Abstract
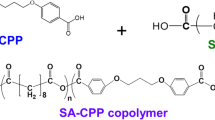
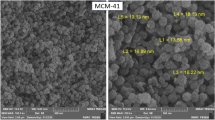
We have developed a controlled-release drug carrier. Smartly controlled-release polymer nanoparticles were firstly synthesized through RAFT polymerization as the controlled-release core. The structural and particle properties of polymer nanoparticles were characterized by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-NMR), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). Mesoporous materials were selected as the shell materials to encapsulate the smart core as the stable shell. The mesoporous shell was characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). All the results showed that a well-defined core-shell structure with mesoporous structure was obtained, and this controllable delivery system will have the great potential in nanomedicine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jeong B, Bae Y H, Lee D S, et al. Biodegradable Block Copolymers as Injectable Drug-Delivery Systems[J]. Nature, 1997, 388(6445): 860–862
Das M, Mardyani S, Chan W C W, et al. Biofunctionalized pH-Responsive Microgels for Cancer Cell Targeting: Rational Design[J]. Adv. Mater., 2006, 18(1): 80–83
Xiong M, Bao Y, Yang X, et al. Lipase-Sensitive Polymeric Triple-Layered Nanogel for “On-Demand” Drug Delivery[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(9): 4 355–4 362
Uhrich K E, Cannizzaro S M, Langer R S, et al. Polymeric Systems for Controlled Drug Release[J]. Chem. Rev., 1999, 99(11): 3 181–3 198
Ekladious I, Colson Y L, Grinstaff M W. Polymer-Drug Conjugate Therapeutics: Advances, Insights and Prospects[J]. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov., 2019, 18(4): 273–294
Bai Y, Teng B, Chen S, et al. Preparation of Magnetite Nanoparticles Coated with an Amphiphilic Block Copolymer: A Potential Drug Carrier with a Core-Shell-Corona Structure for Hydrophobic Drug Delivery[J]. Macromol. Rapid. Comm., 2006, 27(24): 2 107–2 112
Uekama K, Hirayama F, Irie T. Cyclodextrin Drug Carrier Systems[J]. Chem. Rev., 1998, 98(5): 2 045–2 076
Zhang X, Hao L, Wang H, et al. Preparation and Characterization of Superparamagnetic Fe3O4/CNTs Nanocomposites Dual-Drug Carrier[J]. J. Wuhan. Univ. Technol., 2017, 32(1): 42–46
Wang W, Wang Y, Wang Y, et al. Preparation and Characterization of Carboxyl Functionalized Fluorescent Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Containing 8-Hydroxyquinolinate Zinc Complexes[J]. J. Wuhan. Univ. Technol., 2019, 34(4): 973–978
Langer R, Folkman J. Polymers for the Sustained Release of Proteins and Other Macromolecules[J]. Nature, 1976, 263(5580): 797–800
Kamaly N, Yameen B, Wu J, et al. Degradable Controlled-Release Polymers and Polymeric Nanoparticles: Mechanisms of Controlling Drug Release[J]. Chem. Rev., 2016, 116(4): 2 602–2 663
Xu H, Cao W, Zhang X. Selenium-Containing Polymers: Promising Biomaterials for Controlled Release and Enzyme Mimics[J]. Acc. Chem. Res., 2013, 46(7): 1 647–1 658
Nayak S, Lee H, Chmielewski J, et al. Folate-Mediated Cell Targeting and Cytotoxicity Using Thermoresponsive Microgels[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126(33): 10 258–10 2591
Cai K, He X, Song Z, et al. Dimeric Drug Polymeric Nanoparticles with Exceptionally High Drug Loading and Quantitative Loading Efficiency[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(10): 3 458–3 461
Petros R A, Desimone J M. Strategies in the Design of Nanoparticles for Therapeutic Applications[J]. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov., 2010, 9(8): 615–627
Ulbrich K, Holá K, Šubr V, et al. Targeted Drug Delivery with Polymers and Magnetic Nanoparticles: Covalent and Noncovalent Approaches, Release Control, and Clinical Studies[J]. Chem. Rev., 2016, 116(9): 5 338–5 431
Wang Y, Gao S, Ye W, et al. Co-Delivery of Drugs and DNA from Cationic Core-Shell Nanoparticles Self-Assembled from a Biodegradable Copolymer[J]. Nat. Mater., 2006, 5(10): 791–796
Elsabahy M, Heo G S, Lim S-M, et al. Polymeric Nanostructures for Imaging and Therapy[J]. Chem. Rev., 2015, 115(19): 10 967–11 011
Zhang Q, Lee I, Joo J B, et al. Core-Shell Nanostructured Catalysts[J]. Acc. Chem. Res., 2013, 46(8): 1 816–1 824
Seo W S, Lee J H, Sun X, et al. FeCo/Graphitic-Shell Nanocrystals as Advanced Magnetic-Resonance-Imaging and Near-Infrared Agents[J]. Nat. Mater., 2006, 5(12): 971–976
Zhang F, Braun G B, Shi Y, et al. Fabrication of Ag@SiO2@Y2O3:Er Nanostructures for Bioimaging: Tuning of the Upconversion Fluorescence with Silver Nanoparticles[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(9): 2 850–2 851
Laurent S, Forge D, Port M, et al. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Stabilization, Vectorization, Physicochemical Characterizations, and Biological Applications[J]. Chem. Rev., 2008, 108(6): 2 064–2 110
Shah B, Yin P T, Ghoshal S, et al. Multimodal Magnetic Core-Shell Nanoparticles for Effective Stem-Cell Differentiation and Imaging[J]. Angew. Chem., 2013, 52(24): 6 190–6 195
Lu Y, Cheng X, Tian G, et al. Hierarchical CdS/m-TiO2/G Ternary Photocatalyst for Highly Active Visible Light-Induced Hydrogen Production from Water Splitting with High Stability[J]. Nano Energy, 2018, 47: 8–17
Yang X, Li Y, Van Tendeloo G, et al. One-Pot Synthesis of Catalytically Stable and Active Nanoreactors: Encapsulation of Size-Controlled Nanoparticles within a Hierarchically Macroporous Core@Ordered Mesoporous Shell System[J]. Adv. Mater., 2009, 21(13): 1 368–1 372
Gawande M B, Goswami A, Asefa T, et al. Core-Shell Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Applications in Catalysis and Electrocatalysis[J]. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44(21): 7 540–7 590
Oldenburg S J, Averitt R D, Westcott S L, et al. Nanoengineering of Optical Resonances[J]. Chem. Phys. Lett., 1998, 288(2–4): 243–247
Daniel M C, Astruc D. Gold Nanoparticles: Assembly, Supramolecular Chemistry, Quantum-Size-Related Properties, and Applications toward Biology, Catalysis, and Nanotechnology[J]. Chem. Rev., 2004, 104(1): 293–346
Yang X, Chen L, Li Y, et al. Hierarchically Porous Materials: Synthesis Strategies and Structure Design[J]. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46(2): 481–558
Singh N, Karambelkar A, Gu L, et al. Bioresponsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Triggered Drug Release[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(49): 19 582–19 585
Paris J L, Cabañas M V, Manzano M, et al. Polymer-Grafted Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Ultrasound-Responsive Drug Carriers[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(11): 11 023–11 033
Slowing I I, Vivero-Escoto J L, Wu C-W, et al. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Controlled Release Drug Delivery and Gene Transfection Carriers[J]. Adv. Drug. Del. Rev., 2008, 60(11): 1 278–1 288
Ryu J-H, Jiwpanich S, Chacko R, et al. Surface-Functionalizable Polymer Nanogels with Facile Hydrophobic Guest Encapsulation Capabilities[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(24): 8 246–8 247
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51861135313, U1663225, U1662134, 21711530705, 21673282, 21473246), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Nos.19lgpy112, 19lgzd16, 2019IB005), National Key R&D Program of China (No.2017YFC1103800), Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (No. IRT_15R52), International Science & Technology Cooperation Program of China (No.2015DFE52870), and Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Plan (No.20180101208JC)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Hu, Z., Hu, J. et al. Synthesis of the Core-Shell Structure Materials as the Controlled-Release Drug Carrier. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 35, 658–664 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-020-2303-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-020-2303-8