Abstract
Objective
Protein disulfide isomerase A2 (PDIA2), a member of the protein disulfide isomerase family, plays a key role in the folding of nascent proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum by forming disulfide bonds, together with enzymes such as thiol isomerase, oxidase, and reductase. This study investigated the clinical significance and potential functions of PDIA2 in glioma.
Methods
The expression of PDIA2 in gliomas was explored using The Cancer Genome Atlas and Gene Expression Omnibus databases. We analyzed the clinical characteristics of glioma patients and the prognostic and diagnostic value of PDIA2 expression. Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression analyses were used to examine the effect of PDIA2 expression on overall survival, progression-free interval, and disease-specific survival. Furthermore, we performed Gene Set Enrichment Analysis and immune infiltration analysis to investigate the functions of PDIA2. PDIA2 mRNA and protein expression was evaluated in cell lines and glioma tissues.
Results
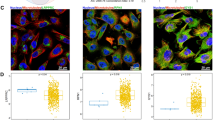
PDIA2 was expressed at low levels in glioma patients. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that glioma patients with low PDIA2 levels had a worse prognosis than those with high PDIA2 levels. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis indicated the diagnostic and prognostic ability of PDIA2 (area under the curve = 0.918). Pathways associated with PD1, PI3K/AKT, cancer immunotherapy via PD1 blockade, Fceri-mediated NF-kB activation, FOXM1, and DNA repair were enriched in glioma patients with low levels of PDIA2. PDIA2 expression levels were negatively correlated with immune cell infiltrate levels.
Conclusion
PDIA2 levels are significantly downregulated in glioma. PDIA2 expression may be a potential biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of glioma patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ostrom QT, Bauchet L, Davis FG, et al. The epidemiology of glioma in adults: a “state of the science” review. Neuro Oncol, 2014,16(7):896–913
Weller M, Wick W, Aldape K, et al. Glioma. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2015,1:15017
Louis DN, Perry A, Wesseling P, et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Neuro Oncol, 2021,23(8):1231–1251
Gusyatiner O, Hegi ME. Glioma epigenetics: From subclassification to novel treatment options. Semin Cancer Biol, 2018,51:50–58
Wen PY, Kesari S. Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med, 2008,359(5):492–507
Xu S, Sankar S, Neamati N. Protein disulfide isomerase: a promising target for cancer therapy. Drug Discov Today, 2014,19(3):222–240
Ramos FS, Serino LT, Carvalho CM, et al. PDIA3 and PDIA6 gene expression as an aggressiveness marker in primary ductal breast cancer. Genet Mol Res, 2015,14(2):6960–6967
Xu X, Wei X, Ling Q, et al. Identification of two portal vein tumor thrombosis associated proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma: protein disulfide-isomerase A6 and apolipoprotein A-I. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2011,26(12):1787–1794
Uyy E, Suica VI, Boteanu RM, et al. Endoplasmic Reticulum Chaperones Are Potential Active Factors in Thyroid Tumorigenesis. J Proteome Res, 2016,15(9):3377–3387
Wang M, Zhang W, Liu Y, et al. PDIA4 promotes glioblastoma progression via the PI3K/AKT/m-TOR pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2022,597:83–90
Desilva MG, Lu J, Donadel G, et al. Characterization and chromosomal localization of a new protein disulfide isomerase, PDIp, highly expressed in human pancreas. DNA Cell Biol, 1996,15(1):9–16
Fu XM, Zhu BT. Human pancreas-specific protein disulfide-isomerase (PDIp) can function as a chaperone independently of its enzymatic activity by forming stable complexes with denatured substrate proteins. Biochem J, 2010,429(1):157–169
Klappa P, Stromer T, Zimmermann R, et al. A pancreas-specific glycosylated protein disulphide-isomerase binds to misfolded proteins and peptides with an interaction inhibited by oestrogens. Eur J Biochem, 1998,254(1):63–69
Vivian J, Rao AA, Nothaft FA, et al. Toil enables reproducible, open source, big biomedical data analyses. Nat Biotechnol, 2017,35(4):314–316
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y, et al. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS, 2012,16(5):284–287
Ceccarelli M, Barthel FP, Malta TM, et al. Molecular Profiling Reveals Biologically Discrete Subsets and Pathways of Progression in Diffuse Glioma. Cell, 2016,164(3):550–563
Hänzelmann S, Castelo R, Guinney J. GSVA: gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinformatics, 2013,14:7
Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Tosolini M, et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of intratumoral immune cells reveal the immune landscape in human cancer. Immunity, 2013,39(4):782–795
Ostrom QT, Patil N, Cioffi G, et al. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2013–2017. Neuro Oncol, 2020,22(12 Suppl 2):iv1–iv96
Lee E, Lee DH. Emerging roles of protein disulfide isomerase in cancer. BMB Rep, 2017,50(8):401–410
Xiong B, Jha V, Min JK, et al. Protein disulfide isomerase in cardiovascular disease. Exp Mol Med, 2020,52(3):390–399
Vitale I, Manic G, Coussens LM, et al. Macrophages and Metabolism in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cell Metab, 2019,30(1):36–50
Liu C, Zhou X, Long Q, et al. Small extracellular vesicles containing miR-30a-3p attenuate the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting SNAP23 gene. Oncogene, 2021,40(2):233–245
Fan Y, Simmen T. Mechanistic Connections between Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Redox Control and Mitochondrial Metabolism. Cells, 2019,8(9):1071
Tao J, Yin L, Wu A, et al. PDIA2 Bridges Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Metabolic Reprogramming During Malignant Transformation of Chronic Colitis. Front Oncol, 2022,12:836087
Raturi A, Gutiérrez T, Ortiz-Sandoval C, et al. TMX1 determines cancer cell metabolism as a thiol-based modulator of ER-mitochondria Ca2+ flux. J Cell Biol, 2016,214(4):433–44
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in the study.
Additional information
This study was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Southwest Medical University (No. 2016XNYD217, No. 2018-ZRQN-032 and No. 2016LZXNYD-G03), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82072780) and Sichuan Science and Technology Program (No. 2022YFS0630).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Zg., Liu, Yx., Zou, N. et al. Protein Disulfide Isomerase A2 Is Correlated with Immune Infiltrates and Is a Novel Prognostic Biomarker in Glioma Patients. CURR MED SCI 43, 1107–1115 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-023-2790-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-023-2790-x