doi.org/10.1061/JSFEAQ.0001885
Krahn J (2004) Stability modeling with SLOPE/W: an engineering methodology, GEO-SLOPE/W International Ltd., Calgary, Alta., Canada.
Lenti L, Martino S (2013) A parametric numerical study of the interaction between seismic waves and landslides for the evaluation of the susceptibility to seismically induced displacements. Bull Seismol Soc Amer 103(1): 33–56. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120120019
Lv Y, Peng J, Wang G (2014) Characteristics and genetic mechanism of the Cuihua Rock Avalanche triggered by a paleo-earthquake in northwest China. Eng Geol 182: 88–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.08.017
Li SH, Wu LZ, Huang JS (2021) A novel mathematical model for predicting landslide displacement. Soft Computing 25(3): 2453–2466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05313-9
Morgenstern NR, Price VE (1965) Analysis of stability of general slip surfaces. Geotechnique 15: 79–93. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1965.15.1.79
Pal S, Kaynia AM, Bhasin RK, et al. (2012) Earthquake stability analysis of rock slopes: a case study. Rock Mech Rock Eng 45(2): 205–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-011-0145-6
Peng JB, Leng Y, Zhu X, et al. (2016) Development of a loess-mudstone landslide in a fault fracture zone. Environ Earth Sci 75(8): 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5336-8
Qiu J, Wang X, Lai J, et al. (2018) Response characteristics and preventions for seismic subsidence of loess in northwest china. Nat Hazards 92: 1909–1935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-018-3272-5
Rahardjo H, Li XW, Toll DG, et al. (2001) The effect of antecedent rainfall on slope stability. Geotech Geol Eng 19: 371–399. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013129725263
Regmi AD, Yoshida K, Cui P, et al. (2017) Development of Taprang landslide, West Nepal. Landslides 14: 929–946. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0752-0
Spencer E (1967) A method of analysis of the stability of embankments assuming parallel inter-slice forces. Geotechnique 17: 11–26. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1967.17.1.11
Sun P, Li R, Jiang H, et al. (2016) Earthquake-triggered landslides by the 1718 Tongwei earthquake in Gansu Province, northwest China. B Eng Geol Environ 76(4): 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0949-4
Sun P, Wang G, Wu LZ, et al. (2019) Physical model experiments for shallow failure in rainfall-triggered loess slope, northwest China. B Eng Geol Environ 78(6): 4363–4382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-1420-5
Whitman RV (2000) Organizing and evaluating uncertainty in geotechnical engineering. J Geotech Geoenviron 126(7): 583–593. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2000)126:7(583)
Wen B, He L (2012) Influence of lixiviation by irrigation water on residual shear strength of weathered red mudstone in Northwest China: implication for its role in landslides’ reactivation. Eng Geol 151: 56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.08.005.
Wang T, Wu SR, Shi JS, et al. (2015) Inversion of the inducing effects of historical strong earthquakes on large-scale landslides around the middle reaches of the Weihe River. Acta Geosci Sin 36(3): 353–361 (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3975/cagsb.2015.03.10
Wu G, Cunningham D, Yuan RM, et al. (2017) Mass-wasting effects induced by the 2015 Gorkha (Nepal) Mw 7.8 earthquake within a large paleo-landslide site adjacent to the Tatopani Border Station, Nepal: implications for future development along the critical Bhote Koshi River valley transport corridor between Nepal and China. Landslides 14: 1147–1160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0792-5
Wang T, Wu SR, Shi JS, et al. (2018) Assessment of the effects of historical strong earthquakes on large-scale landslide groupings in the Wei River midstream. Eng Geol 235: 11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.01.020.
Wang YS, Wu LZ, Gu J (2019) Process analysis of the Moxi earthquake-induced Lantianwan landslide in the Dadu River, China. B Eng Geol Environ 78(7): 4731–4742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-01438-2
Yuan D, Lei Z, He W, et al. (2007) Textual research of Wudu earthquake in 186 B.C. in Gansu Province, China and discussion on its causative structure. Acta Seismologica Sinica 20(6): 696–707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11589-007-0696-5
Yang P, Tang YQ, Zhou NQ, et al. (2011) Characteristics of red clay creep in karst caves and loss leakage of soil in the karst rocky desertification area of Puding County, Guizhou, China. Environ Earth Sci 63(3): 543–549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0721-1
Zhang Y, Xu WY, Shao JF, et al. (2015) Experimental investigation of creep behavior of clastic rock in Xiangjiaba Hydropower Project. Water Sci Eng 8(1): 55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wse.2015.01.005.
Zhang Z, Wang T, Wu S, et al. (2017a) Dynamics stress-strain behavior of Tianshui soils. Landslides 14: 323–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0694-6
Zhang Z, Wang T, Wu S, et al. (2017b) The role of seismic triggering in a deep-seated mudstone landslide, China: Historical reconstruction and mechanism analysis. Eng Geol 226: 122–135.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.06.001
Zhang Z, Wang T, Wu S, et al. (2017c) Seismic performance of loess-mudstone slope in Tianshui — Centrifuge model tests and numerical analysis. Eng Geol 222: 225–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.04.006
Zhang Z (2016) The initating mechanism and runout pattern of typical seismic loess landslides. Doctor Thesis. China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, Hubei, China. (In Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This study was sponsored by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41902269), and Chinese Universities Scientific Fund (2020TC095).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Zl., Wang, T. Stability and deformation of Xiaozhuang landslide: A large-scale creeping landslide in Gansu, China. J. Mt. Sci. 19, 756–770 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-021-6819-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-021-6819-y