Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to investigate the usefulness of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI MRI) for the diagnosis and evaluation of autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP).
Materials and methods
A total of 4 consecutive patients with AIP, 5 patients with chronic alcoholic pancreatitis (CP), and 13 patients without pancreatic disease (controls) were studied. DWI was performed in the axial plane with spin-echo echo-planar imaging single-shot sequence. Apparent diffusion coefficients (ADCs) were measured in circular regions of interest in the pancreas. In AIP patients, abdominal MRI was performed before, and 2–4 weeks after steroid treatment. Follow-up study was performed chronologically for up to 11 months in two patients. The correlation between ADCs of the pancreas and the immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) index (serum IgG4 value/serum IgG4 value before steroid treatment) was evaluated.
Results
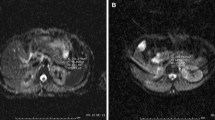
In the AIP patients, DWI of the pancreas showed high signal intensity, and the ADCs of the pancreas (mean ± SD: 0.97 ± 0.18 × 10−3 mm2/s) were significantly lower than those in patients with CP (1.45 ± 0.10 × 10−3 mm2/s) or the controls (1.45 ± 0.16 × 10−3 mm2/s) (Mann-Whitney U-test, P < 0.05). In one AIP patient with focal swelling of the pancreas head that appeared to be a mass, DWI showed high signal intensity throughout the pancreas, indicating diffuse involvement. The ADCs of the pancreas and IgG4 index were significantly inversely correlated (Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient, r s = −0.80, P < 0.05).
Conclusion
Autoimmune pancreatitis showed high signal intensity on DWI, which improved after steroid treatment. ADCs reflected disease activity. Thus, diffusion-weighted MRI might be useful for diagnosing AIP, determining the affected area, and evaluating the effect of treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yoshida K, Toki F, Takeuchi T, Watanabe S, Shiratori K, Hayashi N. Chronic pancreatitis caused by an autoimmune abnormality; proposal of the concept of autoimmune pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci 1995;40:1561–1568.
Okazaki K, Chiba T. Autoimmune pancreatitis (review). Gut 2002;51:1–4.
Nishimori I, Tamakoshi A, Otsuki M, Research Committee on Intractable Disease of the Pancreas, Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare of Japan. Prevalence of autoimmune pancreatitis in Japan from a nationwide survey in 2002. J Gastroenterol 2007:42(suppl XVIII)):6–8.
Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, et al. High serum IgG4 concentration in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 2001;344:732–738.
Horiuchi A, Kawa S, Akamatsu T, Aoki Y, Mukawa K, Furuya N, et al. Characteristic pancreatic duct appearance in autoimmune chronic pancreatitis: a case report and review of the Japanese literature. Am J Gastroenterol 1998;93:260–263.
Irie H, Honda H, Baba S, Kuroiwa T, Yoshimitsu K, Tajima T, et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis: CT and MR characteristics. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1998170:1323–1327.
Furukawa N, Muranaka N, Yasumori K, Matsubayashi R, Hayashida K, Arita. Y. Autoimmune pancreatitis: radiologic findings in three histologically proven cases. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1998;22;880–883.
Yang DH, Kim KW, Kim TK, Park SH, Kim H, Kim MH, et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis; radiologic findings in 20 patients. Abdom Imaging 2006;31:94–102.
Okazaki K, Kawa S, Kamisawa T, Naruse S, Tanaka S, Nishimori I, et al. Clinical diagnostic criteria of autoimmune pancreatitis: revised proposal. J Gastroenterol 2006;41:626–631.
Takahara T, Imai Y, Yamashita T, Yasuda S, Nasu S, Van Cauteren M. Diffusion weighted whole body imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS): technical improvement using free breathing, STIR and high resolution 3D display. Radiat Med 2004;22:275–282.
Muller MF, Prasad P, Siewert B. Abdominal diffusion mapping with use of a whole-body echo-planar system. Radiology 1994;190:475–478.
Le Bihan D, Turner R, Douek PP. Diffusion MR imaging: clinical applications. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1992;159:591–599.
Ichikawa T, Erturk SM, Motosugi U, Sou H, Iino H, Araki T, et al. High-b-value diffusion-weighted MRI for detecting pancreatic adenocarcinoma: preliminary results. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2007;188:409–414.
Taniguchi T, Seko S, Azuma K, Tamegai M, Nishida O, Inoue F, et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis detected as a mass in the tail of the pancreas. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2000;15:461–464.
Taniguchi T, Tanio H, Seko S, Nishida O, Inoue F, Okamoto M, et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis detected as a mass in the head of the pancreas without hypergammaglobulinemia, which relapsed after surgery; case reports and review of the literature. Dig Dis Sci 2003;48:1465–1471.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
T. Taniguchi and H. Kobayashi contributed equally to this study
About this article
Cite this article
Taniguchi, T., Kobayashi, H., Nishikawa, K. et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in autoimmune pancreatitis. Jap J Radiol 27, 138–142 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-008-0311-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-008-0311-2