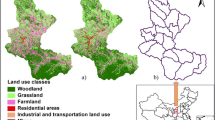
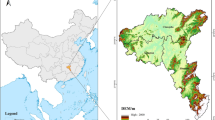
Abstract
China is undergoing a rapid urbanization process, and urbanization will have a direct impact on regional ecosystems and affect regional ecosystem services. Considering the mountainous counties in Southwestern China as the research object, this study reveals the spatial clustering characteristics of four typical ecosystem services (food production, soil conservation, water yield and carbon sequestration) as well as the trade-offs and synergies among ecosystem services in different urbanized areas. At the same time, piecewise linear regression is used to determine the threshold of the influence of urbanization on ecosystem services. The results indicate that: 1) There are spatial autocorrelations among the four typical ecosystem services; with strong clustering characteristics, the positive correlation types are “clustered” locally; and with significant spatial heterogeneity, the negative correlation types are scattered and mainly appear in the highly urbanized area. 2) There are also remarkable differences in the relationship among various ecosystem services in different urbanized areas, and in particular, there are marked trade-offs between food production and carbon sequestration in the moderately urbanized area and the highly urbanized area. However, there are synergies between them in the lowly urbanized area. 3) With an increase in the compounded night light index (CNLI), water yield, carbon sequestration, food production and overall ecosystem services values present an increasing-decreasing trend, the soil conservation function value shows a decreasing-increasing trend. The response of water yield, carbon sequestration, food production, and overall ecosystem services to the compounded night light index (CNLI) has a threshold of 1.2642, 1.4833, 1.3388, 1.5146 and 1.2237, respectively. Based on the detected relationships between urbanization and ecosystem services, this study provides a theoretical reference for the selection of urbanization development models in key ecological functional areas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberti M (2010) Maintaining ecological integrity and sustaining ecosystem function in urban areas. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability 2: 178–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosust.2010.07.002
Baker ME, King RS (2010) A new method for detecting and interpreting biodiversity and ecological community thresholds. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 1: 25–37. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2041-210X.2009.00007.x
Boys CA, Robinson W, Miller B, et al. (2016) A piecewise regression approach for determining biologically relevant hydraulic thresholds for the protection of fishes at river infrastructure. Journal of Fish Biology 88(5): 1677–1692. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfb.12910
Chen TT, Peng L, Wang Q, et al. (2017) Measuring the Coordinated Development of Ecological and Economic Systems in Hengduan Mountain Area. Sustainability 9: 1270–1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9081270
Chung U, Choi J, Yun JI (2004) Urbanization effect on the observed change in mean monthly temperatures between 1951–1980 and 1971–2000 in Korea. Climatic Change 66: 127–136. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:clim.0000043136.58100.ce
Costanza R, D’Arge R, Groot, RD, et al. (1997) The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 387: 253–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-8009(98)00020-2
Costanza R, Groot RD, Braat L, et al. (2017) Twenty years of ecosystem services: how far have we come and how far do we still need to go?. Ecosystem Services 28: 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2017.09.008
Eigenbrod F, Hecnar SJ, Fahrig L (2009) Quantifying the Road-Effect Zone: Threshold Effects of a Motorway on Anuran Populations in Ontario, Canada. Ecology and Society 14: 24–42. https://doi.org/10.5751/es-02691-140124
Hao RF, Yu DY, Liu YP, et al. (2017). Impacts of changes in climate and landscape pattern on ecosystem services. Science of The Total Environment 579: 718–728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.036
Hua LZ, Shao GF, Zhao JZ (2017) A concise review of ecological risk assessment for urban ecosystem application associated with rapid urbanization processes. International Journal of Sustainable Development & World Ecology 24: 248–261. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504509.2016.1225269
Huo XN, Zhang WW, Sun DF, et al. (2011) Spatial Pattern Analysis of Heavy Metals in Beijing Agricultural Soils Based on Spatial Autocorrelation Statistics. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 8(6): 2074–2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph8062074
Hu XS, Wu CZ, Hong W, et al. (2013) Impact of land-use change on ecosystem service values and their effects under different intervention scenarios in Fuzhou City, China. Geosciences Journal 17: 497–504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-013-0040-0
Hu XS, Hong W, Qiu RZ, et al. (2015) Geographic variations of ecosystem service intensity in Fuzhou City. Science of The Total Environment 512–513: 215–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.035
Hu Y, Peng J, Liu Y, et al. (2018) Integrating ecosystem services trade-offs with paddy land-to-dry land decisions: A scenario approach in Erhai Lake Basin, southwest China. Science of the Total Environment, 625: 849–860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.340
Jiang L, Deng X, Seto KC (2012) Multi-level modeling of urban expansion and cultivated land conversion for urban hotspot counties in China. Landscape and Urban Planning 108(2–4): 131–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2012.08.008
Jia XQ, Fu BJ, Feng XM, et al. (2014) The tradeoff and synergy between ecosystem services in the Grain-for-Green areas in Northern Shaanxi, China. Ecological Indicators 43: 103–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.02.028
Kreuter UP, Harris HG, Matlock, MD, et al. (2001) Change in ecosystem service values in the San Antonio area, Texas. Ecological Economics 39(3): 333–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-8009(01)00250-6
Kroll F, Müller F, Haase D, et al. (2012) Rural-urban gradient analysis of ecosystem services supply and demand dynamics. Land Use Policy 29: 521–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2011.07.008
Larondelle N, Haase D (2013) Urban ecosystem services assessment along arural-urban gradient: a cross-analysis of European cities. Ecological Indicators 29: 179–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.12.022
Larondelle N, Lauf S (2016) Balancing demand and supply of multiple urban ecosystem services on different spatial scales. Ecosystem Services 22: 18–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2016.09.008
Leemans HBJ, Groot RSD (2003) Millennium Ecosystem Assessment: Ecosystems and human well-being: a framework for assessment. Physics Teacher 34(9): 534–534. https://doi.org/10.1119/1.2344558
Levin N, Duke Y (2011) High spatial resolution night-time light images for demographic and socio-economic studies. Remote Sensing of Environment 119: 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2011.12.005
Liao J, Wang T, Jiang Z, et al. (2015) WRF/Chem modeling of the impacts of urban expansion on regional climate and air pollutants in Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmospheric Environment 106: 204–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.01.059
Li B, Chen D, Wu S, et al. (2016). Spatio-temporal assessment of urbanization impacts on ecosystem services: Case study of Nanjing City, China. Ecological Indicators 71: 416–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.07.017
Li J, Zhou ZX (2016) Natural and human impacts on ecosystem services in Guanzhong-Tianshui economic region of China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 23: 6803–6815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5867-7
Mach ME, Martone RG, Chan KMA (2015) Human impacts and ecosystem services: insufficient research for trade-off evaluation. Ecosystem Services 16: 112–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2015.10.018
Magney TS, Eitel JUH, Huggins DR, et al. (2016) Proximal NDVI derived phenology improves in-season predictions of wheat quantity and quality. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 217: 46–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2015.11.009
Myers N, Mittermeier RA, Mittermeier CG, et al. (2000) Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 403, 853–858. https://doi.org/10.1038/35002501
Peng J, Tian L, Liu Y, et al. (2015) Ecosystem services response to urbanization in metropolitan areas: thresholds identification. Science of The Total Environment 607–608: 706–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.218
Peng J, Yang Y, Liu Y, et al. (2018) Linking ecosystem services and circuit theory to identify ecological security patterns. Science of The Total Environment 644: 781–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.292
Peng L, Liu S, Sun L (2016) Spatial-temporal changes of rurality driven by urbanization and industrialization: A case study of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area in Chongqing, China. Habitat International 51: 124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2015.10.021
Peng L, Deng W, Zhang H (2019) Focus on economy or ecology? A three-dimensional trade-off based on ecological carrying capacity in southwest China. Natural Resource Modeling 1: 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/nrm.12201
Renard KG, Foster GR, Weesies GA, et al. (1991) RUSLE: revised universal soil loss equation. Journal of Soil and Water conservation 46, 30–33. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781444328455.ch8
Sanchez-Rodriguez R, Seto KC, Simon D, et al. (2005) IHDP Science Plan: urbanization and global environmental change. Bonn: International Human Dimensions Programme on Global Environmental Change Report No. 15.
Su SL, Xiao R, Jiang ZL, et al. (2012) Characterizing landscape pattern and ecosystem service value changes for urbanization impacts at an eco-regional scale. Applied Geography 34: 295–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.218
Terrado M, Acuna V, Ennaanay D, et al. (2014) Impact of climate extremes on hydrological ecosystem services in a heavily humanized Mediterranean basin. Ecological Indicators 37: 199–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.01.016
Wang J, Peng J, Zhao M, et al. (2017). Significant trade-off for the impact of Grain-for-Green Programme on ecosystem services in North-western Yunnan, China. Science of the Total Environment 574: 57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.026
Wang X, Piao S, Ciais P, et al. (2011) Spring temperature change and its implication in the change of vegetation growth in North America from 1982 to 2006. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of Americ 108(4): 1240–1245. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1014425108
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1978) Predicting rainfall erosion lossess-A guide to conservation, agricultural handbook. Planning. United States department of Agriculture—handbook no. 537. United States Government Printing Office, Washington, DC.
Yi H, Güneralp B, Kreuter UP, et al. (2018) Spatial and temporal changes in biodiversity and ecosystem services in the San Antonio River Basin, Texas, from 1984 to 2010. Science of the Total Environment 619–620: 1259–1271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.302
Zhang JC, DeAngelis DL, Zhuang JY (2011) Spatial Variability of Soil Erodibility (K Factor) at a Catchment Scale in Nanjing, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica 28: 2199–2206. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-9679-4_6
Zhang LW, Fu B, Fu BJ, et al. (2015) Balancing multiple ecosystem services in conservation priority setting. Landscape Ecology 30: 535–546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-014-0106-z
Zhang W, Yang D, Huo J (2016) Studies of the Relationship between City Size and Urban Benefits in China Based on a Panel Data Model. Sustainability 8: 554–572. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8060554
Zheng Z, Fu B, Hu H, et al. (2014) A method to identify the variable ecosystem services relationship across time: a case study on Yanhe Basin, China. Landscape Ecology 29(10): 1689–1696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-014-0088-x
Zheng Z, Zeng Y, Zhao Y, et al. (2016) Analysis of land cover changes in southwestern China since the 1990s. Acta Ecologica Sinica 36(23): 7858–7869. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201511102277 (In Chinese)
Zhou L, Shi P, Chen J, et al. (2003) Application of Compound Night Light Index Derived from DMSP/OLS Data to Urbanization Analysis in China in the 1990s. Acta Geographical Sinica 58: 893–902. https://doi.org/10.11821/xb200306013
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the 135 Strategic Program of the Institute of Mountain Hazards and Environment, CAS (NO.SDS-135-1703), the Science and Technology Service Network Initiative (No. KFJ-STS-QYZD-060), Doctor Startup Foundation of China West Normal University (N0. 412650), the Sichuan Center for Rural Development Research Project (No. CR1811), and Scientific Research Innovation Team Projects of China West Normal University (N0. CXTD2018-10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, L., Wang, Xx. What is the relationship between ecosystem services and urbanization? A case study of the mountainous areas in Southwest China. J. Mt. Sci. 16, 2867–2881 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-019-5390-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-019-5390-2