Abstract
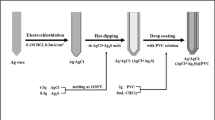
We put forward a method of rapid preparation of chloride selective electrode (Ag/AgCl electrode) by dipping silver wire into sodium hypochlorite solution. The electrodes were prepared through different immersion time. The properties of the electrodes, such as Nernst response, response time and long-term stability, were tested in simulated concrete pore solutions (SCPS). Moreover, the surface morphology of the electrodes was also detected after immersion in solutions over three months. The experimental results reveal that the Ag/AgCl electrode with the fabrication time of 20 minutes (E-20) which is recommended to work as the chloride ion selective electrode has the best performance. Compared to that fabricated by the electrolytic process (E-EP), E-20 can be manufactured in mass. The method has almost the same good performance of Nernst response as E-EP, and has a better response time which is less than 25 seconds. The method also shows a better good long-term stability in SCPS containing chloride ions over three months.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinsa CP, Carterb MA, Scantlebury JD. Sources of Error in Using Silver/Silver Chloride Electrodes to Monitor Chloride Activity in Concrete[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2001, 31: 1207–1211
Jin M, Xu J, Jiang L, et al. Investigation on the Performance Characteristics of Chloride Selective Electrode in Concrete[J]. Ionics, 2015: 1485–1500
Jiang L, Liu H, Wang Y, et al. Influence of Flexural Fatigue on Chloride Threshold Value for the Corrosion of Steels in Ca(OH)2 Solutions[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2015, 164: 23–28
Duffó GS, Farina SB, Giordano CM. Characterization of Solid Embeddable Reference Electrodes for Corrosion Monitoring in Reinforced Concrete Structures[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2009(54): 1010–1020
Climent-Llorca MA, Viqueira-Pcrez E, Lopez-Atalaya MM. Embeddable Ag/AgCI Sensors for In-situ Monitoring Chloride Contents in Concrete[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 1996, 26(8): 1157–1161
Lin H, Li-Kun X, Jun-Tao W, et al. Performance of Ag/AgCl Reference Electrode Prepared by Hot Dip Coating Method[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2009, 21(5): 482–486
Cao C, Liang C, Huang N. Electrochemical Behavior of Niobium Electrodeposited 316 Stainless Steel Bipolar Plate for PEMFC in Choline Chloride Based Ionic Liquids[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Materials Science Edition, 2015, 30(5): 1061–1067
Jin M, Xu J, Jiang L, et al. Electrochemical Characterization of a Solid Embeddable Ag/AgCl Reference Electrode for Corrosion Monitoring in Reinforced Concrete[J]. Electrochemistry, 2014, 82(12): 1040–1046
Hassel AW, Fushimi K, Seo M. An Agar-based Silver/Silver Chloride Reference Electrode for Use in Micro-Electrochemistry[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 1999(1): 180–183
Svegl F, Kalcher K, Grosse-Eschedor YJ, et al. Detection of Chlorides in Pore Water of Cement Based Materials by Potentiometric Sensors[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2006, 35: 232–237
Angst U, Elsener B, Larsen CK, et al. Potentiometric Determination of the Chloride Ion Activity in Cement Based Materials[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2010, 40(3): 561–573
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the National Key Technology Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2015BAB07B04), the Natural Science Foundation of China (51278167), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2016B04514)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, D., Jiang, L. & Jin, M. A Method of Preparation of Ag/AgCl Chloride Selective Electrode. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 33, 767–771 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-018-1890-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-018-1890-0