Abstract
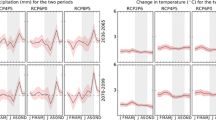
Understanding the impacts of climate change on basin hydrology is critical for developing effective water management practices. This study was conducted to investigate climate change and its impact on the hydrological processes of the Baro–Akobo River basin in Ethiopia. Five bias-corrected regional climate models and their ensemble were developed to examine future climate changes in the 2030s (2021–2050) and 2080s (2071–2100) periods under the two Representative Concentration Pathways (RCP) 4.5 and RCP8.5 scenarios compared to a baseline (1981–2010) period. The calibrated model performed well with Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency and coefficient of determination of each 0.73 for daily and 0.89 and 0.9 for monthly simulation, respectively. Though all RCMs agree concerning the increasing direction of the 2030 and 2080s maximum and minimum temperature changes, there is inconsistency in the magnitude and direction of monthly projected rainfall changes. With the ensemble, the maximum and minimum temperatures will increase by 2.6 and 3.6 °C, respectively, and rainfall will decrease by 5% in the 2080s under RCP8.5 scenarios. The dry and wet season rainfall are expected to decrease by 19 and 3.7% under the RCP8.5 scenarios in the 2080s. Consequently, future climate change could cause a decrease in the annual surface runoff and water yield, while evapotranspiration could increase under the RCP4.5 and RCP8.5 scenarios. This study provides useful insights about potential climate change impacts on the hydrology of the basin, which could be useful to inform decision-makers in developing strategies such as water harvesting to mitigate the impact of climate change.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaspour KC, Yang J, Maximov I et al (2007) Modeling hydrology and water quality in the pre–alpine/alpine Thur watershed using SWAT. J Hydrol 333(2–4):413–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.09.014
Abbaspour KC, Rouholahnejad E, Vaghefi S et al (2015) A continental-scale hydrology and water quality model for Europe: calibration and uncertainty of a high-resolution large-scale SWAT model. J Hydrol 524:733–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.03.027
Abdo KS, Fiseha BM, Rientjes THM et al (2009) Assessment of climate change impacts on the hydrology of Gilgel Abay catchment in Lake Tana basin. Ethiopia 3669:3661–3669. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp
Alemayehu T, Kebede S, Liu L (2016) Nedaw D (2016) groundwater recharge under changing landuses and climate variability : the case of Baro-Akobo River Basin. Ethiopia 6(1):78–95
Baldauf M, Seifert A, Förstner J, Majewski D, Raschendorfer M, Reinhardt T (2011) Operational convective-scale numerical weather prediction with the COSMO model: description and sensitivities. Mon Wea Rev 139:3887–3905. https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-10-05013.1
Bartier PM, Keller CP (1996) Multivariate interpolation to incorporate thematic surface data using inverse distance weighting (IDW). Comput Geosci 22:795–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/0098-3004(96)00021-0
Bayabil HK, Dile YT (2020) Improving hydrologic simulations of a small watershed through soil data integration. Water (switzerland) 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102763
Beyene T, Lettenmaier DP, Kabat P (2010) Hydrologic impacts of climate change on the Nile River Basin : implications of the 2007 IPCC scenarios, pp 433–461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-009-9693-0
Bhattacharya T, Khare D, Arora M (2020) Evaluation of reanalysis and global meteorological products in Beas river basin of North-Western Himalaya. Environ Syst Res 9:1–29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-020-00186-1
Block PJ, Souza Filho FA, Sun L, Kwon HH (2009) A streamflow forecasting framework using multiple climate and hydrological models. J Am Water Resour Assoc 45:828–843. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.2009.00327.x
Bolch T, Kulkarni A, Kääb A, Huggel C, Paul F, Cogley JG, Bajracharya S (2012) The state and fate of Himalayan glaciers. Science 336(6079):310–314
Christensen JH, Boberg F, Christensen OB, Lucas-Picher P (2008) On the need for bias correction of regional climate change projections of temperature and precipitation. Geophys Res Lett 35. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GL035694
Conway D, Schipper ELF (2011) Adaptation to climate change in Africa: Challenges and opportunities identified from Ethiopia. Glob Environ Chang 21:227–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2010.07.013
Cramér H (1999) Mathematical methods of statistics, 9th edn. Princeton University Press, US
Déqué M, Rowell DP, Lüthi D, Giorgi F et al (2007) An intercomparison of regional climate simulations for Europe: assessing uncertainties in model projections. Clim Change 81:53–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-006-9228-x
Dibaba WT, Demissie TA, Miegel K (2020) Watershed hydrological response to combined land use/land cover and climate change in highland ethiopia: finchaa catchment. Water (switzerland) 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061801
Dibaba WT, Miegel K, Demissie TA (2019) Evaluation of the CORDEX regional climate models performance in simulating climate conditions of two catchments in Upper Blue Nile Basin. Dyn Atmos Ocean 87:101104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dynatmoce.2019.101104
Dile YT, Berndtsson R, Setegn SG (2013) Hydrological response to climate change for Gilgel Abay River, in the Lake Tana Basin—Upper Blue Nile Basin of Ethiopia. 8:12–17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0079296
Dile YT, Srinivasan R (2014) Evaluation of CFSR climate data for hydrologic prediction in data- scarce watersheds : an application in the Blue Nile River Basin 1:50. https://doi.org/10.1111/jawr.12182
Elshamy ME, Seierstad IA, Sorteberg A (2009) Impacts of climate change on Blue Nile flows using bias-corrected GCM scenarios, pp 551–565
Fenta AA, Yasuda H, Shimizu K, Ibaraki Y, Haregeweyn N, Kawai T, Belay AS, Sultan D, Ebabu K (2018) Evaluation of satellite rainfall estimates over the Lake Tana basin at the source region of the Blue Nile River. Atmos Res 212:43–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2018.05.009
Fentaw F, Hailu D, Nigussie A, Melesse AM (2018) Climate change impact on the hydrology of Tekeze Basin, Ethiopia: projection of rainfall-runoff for future water resources planning. Water Conserv Sci Eng 3:267–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41101-018-0057-3
Fowler HJ, Ekström M, Blenkinsop S, Smith AP (2007) Estimating change in extreme European precipitation using a multimodel ensemble. J Geophys Res Atmos 112. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JD008619
Fowler HJ, Kilsby CG (2007) Using regional climate model data to simulate historical and future river flows in northwest England. Clim Change 80:337–367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-006-9117-3
Fuka DR, Walter MT, Macalister C et al (2013). Using the climate forecast system reanalysis as weather input data for watershed models. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10073
Getachew F, Bayabil HK, Hoogenboom G, Teshome FT, Zewdu E (2021) Irrigation and shifting planting date as climate change adaptation strategies for sorghum. Agric Water Manag 255:106988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.106988
Giorgi F (2006) Regional climate modeling: status and perspectives. J Phys IV JP 139:101–118. https://doi.org/10.1051/jp4:2006139008
Gudmundsson L, Bremnes JB, Haugen JE, Engen-Skaugen T (2012) Technical Note: downscaling RCM precipitation to the station scale using statistical transformations – A comparison of methods. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 16:3383–3390. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-16-3383-2012
Hawkins E, Sutton R (2011) The potential to narrow uncertainty in projections of regional precipitation change. Clim Dyn 37:407–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-010-0810-6
Hengl T, Heuvelink GBM, Kempen B et al (2015) Mapping soil properties of Africa at 250 m resolution: random forests significantly improve current predictions. PLoS ONE 10:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0125814
Hoegh-Goldberg O, Bruno JF (2010). The impact of climate change on the World’s Marine Ecosystems. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1189930
Houghton JT, Ding Y, Griggs DJ, et al (2001) Climate change 2001: the scientific basis. Contribution of working group I to the third assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge, United Kingdom, and New York, NY: Cambridge University Press
Hulme M, Doherty R, Ngara T, New M, Lister D (2001) African climate change: 1900–2100. Climate Res 17:145–168. https://doi.org/10.3354/cr017145
Hulme M, Doherty R, Ngara T, New MG, Low PS (Ed) (2005). Global warming and African climate change: a reassessment. Clim Change Africa, pp 29–40. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511535864
IPCC (2001) Climate change 2001: the scientific basis. The third assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, New York
IPCC (2007) Climate change 2007: The physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, New York, US
IPCC (2013) Climate change 2013: The physical science basis. In: Working Group I contribution to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change.
IPCC (2014) Climate change 2014: Impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. part a: global and sectoral aspects. In: Contribution of working group II to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change [Field CB, Barros VR, Dokken DJ]
Jackob D, Bärring L, Christensen OB, Christensen JH, de Castro M, Déqué M, Giorgi F, Hagemann S, Hirschi M, Jones R, Kjellström E, Lenderink G, Rockel B, Sánchez E, Schär C, Seneviratne SI, Somot S, van Ulden A, van den Hurk B (2012) An inter-comparison of regional climate models for Europe: model performance in present-day climate. Clim Change 81:31–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-006-9213-4
Kang Y, Khan S, Ma X (2009) Climate change impacts on crop yield, crop water productivity and food security—a review. Prog Nat Sci 19:1665–1674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2009.08.001
Kiesel J, Gericke A, Rathjens H et al (2019) Climate change impacts on ecologically relevant hydrological indicators in three catchments in three European ecoregions. Ecol Eng 127:404–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2018.12.019
Kiprotich P, Wei X, Zhang Z et al (2021) Assessing the impact of land use and climate change on surface runoff response using gridded observations and swat+. Hydrology 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology8010048
Koch FJ, Van Griensven A, Uhlenbrook S, et al (2012) The effects of land use change on hydrological responses in the Choke Mountain Range (Ethiopia)—a new approach addressing land use dynamics in the model SWAT. iEMSs 2012—Manag Resour a Ltd Planet Proc 6th Bienn Meet Int Environ Model Softw Soc 3022–3029
Kundzewicz ZW, Krysanova V, Benestad RE et al (2018) Uncertainty in climate change impacts on water resources. Environ Sci Policy 79:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2017.10.008
Liu X, Liu W, Tang Q et al (2022) Global agricultural water scarcity assessment incorporating blue and green water availability under future climate change Earth’ s future. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021EF002567
López-Ballesteros A, Senent-Aparicio J, Martínez C, Pérez-Sánchez J (2020) Assessment of future hydrologic alteration due to climate change in the Aracthos River basin (NW Greece). Sci Total Environ 733:139299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139299
McCarthy JJ, Canziani OF, Leary NA, Dokken DJ, White KS (2001) Climate change 2001: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability Contribution of Working Group II to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
Mengistu DT, Sorteberg A (2012) Sensitivity of SWAT simulated streamflow to climatic changes within the Eastern Nile River basin. 391–407. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-16-391-2012
Mengistu AG, Woldesenbet TA, Dile YT (2021a) Evaluation of the performance of bias-corrected CORDEX regional climate models in reproducing Baro-Akobo basin climate. Theor Appl Climatol 144:751–767. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-021-03552-w
Mengistu AG, Woldesenbet TA, Taddele YD (2021b) Evaluation of observed and satellite-based climate products for hydrological simulation in data-scarce Baro-Akob River Basin, Ethiopia. Ecohydrol Hydrobiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecohyd.2021.11.006
Moriasi DN, Arnold J, Van Liew M, Bingner RL, Harmel RD, Veith TL (2007) Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans Am Soc Agric Eng (ASAE) 50:885–900
Moss RH, Edmonds JA, Hibbard KA et al (2010) The next generation of scenarios for climate change research and assessment. Nature 463:747–756. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08823
Muleta TN (2021) Climate change scenario analysis for Baro-Akobo river basin. Southwestern Ethiopia Environ Syst Res 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-021-00225-5
Munawar S, Rahman G, Farhan M, et al (2022) Future Climate Projections Using SDSM and LARS-WG Downscaling Methods for CMIP5 GCMs over the Transboundary Jhelum River Basin of the Himalayas Region
Neitsch SL, Arnold JG, Kiniry JR, Williams JR (2011) Soil and water assessment tool theoretical documentation version 2009. Texas Water Resources Institute. https://hdl.handle.net/1969.1/128050
Nikulin G, Jones C, Giorgi F et al (2012) Precipitation climatology in an ensemble of CORDEX-Africa regional climate simulations. J Clim 25:6057–6078. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00375.1
NAPA (2007) Preparation of National Adaptation Programme of Action (NAPA) of Ethiopia. Addis Abeba
Piani C, Haerter JO, Coppola E (2010) Statistical bias correction for daily precipitation in regional climate models over Europe. Theor Appl Climatol 99:187–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-009-0134-9
Prentice IC, Farquhar G, Fasham M, et al (2001) The carbon cycle and atmospheric carbon dioxide. In Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis Clim; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA.
Rathjens H, Bieger K, Srinivasan R, Arnold JG (2016) CMhyd User Manual Documentation for preparing simulated climate change data for hydrologic impact studies. p.16p
Richter BD, Baumgartner JV, Jennifer P, Braun DP (1996) A method for assessing hydrologic alteration within ecosystems | Un metro para evaluar alteraciones hidrologicas dentro de ecosistemas. Conserv Biol 10:1163–1174
Rockel B, Will A, Hense A (2008) The regional climate model COSMOCLM (CCLM4). Meteorol Z 17(4):347–348. https://doi.org/10.1127/0941-2948/2008/0309
Saha S, Moorthi S, Pan HL et al (2010) The NCEP climate forecast system reanalysis. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 91:1015–1057. https://doi.org/10.1175/2010BAMS3001.1
Samuelsson P, Gollvik S, Kupiainen M, Kourzeneva E, van de Berg W (2015) The surface processes of the Rossby Centre regional atmospheric climate model (RCA4), vol 1. SMHI, Norrköping, Sweden, pp 2358–2381
Saxton K, Rawls W (2006) Soil water characteristic estimates by texture and organic matter for hydrologic solutions. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:1569–1578
Setegn SG, Rayner D, Melesse AM et al (2011) Impact of climate change on the hydroclimatology of Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia. Water Resour Res 47:1–13
Soliman ESA, Sayed MAA, Jeuland M (2009) Impact assessment of future climate change for the Blue Nile Basin, Using a RCM nested in a GCM. Nile Basin Water Engin Sci Mag 2:15–30
Taye MT, Dyer E, Hirpa FA, Charles K (2018) Climate change impact on water resources in the Awash basin, Ethiopia. Water (switzerland) 10:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111560
Teutschbein C, Seibert J (2010) Regional climate models for hydrological impact studies at the catchment scale: a review of recent modeling strategies. Geogr Compass 4:834–860. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-8198.2010.00357.x
Teutschbein C, Seibert J (2012) Bias correction of regional climate model simulations for hydrological climate-change impact studies: review and evaluation of different methods. J Hydrol 456–457:12–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.05.052
Tahani MS, ElShamy M, Mohammed AA, Abbas MS (2013) The Development of the Baro-Akobo-Sobat sub basin and its Impact on Downstream Nile Basin Countries. Nile Water Sci Eng J 6:2
Van Vuuren DP, Van Edmonds J, Kainuma M et al (2011) The representative concentration pathways: an overview. 5–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-011-0148-z
UNESCO (2012) United Nation Education, Science and Cultural Organization "Ecological Sciences for Sustainable Development." from www.unesco.org.
Worqlul A, Taddele YD, Ayana EK et al (2018) Impact of climate change on streamflow hydrology in headwater catchments of the upper Blue Nile Basin. Ethiopia Water (switzerland) 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020120
Woldesenbet TA (2022) Impact of land use and land cover dynamics on ecologically-relevant flows and blue-green water resources. Ecohydrol Hydrobiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecohyd.2022.03.002
Woldesenbet TA, Elagib NA (2021) Spatial-temporal evaluation of different reference evapotranspiration methods based on the climate forecast system reanalysis data
Woldesenbet TA, Elagib NA, Ribbe L, Heinrich J (2018) Catchment response to climate and land–use changes in the Upper Blue Nile sub-basins. Ethiopia Sci Total Environ 644:193–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.198
Worku G, Teferi E, Bantider A, Dile YT (2020) Statistical bias correction of regional climate model simulations for climate change projection in the Jemma sub-basin, upper Blue Nile Basin of Ethiopia. Theor Appl Climatol 139:1569–1588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-019-03053-x
Worku G, Teferi E, Bantider A, Dile YT (2021) Modelling hydrological processes under climate change scenarios in the Jemma sub-basin of upper Blue Nile Basin. Ethiopia Clim Risk Manag 31:100272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crm.2021.100272
Zhang X, Xu YP, Fu G (2014) Uncertainties in SWAT extreme flow simulation under climate change. J Hydrol 515:205–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.04.064
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by Dr. Michael Nones (CO-EDITOR-IN-CHIEF).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mengistu, A.G., Woldesenbet, T.A., Dile, Y.T. et al. Modeling the impacts of climate change on hydrological processes in the Baro–Akobo River basin, Ethiopia. Acta Geophys. 71, 1915–1935 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-022-00956-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-022-00956-8