Abstract
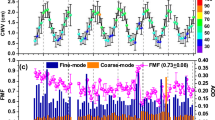
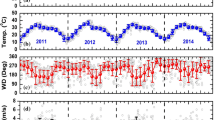
Aerosols erupted from volcanoes may significantly alter climate because they can impact cloud dynamics, radiation budget, and tropospheric chemistry. The optical and physical characteristics of the Spatio-temporal variation of aerosols and gases' impact on the atmosphere during the recent La Palma eruption have been examined in the current paper from 19 September to 31 October 2021. The result shows that before the La Palma eruption, the AOD value was 0.1 showing a clear sky. However, after the eruption daily mean AOD reached the highest values of 0.7 and 0.56, showing that La Palma had high aerosol loading when the eruption occurred. The 0.4 value Aerosol index was observed. The coarse mode aerosols contributed more to the overall aerosol load than fine mode aerosols, confirming their existence above La Palma. Analysis revealed that mixed aerosols were present over La Palma. Due to the powerful ash plume's ability to scatter sunlight, the high value of Single-Scattering Albedo (~ 0.99) was detected. The maximum concentration of SO2, HCHO, NO2, O3, and CO was found to be 60 mmol/m2, 120 µmol/m2, 70 µmol/m2, 129 mmol/m2, and 50 mmol/m2, respectively, over the La Palma region. The ash plume's trajectory by the forward trajectory and the Hybrid Single Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory dispersion model showed the plume moving in the southwest direction.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adach W, Błaszczyk M, Olas B (2020) Carbon monoxide and its donors—chemical and biological properties. Chem Biol Interact 318:1. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CBI.2020.108973
Afonso L (1985) La Palma. In: Geografía de Canarias 4, Afonso L (ed) Interinsular Canaria, S/C de Tenerife - Google Search. (n.d.). https://www.google.com/search?q=Afonso+L+%281985%29+La+Palma.+In%3A+Geografía+de+Canarias+4%2C+Afonso+L+%28ed%29.+Interinsular+Canaria%2C+S%2FC+de+Tenerife&rlz=1C1SQJL_enPK998PK998&ei=PCTcYubhLLC49u8P2IidiAc&ved=0ahUKEwjm776_uY_5AhUwnP0HHVhEB3EQ4dUDCA4&uact=5&oq=Afonso+L+%281985%29+La+Palma.+In%3A+Geografía+de+Canarias+4%2C+Afonso+L+%28ed%29.+Interinsular+Canaria%2C+S%2FC+de+Tenerife&gs_lcp=Cgdnd3Mtd2l6EAMyCAgAEI8BEOoCMggILhCPARDqAjIICAAQjwEQ6gIyCAgAEI8BEOoCMggIABCPARDqAjIICAAQjwEQ6gIyCAgAEI8BEOoCMggIABCPARDqAjIICAAQjwEQ6gIyCAgAEI8BEOoCSgQIQRgASgQIRhgAUK0LWK0LYNMWaAJwAXgAgAEAiAEAkgEAmAEAoAEBoAECsAEKwAEB&sclient=gws-wiz. Retrieved 23 July 23 2022
Anda M, Suparto S (2016) Characteristics of pristine volcanic materials: beneficial and harmful effects and their management for restoration of agroecosystem. Sci Total Environ 543:480–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2015.10.157
Andreae MO, Gelencsér A (2006) Black carbon or brown carbon? The nature of light-absorbing carbonaceous aerosols. Atmos Chem Phys 6(10):3131–3148. https://doi.org/10.5194/ACP-6-3131-2006
Bagheri R, Bagheri F, Karami GH, Jafari H (2019) Chemo-isotopes (18O & 2H) signatures and HYSPLIT model application: clues to the atmospheric moisture and air mass origins. Atmos Environ 215:116892. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ATMOSENV.2019.116892
Becerril L, Galindo I, Gudmundsson A, Morales JM (2013) Depth of origin of magma in eruptions. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02762
Bergstrom RW, Pilewskie P, Russell PB, Redemann J, Bond TC, Quinn PK, Sierau B (2007) Spectral absorption properties of atmospheric aerosols. Atmos Chem Phys 7(23):5937–5943. https://doi.org/10.5194/ACP-7-5937-2007
CAMS monitors transport of SO2 from La Palma volcano|Copernicus. (2022). https://atmosphere.copernicus.eu/cams-monitors-transport-so2-la-palma-volcano. Retrieved 6 April 2022
Chen TM, Gokhale J, Shofer S, Kuschner WG (2007) Outdoor air pollution: nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and carbon monoxide health effects. Am J Med Sci 333(4):249–256. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAJ.0B013E31803B900F
Chen J, Liu Z, Yin Z, Liu X, Li X, Yin L, Zheng W (2023) Predict the effect of meteorological factors on haze using BP neural network. Urban Clim 51:101630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.uclim.2023.101630
Cheng Y, Lan S, Fan X, Tjahjadi T, Jin S, Cao L (2023) A dual-branch weakly supervised learning based network for accurate mapping of woody vegetation from remote sensing images. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 124:103499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2023.103499
Costa S, Ferreira J, Silveira C, Costa C, Lopes D, Relvas H, Borrego C, Roebeling P, Miranda AI, Paulo Teixeira J (2014) Integrating health on air quality assessment—review report on health risks of two major European outdoor air pollutants: PM and NO2. J Toxicol Environ Health Part B 17(6):307–340. https://doi.org/10.1080/10937404.2014.946164
Derimian Y, Dubovik O, Tanre D, Goloub P, Lapyonok T, Mortier A (2012) Optical properties and radiative forcing of the Eyjafjallajökull volcanic ash layer observed over Lille, France, in 2010. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JD016815
Dong W, Zhao J, Qu J, Xiao S, Li N, Hou S, Li Y (2023) Abundance matrix correlation analysis network based on hierarchical multihead self-cross-hybrid attention for hyperspectral change detection. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2023.3235401
Dubovik O, King MD (2000) A flexible inversion algorithm for retrieval of aerosol optical properties from Sun and sky radiance measurements. J Geophys Res Atmos 105(D16):20673–20696. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JD900282
Dubovik O, Holben B, Eck TF, Smirnov A, Kaufman YJ, King MD, Tanré D, Slutsker I (2002) Variability of absorption and optical properties of key aerosol types observed in worldwide locations. J Atmos Sci 59(3):590–608. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(2002)059%3C0590%3AVOAAOP%3E2.0.C
Eck T, Reid JS, Dubovik O, Eck TF, Holben BN, Reid JS, O’neill NT, Schafer JS, Dubovik O, Smirnov A, Yamasoe MA, Artaxo P, Holben BFN (2003) High aerosol optical depth biomass burning events: a comparison of optical properties for different source regions. Wiley Online Library 30(20):2035. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003GL017861
Fabricio Neta ADB, do Nascimento CWA, Biondi CM, van Straaten P, Bittar SMB (2018) Natural concentrations and reference values for trace elements in soils of a tropical volcanic archipelago. Environ Geochem Health 40(1):163–173. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10653-016-9890-5
Franz M, Zaehle S (2021) Competing effects of nitrogen deposition and ozone exposure on northern hemispheric terrestrial carbon uptake and storage, 1850–2099. Biogeosciences 18(10):3219–3241. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-18-3219-2021
García-Cervigón AI, García-Hidalgo M, Martín-Esquivel JL, Rozas V, Sangüesa-Barreda G, Olano JM (2019) The Patriarch: a Canary Islands juniper that has survived human pressure and volcanic activity for a millennium. Ecology 100(10):e02780. https://doi.org/10.1002/ECY.2780
Holben BN, Eck TF, Slutsker I, Tanré D, Buis JP, Setzer A, Vermote E, Reagan JA, Kaufman YJ, Nakajima T, Lavenu F, Jankowiak I, Smirnov A (1998) AERONET—a federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens Environ 66(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(98)00031-5
Hunt WH, Winker DM, Vaughan MA, Powell KA, Lucker PL, Weimer C (2009) CALIPSO lidar description and performance assessment. J Atmos Oceanic Technol 26:1214–1228. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009JTECHA1223.1
Isaksen ISA, Hov Ø (2017) Calculation of trends in the tropospheric concentration of O3, OH, CO, CH4 and NOx. Tellus B 39(3):271–285. https://doi.org/10.3402/TELLUSB.V39I3.15347
Jose S, Kumar Mishra A, Lodhi NK, Kumar Sharma S, Singh S (2021) Characteristics of aerosol size distributions and new particle formation events at Delhi: an urban location in the Indo-Gangetic Plains. Front Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2021.750111
Kremser S, Thomason LW, von Hobe M, Hermann M, Deshler T, Timmreck C, Toohey M, Stenke A, Schwarz JP, Weigel R, Fueglistaler S, Prata FJ, Vernier JP, Schlager H, Barnes JE, Antuña-Marrero JC, Fairlie D, Palm M, Mahieu E, Notholt J, Rex M, Bingen C, Vanhellemont F, Bourassa A, Plane JMC, Klocke D, Carn SA, Clarisse L, Trickl T, Neely R, James AD, Rieger L, Wilson JC, Meland B (2016) Stratospheric aerosol—observations, processes, and impact on climate. Rev Geophys 54(2):278–335. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015RG000511
Longpré MA (2021) Reactivation of Cumbre Vieja volcano. Science 374(6572):1197–1198. https://doi.org/10.1126/SCIENCE.ABM9423
Longpré MA, Felpeto A (2021) Historical volcanism in the Canary Islands; part 1: a review of precursory and eruptive activity, eruption parameter estimates, and implications for hazard assessment. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 419:107363. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JVOLGEORES.2021.107363
Lyapustin A, Martonchik J, Wang Y, Laszlo I, Korkin S (2011a) Multiangle implementation of atmospheric correction (MAIAC): 1. Radiative transfer basis and look-up tables. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JD014985
Lyapustin A, Wang Y, Laszlo I, Kahn R, Korkin S, Remer L, Levy R, Reid JS (2011b) Multiangle implementation of atmospheric correction (MAIAC): 2. Aerosol algorithm. J Geophys Res Atmos 116(3):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JD014986
Ma S, Qiu H, Yang D, Wang J, Zhu Y, Tang B, Sun K, Cao M (2023) Surface multi-hazard effect of underground coal mining. Landslides 20(1):39–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-022-01961-0
Pérez-Hernández E, Peña-Alonso C, Fernández-Cabrera E, Hernández-Calvento L (2021) Assessing the scenic quality of transgressive dune systems on volcanic islands. The case of Corralejo (Fuerteventura island, Spain). Sci Total Environ 784:147050. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2021.147050
Petzold A, Ogren JA, Fiebig M, Laj P, Li SM, Baltensperger U, Holzer-Popp T, Kinne S, Pappalardo G, Sugimoto N, Wehrli C, Wiedensohler A, Zhang XY (2013) Recommendations for reporting black carbon measurements. Atmos Chem Phys 13(16):8365–8379. https://doi.org/10.5194/ACP-13-8365-2013
Qu S, Chen X, Wang Y, Shi P, Shan S, Gou J, Jiang P (2018) Isotopic characteristics of precipitation and origin of moisture sources in Hemuqiao catchment, a small watershed in the lower reach of Yangtze River. Water (switzerland) 10(9):1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091170
Querol X, Alastuey A, Rodríguez S, Viana MM, Artíñano B, Salvador P, Mantilla E, Do Santos SG, Patier RF, De La Rosa J, De La Campa AS, Menéndez M, Gil JJ (2004) Levels of particulate matter in rural, urban and industrial sites in Spain. Sci Total Environ 334–335:359–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2004.04.036
Rao W, Zhang W, Yong B, Tan H, Meredith KT, Jin K, Zheng F, Wang S (2018) Identifying the source of atmospheric moisture over arid deserts using stable isotopes (2H and 18O) in precipitation. Hydrol Process 32(3):436–449. https://doi.org/10.1002/HYP.11431
Risk and Recovery Mapping Portfolio | COPERNICUS EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT SERVICE (2022) https://emergency.copernicus.eu/mapping/ems/risk-and-recovery-mapping-portfolio. Retrieved 17 Aug 2022
Ruggieri F, Saavedra J, Fernandez-Turiel JL, Gimeno D, Garcia-Valles M (2010) Environmental geochemistry of ancient volcanic ashes. J Hazard Mater 183(1–3):353–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2010.07.032
Schafer JS, Eck TF, Holben BN, Thornhill KL, Ziemba LD, Sawamura P, Moore RH, Slutsker I, Anderson BE, Sinyuk A, Giles DM, Smirnov A, Beyersdorf AJ, Winstead EL (2019) Intercomparison of aerosol volume size distributions derived from AERONET ground-based remote sensing and LARGE in situ aircraft profiles during the 2011–2014 DRAGON and DISCOVER-AQ experiments. Atmos Meas Tech 12(10):5289–5301. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-12-5289-2019
Sellitto P, Salerno G, La Spina A, Caltabiano T, Scollo S, Boselli A, Leto G, Zanmar Sanchez R, Crumeyrolle S, Hanoune B, Briole P (2020) Small-scale volcanic aerosols variability, processes and direct radiative impact at Mount Etna during the EPL-RADIO campaigns. Sci Rep 10(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-71635-1
Smith SJ, Van Aardenne J, Klimont Z, Andres RJ, Volke A, Delgado Arias S (2011) Anthropogenic sulfur dioxide emissions: 1850–2005. Atmos Chem Phys 11(3):1101–1116. https://doi.org/10.5194/ACP-11-1101-2011
Soni K, Singh S, Bano T, Tanwar RS, Nath S, Arya BC (2010) Variations in single scattering albedo and Angstrom absorption exponent during different seasons at Delhi, India. Atmos Environ 44(35):4355–4363. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ATMOSENV.2010.07.058
Srivastava AK, Soni VK, Singh S, Kanawade VP, Singh N, Tiwari S, Attri SD (2014) An early South Asian dust storm during March 2012 and its impacts on Indian Himalayan foothills: a case study. Sci Total Environ 493:526–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2014.06.024
Tariq S, ul-Haq Z, Ali M (2016) Satellite and ground-based remote sensing of aerosols during intense haze event of October 2013 over Lahore, Pakistan. Asia Pac J Atmos Sci 52(1):25–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13143-015-0084-3
Tian H, Huang N, Niu Z, Qin Y, Pei J, Wang J (2019) Mapping winter crops in china with multi-source satellite imagery and phenology-based algorithm. Remote Sens (Basel, Switzerland) 11(7):820. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11070820
Tian H, Pei J, Huang J, Li X, Wang J, Zhou B, Qin Y, Wang L (2020) Garlic and winter wheat identification based on active and passive satellite imagery and the Google Earth Engine in Northern China. Remote Sens (Basel, Switzerland) 12(3539):3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213539
Theys N, Hedelt P, De Smedt I, Lerot C, Yu H, Vlietinck J, Pedergnana M, Arellano S, Galle B, Fernandez D, Carlito CJM, Barrington C, Taisne B, Delgado-Granados H, Loyola D, Van Roozendael M (2019) Global monitoring of volcanic SO 2 degassing with unprecedented resolution from TROPOMI onboard Sentinel-5 Precursor. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/S41598-019-39279-Y
Ul-Haq Z, Rana AD, Ali M, Mahmood K, Tariq S, Qayyum Z (2015) Carbon monoxide (CO) emissions and its tropospheric variability over Pakistan using satellite-sensed data. Adv Space Res 56(4):583–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ASR.2015.04.026
Van Kempen TA, Oggionni F, Van Hees RM (2021) Monitoring the Tropospheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) short-wave infrared (SWIR) module instrument stability using desert sites. Atmos Meas Tech 14(10):6711–6722. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-14-6711-2021
Vandenplas O, Fievez P, Delwiche JP, Boulanger J, Thimpont J (2004) Persistent asthma following accidental exposure to formaldehyde. Allergy 59(1):115–116. https://doi.org/10.1046/J.1398-9995.2003.00340.X
Veefkind JP, Aben I, McMullan K, Förster H, de Vries J, Otter G, Claas J, Eskes HJ, de Haan JF, Kleipool Q, van Weele M, Hasekamp O, Hoogeveen R, Landgraf J, Snel R, Tol P, Ingmann P, Voors R, Kruizinga B, Vink R, Visser H, Levelt PF (2012) TROPOMI on the ESA Sentinel-5 Precursor: a GMES mission for global observations of the atmospheric composition for climate, air quality and ozone layer applications. Remote Sens Environ 120:70–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSE.2011.09.027
Wang X, Wang T, Xu J, Shen Z, Yang Y, Chen A, Wang S, Liang E, Piao S (2022) Enhanced habitat loss of the Himalayan endemic flora driven by warming-forced upslope tree expansion. Nat Ecol Evol 6(7):890–899. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-022-01774-3
Wen Z, Wang Q, Ma Y, Jacinthe PA, Liu G, Li S, Shang Y, Tao H, Fang C, Lyu L, Zhang B, Song K (2023) Remote estimates of suspended particulate matter in global lakes using machine learning models. Int Soil Water Conserv Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2023.07.002
Wu H, Zhang X, Xiaoyan L, Li G, Huang Y (2015) Seasonal variations of deuterium and oxygen-18 isotopes and their response to moisture source for precipitation events in the subtropical monsoon region. Hydrol Process 29(1):90–102. https://doi.org/10.1002/HYP.10132
Xingna Y, Bin Z, Yan Y, Shuxian F, Aijun C, Xingna Y, Bin Z, Yan Y, Shuxian F, Aijun C (2011) Seasonal variation of columnar aerosol optical properties in Yangtze River Delta in China. Adv Atmos Sci 28(6):1326–1335. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00376-011-0158-9
Yin L, Wang L, Ge L, Tian J, Yin Z, Liu M, Zheng W (2023) Study on the thermospheric density distribution pattern during geomagnetic activity. Appl Sci 13(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095564
Zhang S, Bai X, Zhao C, Tan Q, Luo G, Wang J, Li Q, Wu L, Chen F, Li C, Deng Y, Yang Y, Xi H (2021) Global CO2 consumption by silicate rock chemical weathering: its past and future. Earth's Future 9(5):e1938Ee2020E. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020EF001938
Zhu W, Chen J, Sun Q, Li Z, Tan W, Wei Y (2022) Reconstructing of high-spatial-resolution three-dimensional electron density by ingesting SAR-derived VTEC into IRI model. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2022.3178242
Zhuo Z, Du L, Lu X, Chen J, Cao Z (2022) Smoothed Lv Distribution Based Three-Dimensional Imaging for Spinning Space Debris. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 60:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2022.3174677
Zielinski T, Petelski T, Strzalkowska A, Pakszys P, Makuch P (2016) Impact of wild forest fires in Eastern Europe on aerosol composition and particle optical properties. Oceanologia 58(1):13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.OCEANO.2015.07.005
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank MODIS data and the AERONET La Palma site for providing data. We are grateful to NOAA Air Resources Laboratory (ARL) for the HYSPLIT model. We also appreciate CALIPSO mission scientists for the data used in this study.
Funding
Not required.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TY made maps and wrote the manuscript. ST conceptualizes the work. IB conducted an analysis and wrote the manuscript. Z.ul-H wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval
Not required.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Edited by Dr. Apostolos Sarris (GUEST EDITOR) / Prof. Gabriela Fernández Viejo (CO-EDITOR-IN-CHIEF).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yaqoob, T., Tariq, S., Bashir, I. et al. Analysis of air quality due to the eruption of La Palma using remote sensing. Acta Geophys. 72, 1397–1411 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-023-01278-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-023-01278-z