Summary
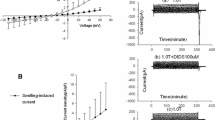
Swelling-activated chloride currents (ICl.swell) are thought to play a role in several physiologic and pathophysiologic processes and thus represent a target for therapeutic approaches. However, the mechanism of ICl.swell regulation remains unclear. In this study, we used the whole-cell patch-clamp technique to examine the role of protein kinase C (PKC) in the regulation of ICl.swell in human atrial myocytes. Atrial myocytes were isolated from the right atrial appendages of patients undergoing coronary artery bypass and enzymatically dissociated. ICl.swell was evoked in hypotonic solution and recorded using the whole-cell patch-clamp technique. The PKC agonist phorbol dibutyrate (PDBu) enhanced ICl.swell in a concentration-dependent manner, which was reversed in isotonic solution and by a chloride current inhibitor, 9-anthracenecarboxylicacid. Furthermore, the PKC inhibitor bis-indolylmaleimide attenuated the effect and 4α-PDBu, an inactive PDBu analog, had no effect on ICl.swell. These results, obtained using the whole-cell patch-clamp technique, demonstrate the ability of PKC to activate ICl,swell in human atrial myocytes. This observation was consistent with a previous study using a single-channel patch-clamp technique, but differed from some findings in other species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hume JR, Duan D, Collier ML, et al. Anion transport in heart. Physiol Rev, 2000, 80(1): 31–81
Baumgarten CM, Clemo HF. Swelling-activated chloride channels in cardiac physiology and pathophysiology. Prog Biophys Mol Biol, 2003, 82(1-3): 25–42
Duan D. Phenomics of cardiac chloride channels: the systematic study of chloride channel function in the heart. J Physiol, 2009, 587(Pt 10): 2163–2177
Demion M, Guinamard R, El CA, et al. An outwardly rectifying chloride channel in human atrial cardiomyocytes. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 2006, 17(1): 60–68
Li Y, Du X. Effects of alpha1-adrenoceptor agonist phenylephrine on swelling-activated chloride currents in human atrial myocytes. J Membr Biol, 2015, 248(1): 7–18
Du XL, Gao Z, Lau CP, et al. Differential effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on volume-sensitive chloride current in human atrial myocytes: evidence for dual regulation by Src and EGFR kinases. J Gen Physiol, 2004, 123(4): 427–439
Li XT, Dyachenko V, Zuzarte M, et al. The stretch-activated potassium channel TREK-1 in rat cardiac ventricular muscle. Cardiovasc Res, 2006, 69(1): 86–97
Kelly D, Mackenzie L, Hunter P, et al. Gene expression of stretch-activated channels and mechanoelectric feedback in the heart. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol, 2006, 33(7): 642–648
Duan D, Cowley S, Horowitz B, et al. A serine residue in ClC-3 links phosphorylation-dephosphorylation to chloride channel regulation by cell volume. J Gen Physiol, 1999, 113(1): 57–70
Duan D, Fermini B, Nattel S. Alpha-adrenergic control of volume-regulated Cl-currents in rabbit atrial myocytes. Characterization of a novel ionic regulatory mechanism. Circ Res, 1995, 77(2): 379–393
Duan D, Cowley S, Horowitz B, et al. A serine residue in ClC-3 links phosphorylation-dephosphorylation to chloride channel regulation by cell volume. J Gen Physiol, 1999, 113(1): 57–70
Du XY, Sorota S. Protein kinase C stimulates swelling-induced chloride current in canine atrial cells. Pflugers Arch, 1999, 437(2): 227–234
Gong W, Xu H, Shimizu T, et al. ClC-3-independent, PKC-dependent activity of volume-sensitive Cl channel in mouse ventricular cardiomyocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2004, 14(4): 213–224
Fedida D, Braun AP, Giles WR. Alpha 1-adrenoceptors in myocardium: functional aspects and transmembrane signaling mechanisms. Physiol Rev, 1993, 73(2): 469–487
Ichishima K, Yamamoto S, Iwamoto T, et al. alpha-Adrenoceptor-mediated depletion of phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-bisphosphate inhibits activation of volume-regulated anion channels in mouse ventricular myocytes. Br J Pharmacol, 2010, 161(1): 193–206
Rohde S, Sabri A, Kamasamudran R, et al. The alpha( 1)-adrenoceptor subtype-and protein kinase C isoform-dependence of norepinephrine’s actions in cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 2000, 32(7): 1193–1209
Rybin VO, Steinberg SF. Protein kinase C isoform expression and regulation in the developing rat heart. Circ Res, 1994, 74(2): 299–309
Catacuzzeno L, Michelucci A, Sforna L, et al. Identification of key signaling molecules involved in the activation of the swelling-activated chloride current in human glioblastoma cells. J Membr Biol, 2014, 247(1): 45–55
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project was supported by grants from the Scientific Research Foundation for Returned Scholars, Ministry of Education of China (No. 2004-527) and the Project on Social Development, Department of Science and Technology of Guizhou Province, China (No. 2011-040).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Yt., Du, Xl. Protein kinase C enhances the swelling-induced chloride current in human atrial myocytes. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 36, 383–388 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-016-1596-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-016-1596-5