Abstract
Background
While observation of T1(≤2cm) nonfunctioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (NF-PanNETs) is an accepted practice, an ill-defined subgroup of patients with T1 tumors develops metastases. This study aimed to identify those patients via clinical factors.
Methods
Patients from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) registry who were diagnosed with NF-PanNET with size ≤2cm between 1998 and 2014 and who underwent primary tumor resection were identified. Binary logistic regression analyses were performed to evaluate factors associated with pathological nodal and systemic metastatic disease.
Results
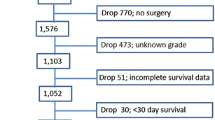
A total of 612 patients with T1 NF-PanNETs were identified. Of those, 72 (11.7%) developed nodal metastasis and 35 (5.7%) distant metastasis (M1). In the multivariable analysis, tumor location in the pancreatic body (OR 1.903, p=0.03) (OR 1.407, p=0.038) or tail (OR 1.258, p=0.04) (OR 1.612, p=0.021); tumor grade III–IV (OR 2.042, p=0.022) (OR 5.379, p≤0.001); and younger age (OR 0.963, p=0.01) (OR 0.919, p=0.009) were associated with nodal metastases and the presence of M1 disease, respectively.
Conclusion
While the low metastatic potential of ≤2cm NF-PanNET implies watchful waiting to be an appropriate strategy for most patients, the increased risk of metastatic disease in younger patients with high grade (III–IV) body/tail tumors suggests individualized risk stratification to be optimal.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dasari A, Shen C, Halperin D, Zhao B, Zhou S, Xu Y, et al. Trends in the Incidence, Prevalence, and Survival Outcomes in Patients With Neuroendocrine Tumors in the United States. JAMA Oncol. 2017; 3(10):1335-42.
Zerbi A, Falconi M, Rindi G, Delle Fave G, Tomassetti P, Pasquali C, et al. Clinicopathological features of pancreatic endocrine tumors: a prospective multicenter study in Italy of 297 sporadic cases. American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2010;105(6):1421-9.
Vagefi PA, Razo O, Deshpande V, McGrath DJ, Lauwers GY, Thayer SP, et al. Evolving patterns in the detection and outcomes of pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms: the Massachusetts General Hospital experience from 1977 to 2005. Archives of Surgery. 2007;142(4):347-54.
Sadot E, Reidy-Lagunes DL, Tang LH, Do RK, Gonen M, D'Angelica MI, et al. Observation versus Resection for Small Asymptomatic Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Matched Case-Control Study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016;23(4):1361-70.
Gaujoux S, Partelli S, Maire F, D'Onofrio M, Larroque B, Tamburrino D, et al. Observational study of natural history of small sporadic nonfunctioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(12):4784-9.
Rosenblum RE, Harris CK, Baeg KJ, Starr JA, Brais LK, Stashek KM, et al. Predictors of Recurrence and Survival in Patients With Surgically Resected Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Pancreas. 2020;49(2):249-54.
Bettini R, Partelli S, Boninsegna L, Capelli P, Crippa S, Pederzoli P, et al. Tumor size correlates with malignancy in nonfunctioning pancreatic endocrine tumor. Surgery. 2011;150(1):75-82.
Yao JC, Eisner MP, Leary C, Dagohoy C, Phan A, Rashid A, et al. Population-based study of islet cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14(12):3492-500.
Jiao Y, Shi C, Edil BH, de Wilde RF, Klimstra DS, Maitra A, et al. DAXX/ATRX, MEN1, and mTOR pathway genes are frequently altered in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Science. 2011;331(6021):1199-203.
Missiaglia E, Dalai I, Barbi S, Beghelli S, Falconi M, della Peruta M, et al. Pancreatic endocrine tumors: expression profiling evidences a role for AKT-mTOR pathway. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(2):245-55.
Scarpa A, Chang DK, Nones K, Corbo V, Patch AM, Bailey P, et al. Whole-genome landscape of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours. Nature. 2017;543(7643):65-71.
Cejas P, Drier Y, Dreijerink KMA, Brosens LAA, Deshpande V, Epstein CB, et al. Enhancer signatures stratify and predict outcomes of non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Nat Med. 2019;25(8):1260-5.
Roy S, LaFramboise WA, Liu TC, Cao D, Luvison A, Miller C, et al. Loss of Chromatin-Remodeling Proteins and/or CDKN2A Associates With Metastasis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors and Reduced Patient Survival Times. Gastroenterology. 2018;154(8):2060-3.e8.
Ro C, Chai W, Yu VE, Yu R. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: biology, diagnosis,and treatment. Chin J Cancer. 2013;32(6):312-24.
Howe JR, Merchant NB, Conrad C, Keutgen XM, Hallet J, Drebin JA, et al. The North American Neuroendocrine Tumor Society Consensus Paper on the Surgical Management of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Pancreas. 2020;49(1):1-33.
Falconi M, Eriksson B, Kaltsas G, Bartsch DK, Capdevila J, Caplin M, et al. ENETS Consensus Guidelines Update for the Management of Patients with Functional Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors and Non-Functional Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Neuroendocrinology. 2016;103(2):153-71.
Shah MH, Goldner WS, Halfdanarson TR, Bergsland E, Berlin JD, Halperin D, et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Neuroendocrine and Adrenal Tumors, Version 2.2018 J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2018;16(6):693-702.
Strosberg JR, Cheema A, Weber J, Han G, Coppola D, Kvols LK. Prognostic validity of a novel American Joint Committee on Cancer Staging Classification for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(22):3044-9.
Lee LC, Grant CS, Salomao DR, Fletcher JG, Takahashi N, Fidler JL, et al. Small, nonfunctioning, asymptomatic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs): role for nonoperative management. Surgery. 2012;152(6):965-74.
Sharpe SM, In H, Winchester DJ, Talamonti MS, Baker MS. Surgical resection provides an overall survival benefit for patients with small pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. J Gastrointest Surg. 2015;19(1):117-23; discussion 23.
Finkelstein P, Sharma R, Picado O, Gadde R, Stuart H, Ripat C, et al. Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors (panNETs): Analysis of Overall Survival of Nonsurgical Management Versus Surgical Resection. J Gastrointest Surg. 2017;21(5):855-66.
Kim MJ, Choi DW, Choi SH, Heo JS, Park HJ, Choi KK, et al. Surgical strategies for non-functioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours. Br J Surg. 2012;99(11):1562-8.
Sallinen VJ, Le Large TYS, Tieftrunk E, Galeev S, Kovalenko Z, Haugvik SP, et al. Prognosis of sporadic resected small (</=2 cm) nonfunctional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors - a multi-institutional study. HPB (Oxford). 2018;20(3):251-9.
Halfdanarson TR, Strosberg JR, Tang L, Bellizzi AM, Bergsland EK, O'Dorisio TM, et al. The North American Neuroendocrine Tumor Society Consensus Guidelines for Surveillance and Medical Management of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Pancreas. 2020;49(7):863-81.
Dong DH, Zhang XF, Poultsides G, Rocha F, Weber S, Fields R, et al. Impact of tumor size and nodal status on recurrence of nonfunctional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors </=2 cm after curative resection: A multi-institutional study of 392 cases. J Surg Oncol. 2019;120(7):1071-9.
Zhang IY, Zhao J, Fernandez-Del Castillo C, Braun Y, Razmdjou S, Warshaw AL, et al. Operative Versus Nonoperative Management of Nonfunctioning Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. J Gastrointest Surg. 2016;20(2):277-83.
Royston P, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W. Dichotomizing continuous predictors in multiple regression: a bad idea. Stat Med. 2006;25(1):127-41.
Austin PC, Brunner LJ. Inflation of the type I error rate when a continuous confounding variable is categorized in logistic regression analyses. Stat Med. 2004;23(7):1159-78.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Substantial contributions to:
- The conception or design of the work: all authors.
- The acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work: EAV, OCK, OS, SVA, and CC.
- Drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content: all authors.
- Final approval of the version to be published: all authors.
- Agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved: all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vega, E.A., Kutlu, O.C., Alarcon, S.V. et al. Clinical Prognosticators of Metastatic Potential in Patients with Small Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. J Gastrointest Surg 25, 2593–2599 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-021-04946-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-021-04946-x