Abstract
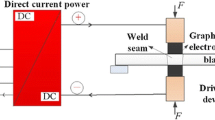
7XXX series aluminium alloys generally present low weldability by fusion welding methods because of the sensitivity to weld solidification cracking, vaporization of strengthening alloys and other defects in the fusion zone. Friction stir welding (FSW) can be deployed successfully with aluminium alloys. We presented the effect of post-weld heat treatment (PWHT) on the microstructure and mechanical properties of SSM7075 joints. Semi solid plates were butt-welded by FSW at a rotation speed of 1110 r/min, welding speeds of 70 and 110 mm/min. Solution treatment, artificial aging, and T6 (solution treatment and artificial aging combined) were applied to the welded joints, each with three samples. It was found that the T6 joints at the speed of 70 mm/min yielded the highest tensile strength of 459.23 MPa. This condition best enhanced the mechanical properties of FSW SSM7075 aluminium alloy joints.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Linert TJ, Stellwag WL, JR., Grimmett BB, et al. Friction Stir Welding Studies on Mild Steel[J]. Weld. J., 2003, 1S–9S
Atkinson HV, Burke K, Vaneetveld G. Recrystallisation in The Semi- Solid State in 7075 Aluminium Alloy[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 490: 266–276
Cavaliere P, Squillace A. High Temperature Deformation of Friction Stir Processed 7075 Aluminium Alloy[J]. Mater. Character., 2005, 55: 136–142
Fuller CB, Mahoney MW, Calabrese M, et al. Evolution of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in Naturally Aged 7050 and 7075 Al Friction Stir Welds[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527(9): 2 233–2 240
Liu C, Northwood DO, Bhole SD. Tensile Fracture Behavior in CO2 Laser Beam Welds of 7075-T6 Aluminum Alloy[J]. Mater. & Design, 2004, 25(7): 573–577
Mahoney MW, Rhodes CG, Flintoff JG, et al. Properties of Friction-Stir-Welded 7075 T651 Aluminum[J]. Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, 29(7): 1 995–2 005
Elangovan K, Balasubramanian V. Influences of Post-weld Heat Treatment on Tensile Properties of Friction Stir-Welded AA6061 Aluminum Alloy Joints[J]. Mater. Character., 2008, 59(9): 1 168–1 177
Rhodes CG, Mahoney MW, Bingel WH. Effects of Friction Stir Welding on Microstructure of 7075 Aluminum[J]. Scripta Mater., 1997, 36(1): 69–75
Feng JC, Chen YC, Liu HJ. Effects of Post-Weld Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded Joints of 2219-O Aluminium Alloy[J]. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2006, 22(1): 86–90
Azimzadegan T, Serajzadeh S. An Investigation into Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AA7075-T6 during Friction Stir Welding at Relation High Rotational Speeds[J]. Mater. Eng. Perform, 2010, 19(9): 1 256–1 263
Kumar K, Kailash SV. On the Role of Axial Load and Effect of Interface Position on The Tensile Strength of A Friction Stir Welded Aluminium Alloy[J]. Mater. & Design, 2008, 29(4): 791–797
Rajajumar S, Muralidharan C, Balasubramanian V. Influence of Friction Stir Welding and Tool Parameters on Strength Properties of AA7075-T6 Aluminium Alloy Joints[J]. Mater. & Design, 2011, 32(2): 535–549
Shivaraj MK, Dinakaran V, Mahadevan V. Friction Stir Welding on Aluminum Alloys AA2024-T4 and AA7075-T6[C]. In: 2nd International Conference on Computer Engineering and Technology (ICCET), Chengdu, China, 2010, 5: V5-1-V5-5
Mishra RS, Ma ZY. Friction Stir Welding and Processing[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. R: Report, 2005, 50(1-2): 1–78
Singh RKR, Sharma C, Dwivdi DK, et al. The Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded Al-Zn-Mg Alloy in As Welded and Heat Treated Conditions[J]. Mater. & Design, 2011, 32(2): 682–687
Aydin H, Bayram A, Durgun I. The Effect of Post-weld Heat Treatment on The Mechanical Properties of 2024-T4 Friction Stir-Welded Joints[J]. Mater. & Design, 2010, 31(5): 2 568–2 577
Fan X, Jiang D, Meng Q, et al. Evolution of Eutectic Structure in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloys during Heat Treatment[J]. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2006, 16(3): 577–581
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Department of Mining and Materials Engineering, Prince of Songkla University, as well as the PSU Graduate School, for their combined scholarships and research fund as well as partially funded by National Research Universities (NRU). Assistance from the Welding and Joining Research Team at the Department, especially Mr. Jarun Tamjai and Mr. Chaiyoot Meengam for their kind supports, is also appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Partially Funded by National Research Universities (NRU) (ENG 5805855), Faculty of Engineering, Prince of Songkla University, Hatyai Songkhla, Thailand
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prapas, M., Jennarong, N. & Woraphot, P. Effect of post-weld heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded SSM7075 aluminium alloy. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 32, 1420–1425 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-017-1763-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-017-1763-y