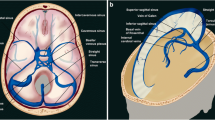
Abstract
Cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT) is an uncommon but potentially fatal condition which presents with a wide range of symptoms. Some of these presenting features are vague thus contributing to the delay in diagnosis. A prompt diagnosis and initiation of appropriate therapy are therefore of paramount importance. In this pictorial, we have tried to illustrate the direct and indirect imaging features of CVT in detail on multiple imaging modalities, along with the potential pitfalls of imaging.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bousser MG, Ferro JM. Cerebral venous thrombosis: an update. The Lancet Neurology. 2007;6(2):162–70.
Price EB, Moss HE. Osborn’s Brain: Imaging, Pathology, and Anatomy.
Poon CS, Chang JK, Swarnkar A, Johnson MH, Wasenko J. Radiologic diagnosis of cerebral venous thrombosis: pictorial review. Am J Roentgenol. 2007;189(6 Suppl):S64-75.
Rezoagli E, Bonaventura A, Coutinho JM, Vecchié A, Gessi V, Re R, et al. Incidence rates and case-fatality rates of cerebral vein thrombosis: a population-based study. Stroke. 2021;52(11):3578–85.
Stam J. Cerebral venous and sinus thrombosis: incidence and causes. Adv Neurol. 2003;92:225–32.
Ferro JM, Canhão P, Stam J, Bousser MG, Barinagarrementeria F. Prognosis of cerebral vein and dural sinus thrombosis. Stroke. 2004;35(3):664–70.
Stam J. Thrombosis of the cerebral veins and sinuses. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(17):1791–8.
Masuhr F, Mehraein S, Einhäupl K. Cerebral venous and sinus thrombosis. J Neurol. 2004;251(1):11–23.
Zimmerman RD, Ernst RJ. Neuroimaging of cerebral venous thrombosis. Neuroimaging Clin North Am. 1992;2:463–85.
Caso V, Agnelli G, Paciaroni M. Handbook on Cerebral Venous Thrombosis. Basel, Karger: Front Neurol Neurosci; 2008. p. 4–15.
Shroff M. Sinovenous thrombosis in children. Neuroimaging Clin. 2003;13(1):115–389.
Vijay RK. The cord sign. Radiology. 2006;240(1):299–300.
Virapongse C, Cazenave C, Quisling R, Sarwar MO, Hunter S. The empty delta sign: frequency and significance in 76 cases of dural sinus thrombosis. Radiology. 1987;162(3):779–85.
Teasdale E. Cerebral venous thrombosis: making the most of imaging. J R Soc Med. 2000;93(5):234–7.
Bonatti M, Valletta R, Lombardo F, et al. Accuracy of unenhanced CT in the diagnosis of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Radiol Med (Torino). 2021;126(3):399–404.
Alsafi A, Lakhani A, Carlton Jones L, et al. Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, a nonenhanced CT diagnosis? Radiol Res Pract. 2015;4:2015.
Provenzale JM, Barboriak DP, Ortel TL. Dural sinus thrombosis associated with activated protein C resistance: MR imaging findings and proband identification. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998;170(2):499–502.
Yoshikawa T, Abe O, Tsuchiya K, et al. diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging of dural sinus thrombosis. Neuroradiology. 2002;44:481–8.
Van Gijn J. Cerebral venous thrombosis: pathogenesis, presentation and prognosis. J R Soc Med. 2000;93(5):230–3.
Favrole P, Guichard J, Crassard I, Bousser MG, Chabriat H. Diffusion-weighted imaging of intravascular clots in cerebral venous thrombosis. Stroke. 2004;35:99–103.
Baumgartner RW, Studer A, Arnold M, Georgiadis D. Recanalisation of cerebral venous thrombosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2003;74:459–61.
Afifi K, Bellanger G, Buyck PJ, et al. Features of intracranial hemorrhage in cerebral venous thrombosis. J Neurol. 2020;267(11):3292–8.
Barboza MA, Mejías C, Colin-Luna J, Quiroz-Compean A, Arauz A. Intracranial venous collaterals in cerebral venous thrombosis: clinical and imaging impact. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015;86(12):1314–8.
Moudrous W, Tijssen C. Juxtacortical haemorrhage in cerebral venous sinus thrombosis:‘The Cashew Nut Sign.’ Case Rep. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2015-211978.
Oppenheim C, Domigo V, Gauvrit JY, et al. Subarachnoid hemorrhage as the initial presentation of dural sinus thrombosis. Am J Neuroradiol. 2005;26(3):614–7.
deVeber G, Andrew M, Adams C, et al. Cerebral sinovenous thrombosis in children. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(6):417–23.
Meckel S, Reisinger C, Bremerich J, Damm D, Wolbers M, Engelter S, Scheffler K, Wetzel SG. Cerebral venous thrombosis: diagnostic accuracy of combined, dynamic and static, contrast-enhanced 4D MR venography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31(3):527–35.
Rollins N, Ison C, Reyes T, Chia J. Cerebral MR venography in children: comparison of 2D time-of-flight and gadolinium-enhanced 3D gradient-echo techniques. Radiology. 2005;235(3):1011–7.
Majoie CB, van Straten M, Venema HW, den Heeten GJ. Multisection CT venography of the dural sinuses and cerebral veins by using matched mask bone elimination. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004;25(5):787–91.
Hinman JM, Provenzale JM. Hypointense thrombus on T2-weighted MR imaging: a potential pitfall in the diagnosis of dural sinus thrombosis. Eur J Radiol. 2002;41(2):147–52.
Kang JH, Yun TJ, Yoo RE, et al. Bright sinus appearance on arterial spin labeling MR imaging aids to identify cerebral venous thrombosis. Medicine. 2017;96(41):8244.
Leach JL, Bulas RV, Ernst RJ, Cornelius RS. MR imaging of isolated cortical vein thrombosis: the hyperintense vein sign. J Neurovasc Dis. 1996;1:32–8.
Crombe D, Haven F, Gille M. Isolated deep cerebral venous thrombosis diagnosed on CT and MR imaging. A case study and literature review. JBR BTR. 2003;86(5):257–61.
Herrmann KA, Sporer B, Yousry TA. Thrombosis of the internal cerebral vein associated with transient unilateral thalamic edema: a case report and review of the literature. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004;25(8):1351–5.
Alper F, Kantarci M, Dane S, Gumustekin K, Onbas O, Durur I. Importance of anatomical asymmetries of transverse sinuses: an MR venographic study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2004;18(3):236–9.
Ayanzen RH, Bird CR, Keller PJ, McCully FJ, Theobald MR, Heiserman JE. Cerebral MR venography: normal anatomy and potential diagnostic pitfalls. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000;21(1):74–8.
Gökçe E, Pınarbaşılı T, Acu B, Fırat MM, Erkorkmaz Ü. Torcular Herophili classification and evaluation of dural venous sinus variations using digital subtraction angiography and magnetic resonance venographies. Surg Radiol Anat. 2014;36(6):527–36.
Arjona A, Delgado F, Fernandez-Romero E. Intracranial hypertension secondary to giant arachnoid granulations. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2003;74(4):418.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Mahal, S., Yadav, T., Panda, S. et al. Multimodality imaging in cerebral venous thrombosis: a synopsis for emergency radiologist. Jpn J Radiol 42, 437–449 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-023-01522-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-023-01522-y