Abstract
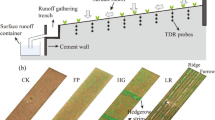
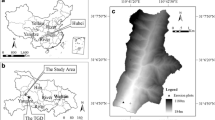
Under global warming, storm events tend to intensify, particularly in monsoon-affected regions. As an important agricultural area in China, the purple soil region in the Sichuan Basin, where it has a prevailing monsoon climate, is threatened by serious soil erosion. Tillage operations alter runoff and soil erosion processes on croplands by changing the physical properties of the soil surface. To clarify the relationship between tillage and soil erosion in the purple soil region, three different tillage practices in this region were investigated at the plot scale over 4 years: bare land with minimum tillage (BL), conventional tillage (CT) and seasonal no-tillage ridges (SNTR) which was initially designed to prevent soil erosion by contoured ridges and no-tillage techniques. The results showed that although there were no significant differences in the surface runoff and soil erosion among the three practices, BL caused relatively high surface runoff and soil erosion, followed by CT and SNTR. Classification and comparison of the rainfall events based on cluster analysis (CA) verified that the surface runoff was not significantly different between most intensive event and long intensive events but was significantly different between most intensive and short and medium-duration events. Only the rainfall events with the highest rainfall intensity could trigger serious soil erosion, up to 1000 kg ha−1 in the region. Further detailed investigations on the effects of tillage operations on the soil erosion in a subtropical region with a monsoon climate are needed to provide a basis for modeling catchments and designing better management practices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boulal H, Gómez-Macpherson H, Gómez JA, Mateos L, 2011. Effect of soil management and traffic on soil erosion in irrigated annual crops. Soil & Tillage Research 115–116: 62–70. DOI: 10.1016/j.still.2011.07.003
Braud I, Vich AIJ, Zuluaga J, et al. (2001) Vegetation influence on runoff and sediment yield in the Andes region: observation and modelling. Journal of Hydrology 254: 124–144. PII: S0022-1694(01)00500-5
Canton Y, Sole-Benet A, de Vente J, et al. (2011) A review of runoff generation and soil erosion across scales in semiarid south-eastern Spain. Journal of Arid Environments 75: 1254–1261. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaridenv.2011.03.004
Chahinian N, Moussa R, Andrieux P, et al. (2006). Accounting for temporal variation in soil hydrological properties when simulating surface runoff on tilled plots. Journal of Hydrology 326: 135–152. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.10.038
Chen S, Li T, Zhang X (1996) A further study on sub-surface layers amelioration under SNTRCS. Mountain Research 14: 55–58. (In Chinese)
Chen S, Liu G, Zhang X (2001) A review upon the importance and effect of piling soil to ridge with non-tillage for agro-ecosystem in central hilly area of Sichuan Basin. Journal of Mountain Science 19: 20–50.
Curci M, Pizzigallo MDR, Crecchio C, Mininni R, Ruggiero P. (1997) Effects of conventional tillage on biochemical properties of soils. Biology and Fertility of Soils 25(1): 1–6.
Endale DM, Fisher DS, Steiner JL (2006) Hydrology of a zeroorder Southern Piedmont watershed through 45 years of changing agricultural land use. Part 1. Monthly and seasonal rainfall-runoff relationships. Journal of Hydrology 316: 1–12. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.04.008
FAO. (2008) Conservation Agriculture, 2008-07-08. Available online at:http://www.fao.org/ag/ca/index.html (Accessed on 2 November 2013).
Fasinmirin JT, Reichert JM (2011) Conservation tillage for cassava (Manihot esculenta crantz) production in the tropics. Soil & Tillage Research 113: 1–10. DOI: 10.1016/j.still.2011.01.008
Gong ZT (1999) Chinese Soil Taxonomy. Science Press, Beijing, China.
Govaerts B, Verhulst N, Castellanos-Navarrete A, et al. (2009) Conservation agriculture and soil carbon sequestration: between mythand farmer reality. Critical Review In Plant Science 28: 97–122.
Guo ZL, Zhong C, Cai CF, et al. (2008) Nitrogen competition in contour hedgerow systems in subtropical China. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystem 81: 71–83. DOI: 10.1007/s10705-007-9153-z
Horváth S (2002) Spatial and temporal patterns of soil moisture variations in a sub-catchment of River Tisza. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C 27: 1051–1062.
Hu L (2010) SAS statistical analysis course. Publishing House of Electronics Industry, Beijing, China.
Karvonen T, Koivusalo H, Jauhiainen M, et al. (1999). A hydrological model for predicting runoff from different land use areas. Journal of Hydrology 217: 253–265. PII: S0022-1694(98)00280-7
Kim W, Kanae S, Agata Y, et al. (2005) Simulation of potential impacts of land use/cover changes on surface water fluxes in the Chaophraya river basin, Thailand. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 110: DOI: 10.1029/2004JD004825.
Kinnell PIA (2005) Raindrop-impact-induced erosion processes and prediction: a review. Hydrological Processes 19: 2815–2844. DOI: 10.1002/hyp.5788
Li FR, Cook S, Geballe GT, et al. (2000) Rainwater harvesting agriculture: An integrated system for water management on rainfed land in China’s semiarid areas. Ambio 29: 477–483.
Li ZM, Zhang XW, He YR, et al. (1991) Purple soil in China (A). Science Press, Beijing, China. (In Chinese)
Lin CW, Tu SH, Huang JJ, et al. (2009) The effect of plant hedgerows on the spatial distribution of soil erosion and soil fertility on sloping farmland in the purple-soil area of China. Soil & Tillage Research 105: 307–312. DOI: 10.1016/j.still.2009.01.001
Morin E, Goodrich DC, Maddox RA, et al. (2006) Spatial patterns in thunderstorm rainfall events and their coupling with watershed hydrological response. Advances in Water Resources 29: 843–860. DOI: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2005.07.014
Nearing MA (2001) Potential changes in rainfall erosivity in the US with climate change during the 21(st) century. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 56: 229–232.
Puigdefabregas J (2005) The role of vegetation patterns in structuring runoff and sediment fluxes in drylands. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms 30: 133–147. DOI: 10.1002/esp.1181
Qu Q, Zhao X, Ruan G, et al. (2004) Statistical analysis method — SAS examples. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing, China.
Shi XZ, Yu DS, Sun WX, et al. (2004) Reference bases of the Chinese and American soil classification systems: Comparison of great soil group of Chinese Soil Taxonomy and soil order of American Soil Taxonomy. Chinese Science Bulletin 49(13): 1299–1303.
Singh R, Tiwari KN, Mal BC (2006) Hydrological studies for small watershed in India using the ANSWERS model. Journal of Hydrology 318: 184–199. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.06.011
Spaan WP, Sikking AFS, Hoogmoed WB (2005) Vegetation barrier and tillage effects on runoff and sediment in an alley crop system on a Luvisol in Burkina Faso. Soil and Tillage Research 83: 194–203. DOI: 10.1016/j.still.2004.07.016
Stolte J, Shi XZ, Ritsema CJ (2009) Introduction: Soil erosion and nutrient losses in the Hilly Purple Soil area in China. Soil & Tillage Research 105: 283–284. DOI: 10.1016/j.still.2009.09. 010
Tang JL, Zhang B, Gao C, et al. (2008) Hydrological pathway and source area of nutrient losses identified by a multi-scale monitoring in an agricultural catchment. Catena 72: 374–385. DOI: 10.1016/j.catena.2007.07.004
Tang JL, Zhu B, Wang T, et al. (2012) Subsurface Flow Processes in Sloping Cropland of Purple Soil. Journal of Mountain Science 9: 1–9. DOI: 10.1007/s11629-012-2199-7
van Dijk AIJM, Bruijnzeel LA, Rosewell CJ (2002) Rainfall intensity-kinetic energy relationships: a critical literature appraisal. Journal of Hydrology 261: 1–23. PII: S0022-1694(02)00020-3
Wang T, Zhu B, Gao MR, et al. (2006) Nitrate pollution of groundwater in a typical small watershed in the central Sichuan hilly region. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment 22(3): 84–87. (In Chinese)
Wei W, Chen L, Fu B, et al. (2007) The effect of land uses and rainfall regimes on runoff and soil erosion in the semi-arid loess hilly area, China. Journal of Hydrology 335: 247–258. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.11.016
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1978) Predicting rainfall erosion losses. Agriculture Handbook. U. S. Deparment of Agriculture, Washington, DC, USA.
Zhang JH, Lobb DA, Li Y, et al. (2004) Assessment of tillage translocation and tillage erosion by hoeing on the steep land in hilly areas of Sichuan, China. Soil & Tillage Research 75: 99–107. DOI: 10.1016/j.still.2003.08.003
Zhang X, Chen S, Li T, et al. (1995) Seasonal No-tillage Ridge Cropping System: a multiple objective tillage system for hilly land management in south China, In: El-Swaify SA, Yakowitz DS (Eds.), Multiple Objective Dicision Making for Land, Water, and Environmental Management. Lewis Publishers, New York, NY, USA. pp 685–696.
Zhang XX, Zhu QK, Wu GM, et al. (2008) Vegetation coverage assessment by digital photos. Journal of Beijing Forestry University 30(1): 164–169. (In Chinese)
Zheng TG, Mao JQ, Dai HC, et al. (2011) Impacts of water release operations on algal blooms in a tributary bay of Three Gorges Reservoir. Science China(Technological Sciences) 54: 1588–1598. DOI: 10.1007/s11431-011-4371-7.
Zhu AX, Wang P, Zhu TX, et al. (2013) Modeling runoff and soil erosion in the Three-Gorge Reservoir drainage area of China using limited plot data. Journal of Hydrology 492: 163–175. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.03.038
Zhu B, Wang T, Kuang FH, et al. (2009) Measurements of Nitrate Leaching from a Hillslope Cropland in the Central Sichuan Basin, China. Soil Science Society of America Journal 73: 1419–1426. DOI: 10.2136/sssaj2008.0259
Zhu B, Wang T, You X, et al. (2008) Nutrient release from weathering of purplish rocks in the Sichuan Basin, China. Pedosphere 18: 257–264. DOI: 10.1016/S1002-0160(08) 60015-6
Zokaib S, Naser G (2012) A study on rainfall, runoff, and soil loss relations at different landuses — A case in Hilkot watershed in Pakistan. International Journal of Sediment Research 27: 388–393.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
0000-0001-8006-153X
0000-0002-8964-2856
0000-0002-7575-1701
0000-0002-0261-0035
0000-0003-4452-7800
0000-0003-0168-4101
0000-0002-1828-4967
0000-0001-6558-2361
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Jl., Cheng, Xq., Zhu, B. et al. Rainfall and tillage impacts on soil erosion of sloping cropland with subtropical monsoon climate — A case study in hilly purple soil area, China. J. Mt. Sci. 12, 134–144 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-014-3241-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-014-3241-8