Summary
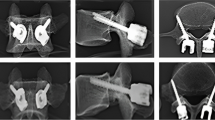
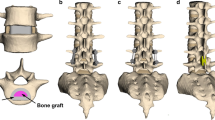
Anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) followed by posterior pedicle screw fixation (PSF) in a second procedure is mostly used to implement lumbar spine fusion. ALIF followed by anterior lumbar screw-plate has a lot of advantages, but its biomechanical stability requires confirmation. This study evaluated the biomechanical stability of a novel anterior lumbar locked screw-plate (ALLSP) by comparison with posterior lumbar PSF. Twelve fresh human cadaveric lumbar specimens (L4–L5) were assigned to four groups: ALIF+PSF group, ALIF+ALLSP (both fixed) group, ALIF group and an untreated control (both non-fixed) group. The first three groups received implantation of a rectangular titanium cage. Tests under axial compression, flexion, extension, lateral bending, or rotation showed that the fixed groups had significantly stronger stability than the non-fixed groups (P=0.000 for all). The ALIF+ALLSP group had significantly greater axial stiffness under applied axial compression and significantly less angular displacement under rotational forces than the ALIF+PSF group. The angular displacement of the ALIF+ALLSP group was less under flexion than that of the ALIF+PSF, and the angular displacement under lateral bending and extension was greater, but these differences were not statistically significant. In summary, the ALLSP conforms to the anterior lumbar spine and has good biomechanical stability. It is a reliable choice for enhancing the stability of ALIF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Niosi CA, Oxland TR. Degenerative mechanics of the lumbar spine. Spine J, 2004,4(6 Suppl):202S–208S
Kozak JA, O’Brien JP. Simultaneous combined anterior and posterior fusion. An independent analysis of a treatment for the disabled low-back pain patient. Spine, 1990,15(4):322–328
Deyo RA, Gray DT, Kreuter W, et al. United States trends in lumbar fusion surgery for degenerative conditions. Spine, 2005,30(12):1441–1445
Blumenthal SL, Ohnmeiss DD. Intervertebral cages for degenerative spinal diseases. Spine J, 2003,3(4):301–309
Tzermiadianos MN, Mekhail A, Voronov LI, et al. Enhancing the stability of anterior lumbar interbody fusion: a biomechanical comparison of anterior plate versus posterior transpedicular instrumentation. Spine, 2008,33(2): E38–E43
Moore KR, Pinto MR, Butler LM. Degenerative disc disease treated with combined anterior and posterior arthrodesis and posterior instrumentation. Spine, 2002, 7(15):1680–1686
Thomsen K, Christensen FB, Eiskjaer SP, et al. 1997 Volvo Award winner in clinical studies. The effect of pedicle screw instrumentation on functional outcome and fusion rates in posterolateral lumbar spinal fusion: a prospective, randomized clinical study. Spine, 1997,22(24): 2813–2822
Beaubien BP, Derincek A, Lew WD, et al. In vitro, biomechanical comparison of an nterior lumbar interbody fusion with an anteriorly placed, low-profile lumbar plate and posteriorly placed pedicle screws or translaminar crews. Spine, 2005,30(16):1846–1851
Bendo J, Quirno, Errico T, et al. A comparson of two retroperitoneal surgical approaches for total disc arthroplasty of the lumbar spine. Spine, 2008,33(2):205–209
Mehren C, Korge A, Siepe C, et al. Minimal invasive anterior midline approach to L2–L5. Oper Orthop Traumatol, 2010,22(5–6):573–581
Mehren C, Mayer HM, Siepe C, et al. The minimal invasive anterolateral approach to L2–L5. Oper Orthop Traumatol, 2010,22(2):221–228
Zhang H, Brown L, Blunt L, et al. Influence of femoral stem surface finish on the apparent static shear strength at the stem-cement interface. J Mech Beh Biomed Mater, 2008,1(1):96–104
Zhang HY, Blunt L, Jiang XQ, et al. Femoral stem wear in cemented total hip replacement. Proc Inst Mech Eng H, 2008,222(5):583–592
Zhang H, Blunt L, Jiang X, et al. The influence of bone cement type on production of fretting wear on the femoral stem surface. Clin Biomech, 2012,27(7):666–672
Johnson WM, Nichols TA, Jethwani D, et al. In vitro biomechanical comparison of an anterior and anterolateral lumbar plate with posterior fixation following single-level anterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Neurosurg Spine, 2007,7(3):332–335
Gerber M, Crawford NR, Chamberlain RH, et al. Biomechanical assessment of anterior lumbar interbody fusion with an anterior lumbosacral fixation screw-plate: comparison to stand-alone anterior lumbar interbody fusion and anterior lumbar interbody fusion with pedicle screws in an unstable human cadaver model. Spine, 2006, 31(7):762–768
Loguidice VA, Johnson RG, Guyer RD, et al. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine, 1988,13(3):366–369
Wang JM, Kim DJ, Yun YH. Posterior pedicular screw instrumentation and anterior interbody fusion in adult lumbar spondylolysis or grade I spondylolisthesis with segmental instability. J Spinal Disord, 1996,9(2):83–88
Madan SS, Harley JM, Boeree NR. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion: Does stable anterior fixation matter? Eur Spine J, 2003,12(4):386–392
Jacobs RR, Montesano PX, Jackson RP. Enhancement of lumbar spine fusion by use of transliminar facet joint screws. Spine, 1989,14(1):12–15
Volkman T, Horton WC, Hutton WC. Transfacet screws with lumbar interbody reconstruction: biomechanical study of motion segment stiffness. J Spinal Disord, 1996,9(5):425–432
Schofferman J, Slosar P, Reynolds J, et al. A prospective randomized comparison of 270 degrees fusions to 360 degrees fusions (circumferential fusions). Spine, 2001,26(10):E207–212
Suk KS, Jeon CH, Park MS, et al. Comparison between posterolateral fusion with pedicle screw fixation and anterior interbody fusion with pedicle screw fixation in adult spondylolytic spondylolisthesis. Yonsei Med J, 2001, 42(3):316–323
Cuningh BW, Stefter JC. Static and cyclical biomechanical analysis of pedicle screw spinal constructs. Spine, 1993,18(12):1677–1688
Min JH, Jang JS, Lee SH. Comparison of anterior- and posterior-approach instrumented lumbar interbody fusion for spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine, 2007,7(1):21–26
Ferrara LA, Secor JL, Jin BH, et al. A biomechanical comparison of facet screw fixation and pedicle screw fixation: Effects of short-term and long-term repetitive cycling. Spine, 2003,28(12):1226–1234
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors contributed equally to this work.
This project was supported by the Chongqing Key Technologies R&D Program (CSTC, No. 2010AB5118-4).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Lh., Guo, Ct., Zhou, Q. et al. Biomechanical comparison of anterior lumbar screw-plate fixation versus posterior lumbar pedicle screw fixation. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 34, 907–911 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-014-1372-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-014-1372-3