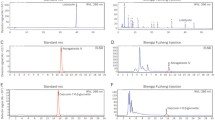
Summary
Shenqi Fuzheng injection (SFI) has been confirmed to be able to alleviate brain injury in mice. This study examined the brain-protective effect of SFI on patients after cranial radiation. Lung cancer patients with brain metastasis were randomly assigned to two groups. The SFI group received cranial radiation in combination with SFI. The control group received cranial radiation alone. The changes in cognitive function were evaluated pre- and post-radiation against the Mini-Mental State Exam (MMSE), Montreal Cognitive Assessement (MoCA), Zung Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS) and Zung Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS). The changes in inflammatory factors, such as TGF-β1, TNF-α and IL-10, were also detected before, during and after radiation (15Gy/5F). The results showed that 6 months after cranial radiation, the total scores on the MMSE and MoCA scales of the patients decreased, especially memory ability. The control group experienced a more evident decline, the memory ability being the greatest. TGF-β1 and TNF-a increased shortly after radiation and decreased one month later, and the change was more conspicuous in SFI group than in control group. IL-10 increased after radiation and stayed at a high level one month later in both groups, the level being higher in the SFI group than in the control group. Our study indicated that cognitive functions, especially memory ability, were impaired after cranial radiation. SFI could alleviate radiation-induced brain injury by regulating inflammatory factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khuntia D, Brown P, Li J, et al. Whole-brain radiotherapy in the management of brain metastasis. J Clin Oncol, 2006,24(8):1295–1304
Perry A, Schmidt RE. Cancer therapy-associated CNS neuropathology: an update and review of the literature. Acta Neuropathol, 2006,111(3):197–212
Ahles TA, Root JC, Ryan EL, et al. Cancer- and cancer treatment-associated cognitive change: an update on the state of the science. J Clin Oncol, 2012,30(30):3675–3686
Meyers CA, Smith JA, Bezjak A, et al. Neurocognitive function and progression in patients with brain metastases treated with whole-brain radiation and motexafin gadolinium: results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol, 2004,22(1):157–165
DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin, 2014,64(4):252–271
Glass CK, Saijo K, Winner B, et al. Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell, 2010,140(6):918–934
Lee WH, Sonntag WE, Mitschelen M, et al. Irradiation induces regionally specific alterations in pro-inflammatory environments in rat brain. Int J Radiat Biol, 2010,86(2):132–144
Conner KR, Payne VS, Forbes ME, et al. Effects of the AT1 receptor antagonist L-158,809 on microglia and neurogenesis after fractionated whole-brain irradiation. Radiat Res, 2010,173(1):49–61
Kim S U, de Vellis J. Microglia in health and disease. J Neurosci Res, 2005,81(3):302–313
Kyrkanides S, Moore AH, Olschowka JA, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 modulates brain inflammation-related gene expression in central nervous system radiation injury. Brain Res Mol Brain Res, 2002,104(2):159–169
Tong F, Zhang J, Liu L, et al. Corilagin Attenuates Radiation-Induced Brain Injury in Mice. Mol Neurobiol, 2016,53(10):6982–6996
Dong X, Luo M, Huang G, et al. Relationship between irradiation-induced neuro-inflammatory environments and impaired cognitive function in the developing brain of mice. Int J Radiat Biol, 2015,91(3):224–239
Monnier J, Zabel BA. Anti-asialo GM1 NK cell depleting antibody does not alter the development of bleomycin induced pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS One, 2014,9(6):e99350
Zhou P, Streutker C, Borojevic R, et al. IL-10 modulates intestinal damage and epithelial cell apoptosis in T cellmediated enteropathy. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2004,287(3):G599–604
Leask A, Abraham DJ. TGF-beta signaling and the fibrotic response. FASEB J, 2004,18(7):816–827
Greene-Schloesser D, Robbins ME. Radiation-induced cognitive impairment—from bench to bedside. Neuro Oncol, 2012, Suppl 4:iv37-44
Rapp SR, Case LD, Peiffer A, et al. Donepezil for Irradiated Brain Tumor Survivors: A Phase III Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. J Clin Oncol, 2015,33(15):1653–1659
Dong XR, Wang JN, Liu L, et al. Modulation of radiation-induced tumour necrosis factor-alpha and transforming growth factor beta1 expression in the lung tissue by Shengqi Fuzheng injection. Mol Med Rep, 2010,3(4):621–627
Zhang J, Tong F, Cai Q, et al Shenqi fuzheng injection attenuates irradiation-induced brain injury in mice via inhibition of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway and microglial activation. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2015,36(11):1288–1299
Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bedirian V, et al. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2005,53(4):695–699
McLennan SN, Mathias JL, Brennan LC, et al. Validity of the montreal cognitive assessment (MoCA) as a screening test for mild cognitive impairment (MCI) in a cardiovascular population. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol, 2011,24(1):33–38
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res, 1975,12(3):189–198
Zung WW. A rating instrument for anxiety disorders. Psychosomatics, 1971,12(6):371–379
Zung WW. A Self-Rating Depression Scale. Arch Gen Psychiatry, 1965,12:63–70
Makale MT, McDonald CR, Hattangadi-Gluth JA, et al. Mechanisms of radiotherapy-associated cognitive disability in patients with brain tumours. Nat Rev Neurol, 2017,13(1):52–64
Armstrong CL, Corn BW, Ruffer JE, et al. Radiotherapeutic effects on brain function: double dissociation of memory systems. Neuropsychiatry Neuropsychol Behav Neurol, 2000,13(2):101–111
Lin NU, Wefel JS, Lee EQ, et al. Challenges relating to solid tumour brain metastases in clinical trials, part 2: neurocognitive, neurological, and quality-of-life outcomes. A report from the RANO group. Lancet Oncol, 2013,14(10):e407–416
Kureshi SA, Hofman FM, Schneider JH, et al. Cytokine expression in radiation-induced delayed cerebral injury. Neurosurgery, 1994,35(5):822–829; discussion 829–830
Ballesteros-Zebadua P, Chavarria A, Celis MA, et al. Radiation-induced neuroinflammation and radiation somnolence syndrome. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets, 2012,11(7):937–949
Daams M, Schuitema I, van Dijk BW, et al. Long-term effects of cranial irradiation and intrathecal chemotherapy in treatment of childhood leukemia: a MEG study of power spectrum and correlated cognitive dysfunction. BMC Neurol, 2012,12:84
Greene-Schloesser D, Moore E, Robbins ME. Molecular pathways: radiation-induced cognitive impairment. Clin Cancer Res, 2013,19(9):2294–2300
Ness KK, Armstrong GT, Kundu M, et al. Frailty in childhood cancer survivors. Cancer, 2015,121(10):1540–1547
Stoll G, Jander S. The role of microglia and macrophages in the pathophysiology of the CNS. Prog Neurobiol, 1999,58(3):233–247
Gebicke-Haerter PJ. Microglia in neurodegeneration: molecular aspects. Microsc Res Tech, 2001,54(1):47–58
Pocock JM, Liddle AC. Microglial signalling cascades in neurodegenerative disease. Prog Brain Res, 2001,132:555–565
Marshall SA, McClain JA, Kelso ML, et al. Microglial activation is not equivalent to neuroinflammation in alcohol-induced neurodegeneration: The importance of microglia phenotype. Neurobiol Dis, 2013,54:239–251
Boche D, Perry VH, Nicoll JA. Review: activation patterns of microglia and their identification in the human brain. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol, 2013,39(1):3–18
Najjar S, Pearlman DM, Alper K, et al. Neuroinflammation and psychiatric illness. J Neuroinflammation, 2013,10:43
Reus GZ, Fries GR, Stertz L, et al. The role of inflammation and microglial activation in the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders. Neuroscience, 2015,300:141–154
Rosenthal E, McCrory A, Talbert M, et al. Elevated expression of TGF-beta1 in head and neck cancer-associated fibroblasts. Mol Carcinog, 2004,40(2):116–121
Vujaskovic Z, Marks LB, Anscher MS. The physical parameters and molecular events associated with radiation-induced lung toxicity. Semin Radiat Oncol, 2000,10(4):296–307
Sanderson N, Factor V, Nagy P, et al. Hepatic expression of mature transforming growth factor beta 1 in transgenic mice results in multiple tissue lesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1995,92(7):2572–2576
Eugenin EA, Branes MC, Berman JW, et al. TNF-alpha plus IFN-gamma induce connexin43 expression and formation of gap junctions between human monocytes/macrophages that enhance physiological responses. J Immunol, 2003,170(3):1320–1328
Marples B, McGee M, Callan S, et al. Cranial irradiation significantly reduces beta amyloid plaques in the brain and improves cognition in a murine model of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD). Radiother Oncol, 2016,118(3):579–580
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
This work was supported by grants from National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 81573090 and No. 81172595), Post-doctor Foundation of China (No. 20100480905) and Post-doctor Special Foundation of China (No. 201104440).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Lj., Zhang, Rg., Yu, Dd. et al. Shenqi Fuzheng Injection Ameliorates Radiation-induced Brain Injury. CURR MED SCI 39, 965–971 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-019-2129-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-019-2129-9