Abstract
Objective
Aberrant activating mutations in cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) are common in various cancers, including gastroesophageal malignancies. Although CDK4/6 inhibitors, such as abemaciclib and palbociclib, have been approved for breast cancer treatment, their effectiveness as a monotherapy remains limited for gastroesophageal tumors. The present study explored the underlying mechanism of abemaciclib resistance.
Methods
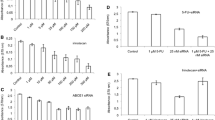
Abemaciclib-resistant gastric cancer cell lines were generated, and the phospho-eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (p-eIF4E) and eIF4E expression was compared between resistant and parental cell lines. In order to analyze the role of eIF4E in cell resistance, siRNA knockdown was employed. The effectiveness of ribavirin alone and its combination with abemaciclib was evaluated in the gastric cancer xenograft mouse model.
Results
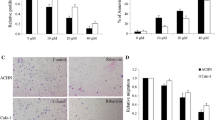
The upregulation of eIF4E was a common feature in gastric cancer cells exposed to prolonged abemaciclib treatment. Gastric cancer cells with increased eIF4E levels exhibited a better response to eIF4E inhibition, especially those that were resistant to abemaciclib. Ribavirin, which is an approved anti-viral drug, significantly improved the efficacy of abemaciclib, both in vitro and in vivo, by inhibiting eIF4E. Importantly, ribavirin effectively suppressed the abemaciclib-resistant gastric cancer growth in mice without causing toxicity.
Conclusion
These findings suggest that targeting eIF4E can enhance the abemaciclib treatment for gastric cancer, proposing the potential combination therapy of CDK4/6 inhibitors with ribavirin for advanced gastric cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018,68(6):394–424
Sexton RE, Al Hallak MN, Diab M, et al. Gastric cancer: a comprehensive review of current and future treatment strategies. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2020,39(4):1179–1203
Chia NY, Tan P. Molecular classification of gastric cancer. Ann Oncol, 2016,27(5):763–769
Machlowska J, Baj J, Sitarz M, et al. Gastric Cancer: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Classification, Genomic Characteristics and Treatment Strategies. Int J Mol Sci, 2020,21(11):1–20
Schettini F, De Santo I, Rea CG, et al. CDK 4/6 Inhibitors as Single Agent in Advanced Solid Tumors. Front Oncol, 2018,8:608
Migliaccio I, Di Leo A, Malorni L. Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer therapy. Curr Opin Oncol, 2014,26(6):568–575
Mikhail S, Albanese C, Pishvaian MJ. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors and the treatment of gastrointestinal cancers. Am J Pathol, 2015,185(5):1185–1197
Karasic TB, O’Hara MH, Teitelbaum UR, et al. Phase II Trial of Palbociclib in Patients with Advanced Esophageal or Gastric Cancer. Oncologist, 2020,25(12):e1864–e1868
Romagnoli A, D’Agostino M, Ardiccioni C, et al. Control of the eIF4E activity: structural insights and pharmacological implications. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2021,78(21–22):6869–6885
Larsson O, Li S, Issaenko OA, et al. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E induced progression of primary human mammary epithelial cells along the cancer pathway is associated with targeted translational deregulation of oncogenic drivers and inhibitors. Cancer Res, 2007,67(14):6814–6824
Zheng J, Li X, Zhang C, et al. eIF4E Overexpression Is Associated with Poor Prognoses of Ovarian Cancer. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst), 2020,2020:8984526
Lu J, Zang H, Zheng H, et al. Overexpression of p-Akt, p-mTOR and p-eIF4E proteins associates with metastasis and unfavorable prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One, 2020,15(2):e0227768
Xu T, Zong Y, Peng L, et al. Overexpression of eIF4E in colorectal cancer patients is associated with liver metastasis. Onco Targets Ther, 2016,9:815–822
Martinez-Saez E, Peg V, Ortega-Aznar A, et al. peIF4E as an independent prognostic factor and a potential therapeutic target in diffuse infiltrating astrocytomas. Cancer Med, 2016,5(9):2501–2512
Ge Y, Wu Q, Ma G, et al. Hypermethylation of EIF4E promoter is associated with early onset of gastric cancer. Carcinogenesis, 2018,39(1):66–71
Tapia O, Riquelme I, Leal P, et al. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is activated in gastric cancer with potential prognostic and predictive significance. Virchows Arch, 2014,465(1):25–33
Chen CN, Hsieh FJ, Cheng YM, et al. Expression of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E in gastric adenocarcinoma and its association with clinical outcome. J Surg Oncol, 2004,86(1):22–27
Liang S, Guo R, Zhang Z, et al. Upregulation of the eIF4E signaling pathway contributes to the progression of gastric cancer, and targeting eIF4E by perifosine inhibits cell growth. Oncol Rep, 2013,29(6):2422–2430
Graff JR, Konicek BW, Carter JH, et al. Targeting the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E for cancer therapy. Cancer Res, 2008,68(3):631–634
Hu K, Zhang J, Yu M, et al. Inhibition of Mnk-eIF4E pathway sensitizes the efficacy to chemotherapy in anaplastic thyroid cancer. Future Oncol, 2017,13(6):489–498
Grzmil M, Seebacher J, Hess D, et al. Inhibition of MNK pathways enhances cancer cell response to chemotherapy with temozolomide and targeted radionuclide therapy. Cell Signal, 2016,28(9):1412–1421
Borden KL, Culjkovic-Kraljacic B. Ribavirin as an anticancer therapy: acute myeloid leukemia and beyond? Leuk Lymphoma, 2010,51(10):1805–1815
Chou TC. Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res, 2010,70(2):440–446
Culjkovic-Kraljacic B, Fernando TM, Marullo R, et al. Combinatorial targeting of nuclear export and translation of RNA inhibits aggressive B-cell lymphomas. Blood, 2016,127(7):858–868
Liu Y, Zhao Y, Han C, et al. Expression of CDK6 in Stomach Cancer and the Effect of CDK4/6 Inhibitor PD-0332991 on the Function of Stomach Cancer Cells. Comput Math Methods Med, 2022,2022:2402567
Valenzuela CA, Vargas L, Martinez V, et al. Palbociclib-induced autophagy and senescence in gastric cancer cells. Exp Cell Res, 2017,360(2):390–396
Bae HJ, Kang SK, Kwon WS, et al. p16 methylation is a potential predictive marker for abemaciclib sensitivity in gastric cancer. Biochem Pharmacol, 2021,183:114320
Min A, Kim JE, Kim YJ, et al. Cyclin E overexpression confers resistance to the CDK4/6 specific inhibitor palbociclib in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett, 2018,430:123–132
Zhang Y, He LJ, Huang LL, et al. Oncogenic PAX6 elicits CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance by epigenetically inactivating the LATS2-Hippo signaling pathway. Clin Transl Med, 2021,11(8):e503
Zhu Y, Wang C, Li M, et al. Targeting of MNK/eIF4E overcomes chemoresistance in cervical cancer. J Pharm Pharmacol, 2021,73(10):1418–1426
Liu T, Li R, Zhao H, et al. eIF4E promotes tumorigenesis and modulates chemosensitivity to cisplatin in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget, 2016,7(41):66851–66864
Fischer PD, Papadopoulos E, Dempersmier JM, et al. A biphenyl inhibitor of eIF4E targeting an internal binding site enables the design of cell-permeable PROTAC-degraders. Eur J Med Chem, 2021,219:113435
Volpon L, Osborne MJ, Borden KLB. Biochemical and Structural Insights into the Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor eIF4E. Curr Protein Peptide Sci, 2019,20(6):525–535
Kentsis A, Topisirovic I, Culjkovic B, et al. Ribavirin suppresses eIF4E-mediated oncogenic transformation by physical mimicry of the 7-methyl guanosine mRNA cap. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2004,101(52):18105–18110
Pettersson F, Yau C, Dobocan MC, et al. Ribavirin treatment effects on breast cancers overexpressing eIF4E, a biomarker with prognostic specificity for luminal B-type breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res, 2011,17(9):2874–2884
Bodenheimer HC Jr, Lindsay KL, Davis GL, et al. Tolerance and efficacy of oral ribavirin treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a multicenter trial. Hepatology, 1997,26(2):473–477
Assouline S, Culjkovic B, Cocolakis E, et al. Molecular targeting of the oncogene eIF4E in acute myeloid leukemia (AML): a proof-of-principle clinical trial with ribavirin. Blood, 2009,114(2):257–260
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
This work was supported by the Nature Science Foundation of Hubei Province (No. 2017CFB606).
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zha, Hl., Chen, W., Shi, W. et al. Inhibition of Eukaryotic Initiating Factor eIF4E Overcomes Abemaciclib Resistance in Gastric Cancer. CURR MED SCI 43, 927–934 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-023-2789-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-023-2789-3