Abstract
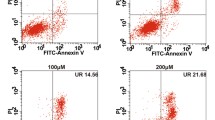
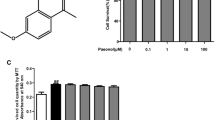
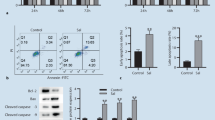
The synovial intimal lining is mainly governed by fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS), which portray a transformed tumor-like phenotype in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Among the diverse cytokines that engender FLS, interleukin-21 (IL-21) was reported to stimulate hyperproliferation and perpetuate inflammation. Recently, choline kinase (ChoKα) has been reported to be an essential enzyme aiding RA-FLS hyperproliferation by altering phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis. The current study aimed to elucidate the therapeutic efficacy of myricetin, a flavonoid, in abating the IL-21-induced tumor-like phenotype of adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA)-FLS via the ChoKα signaling cascade. Our results showed that myricetin suppressed IL-21 receptor expression and activation of the ChoKα signaling cascade (N-Ras, Ral-GDS, and PI3K) in IL-21-induced AIA-FLS. Consequently, myricetin treatment decreased ChoKα and PLD2 enzymatic activity and inhibited the proliferative, migratory, and invasive properties of AIA-FLSs. Our results demonstrated that myricetin could be a promising anti-arthritic compound by abating IL-21-induced hyperproliferation, migration, and invasive behavior of AIA-FLS by downregulating the ChoKα signaling cascade.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data of this article will be available upon request.
References
Bartok B, Firestein GS (2010) Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev 233(1):233–255
Dinesh P, Rasool M (2018) Berberine inhibits IL-21/IL-21R mediated inflammatory proliferation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes through the attenuation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and ameliorates IL-21 mediated osteoclastogenesis. Cytokine 106:54–56
Guma M, Sanchez-Lopez E, Lodi A, Garcia-Carbonell R, Tiziani S, Karin M, Lacal JC, Firestein GS (2015) Choline kinase inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 74(7):1399–1407
Hao Y, Xie L, Xia J, Liu Z, Yang B, Zhang M (2021) Plasma interleukin-21 levels and genetic variants are associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 22(1):246
Janardhan S, Srivani P, Sastry GN (2006) Choline kinase: an important target for cancer. Curr Med Chem 13(10):1169–1186
Jüngel A, Distler JH, Kurowska-Stolarska M, Seemayer CA, Seibl R, Forster A, Michel BA, Gay RE, Emmrich F, Gay S, Distler O (2004) Expression of interleukin-21 receptor, but not interleukin-21, in synovial fibroblasts and synovial macrophages of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 50(5):1468–1476
Katz-Brull R, Degani H (1996) Kinetics of choline transport and phosphorylation in human breast cancer cells; NMR application of the zero trans method. Anticancer Res 16(3B):1375–1380
Ko SY (2012) Myricetin suppresses LPS-induced MMP expression in human gingival fibroblasts and inhibits osteoclastogenesis by downregulating NFATc1 in RANKL-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Arch Oral Biol 57(12):1623–1632
Park KS, Chong Y, Kim MK (2016) Myricetin: biological activity related to human health. Appl Biol Chem 59:259–269
Ramírez de Molina A, Gutiérrez R, Ramos MA, Silva JM, Silva J, Bonilla F, Sánchez JJ, Lacal JC (2002a) Increased choline kinase activity in human breast carcinomas: clinical evidence for a potential novel antitumor strategy. Oncogene 21(27):4317–4322
Ramírez de Molina A, Penalva V, Lucas L, Lacal JC (2002b) Regulation of choline kinase activity by Ras proteins involves Ral-GDS and PI3K. Oncogene 21(6):937–946
Ramírez de Molina A, Rodríguez-González A, Gutiérrez R, Martínez-Piñeiro L, Sánchez J, Bonilla F, Rosell R, Lacal J (2002c) Overexpression of choline kinase is a frequent feature in human tumor-derived cell lines and in lung, prostate, and colorectal human cancers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 296(3):580–583
Ramírez de Molina A, Sarmentero-Estrada J, Belda-Iniesta C, Tarón M, Ramírez de Molina V, Cejas P, Skrzypski M, Gallego-Ortega D, de Castro J, Casado E, García-Cabezas MA, Sánchez JJ, Nistal M, Rosell R, González-Barón M, Lacal JC (2007) Expression of choline kinase alpha to predict outcome in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: a retrospective study. Lancet Oncol 8(10):889–897
Rodríguez-González A, Ramírez de Molina A, Bañez-Coronel M, Megias D, Lacal JC (2005) Inhibition of choline kinase renders a highly selective cytotoxic effect in tumour cells through a mitochondrial independent mechanism. Int J Oncol 26(4):999–1008
Samarpita S, Ganesan R, Rasool M (2020) Cyanidin prevents the hyperproliferative potential of fibroblast-like synoviocytes and disease progression via targeting IL-17A cytokine signalling in rheumatoid arthritis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 391:114917
Sanchez-Lopez E, Zimmerman T, Gomez del Pulgar T, Moyer MP, LacalSanjuan JC, Cebrian A (2013) Choline kinase inhibition induces exacerbated endoplasmic reticulum stress and triggers apoptosis via CHOP in cancer cells. Cell Death Dis 4(11):e933
Varkey R, Du Q, Karnell JL, Xiao X, Casey KA, Woods R, Rosenthal K, Wilson S, Dall’Acqua WF, Wu H, Herbst R, Ettinger R, Damschroder M (2019) Discovery and characterization of potent IL-21 neutralizing antibodies via a novel alternating antigen immunization and humanization strategy. PloS one 14(1):e0211236
Wang P, Li S, Wang X (2016) Myricetin exerts anti-osteoarthritic effects in IL-1β stimulated SW1353 cells via regulating matrix metalloproteinases and modulating JNK/P38MAPK/Ap-1/c-Fos and JAK/STAT signalling. Int J Pharmacol 12:440–450
Xing R, Jin Y, Sun L, Yang L, Li C, Li Z, Liu X, Zhao J (2016) Interleukin-21 induces migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol 184(2):147–158
Yalcin A, Clem B, Makoni S, Clem A, Nelson K, Thornburg J, Siow D, Lane AN, Brock SE, Goswami U, Eaton JW, Telang S, Chesney J (2010) Selective inhibition of choline kinase simultaneously attenuates MAPK and PI3K/AKT signaling. Oncogene 29(1):139–149
Young DA, Hegen M, Ma HL, Whitters MJ, Albert LM, Lowe L, Senices M, Wu PW, Sibley B, Leathurby Y, Brown TP, Nickerson-Nutter C, Keith JC Jr, Collins M (2007) Blockade of the interleukin-21/interleukin-21 receptor pathway ameliorates disease in animal models of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 56(4):1152–1163
Yuan X, Liu Y, Hua X, Deng X, Sun P, Yu C, Chen L, Yu S, Liu S, Pang H (2015) Myricetin ameliorates the symptoms of collagen-induced arthritis in mice by inhibiting cathepsin K activity. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 37(6):513–519
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ann Miriam Jose designed the research, conducted the study, and drafted the manuscript. Mahaboobkhan Rasool supervised the study and drafted the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Animal ethics approval
All experiments were certified and reviewed by the Institutional Animal Ethical Committee (IAEC) members with approval number (vide registration no: VIT/IAEC/20/DEC2021/15). All experimental procedures were performed according to the guidelines proposed by the Committee for Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animals (CPCSEA) in New Delhi, India.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jose, A.M., Rasool, M. Myricetin ameliorates the IL-21-induced tumorigenic phenotype of adjuvant-induced arthritis FLS by modulating the choline kinase signaling cascade. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 59, 811–820 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-023-00827-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-023-00827-6