Abstract
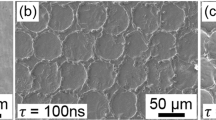
We put forward a protocol combining laser treatment and acid etching to obtain multiscale micro/nano-texture surfaces of titanium alloy implant. Firstly, the operational parameters of the laser were optimized to obtain an optimum current. Secondly, the laser with the optimum operational parameters was used to fabricate micro pits. Thirdly, multiple acid etching was used to clean the clinkers of micro pits and generate submicron and nanoscale structures. Finally, the bioactivity of the samples was measured in a simulated body fluid. The results showed that the micropits with a diameter of 150 μm and depth of 50 μm were built successfully with the optimized working current of 13 A. In addition, submicron and nanoscale structures, with 0.5-2 μm microgrooves and 10-20 nm nanopits, were superimposed on micro pits surface by multiple acid etching. There was thick and dense HA coating only observed on the multiscale micro/nano-textured surface compared with polished and micro-textured surface. This indicated that the multiscale micro/nano-texture surface showed better ability toward HA formation, which increased the bioactivity of implants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jarcho M, Kay JF, Gumaer KI, et al. Tissue, Cellular and Subcellular Events at a Bone-ceramic Hydroxylapatite Interface[J]. Journal of Bioengineering, 1977, 1(2): 79–92
Barros RRM, Novaes AB, Papalexiou V, et al. Effect of Biofunctionalized Implant Surface on Osseointegration: a Histomorphometric Study in Dogs[J]. Brazilian Dental Journal, 2009, 20(2): 91–98
Le Guéhennec L, Soueidan A, Layrolle P, et al. Surface Treatments of Titanium Dental Implants for Rapid Osseointegration[J]. Dental Materials, 2007, 23(7): 844–854
Yang X, Zhang S, Jiang T. Bone Tissue Response to the Bone-like Tissue Coating on Titanium[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2015, 30(1): 203–209
Owen G R, Jackson J, Chehroudi B, et al. A PLGA Membrane Controlling Cell Behaviour for Promoting Tissue Regeneration[J]. Biomaterials, 2005, 26(35): 7447–7456
Yang H, Zou H. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope Evaluation of Early Bacterial Colonization on Zirconium Oxide and Titanium Surfaces: An in vivo Study[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2013, 28(2): 396–399
Sykaras N, Iacopino AM, Marker VA, et al. Implant Materials, Designs, and Surface Topographies: Their Effect on Osseointegration. A Literature Review[J]. The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants, 1999, 15(5): 675–690
Bormann KH, Gellrich NC, Kniha H, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of a Microstructured Zirconia Implant by a Removal Torque Comparison with a Standard Ti-SLA Implant[J]. Clinical Oral Implants Research, 2012, 23(10): 1210–1216
Liao H, Andersson AS, Sutherland D, et al. Response of Rat Osteoblastlike Cells to Microstructured Model Surfaces in Vitro[J]. Biomaterials, 2003, 24(4): 649–654
Chappuis V, Buser R, Brägger U, et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Dental Implants with a Titanium Plasma-Sprayed Surface: A 20-Year Prospective Case Series Study in Partially Edentulous Patients[J]. Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research, 2013, 15(6): 780–790
Tang B, Lin N, Li X, et al. Bacteria Adherence Properties of Nitrogendoped TiO2 Coatings by Plasma Surface Alloying Technique[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2012, 27(3): 542–546
Yoshida Y, Kuroda K, Ichino R, et al. Influence of Surface Properties on Bioactivity and Pull-out Torque in Cold Thread Rolled Ti Rod-Development of Bioactive Metal-forming Technology[J]. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, 2012, 61(1): 579–582
Webster TJ, Ejiofor JU. Increased Osteoblast Adhesion on Nanophase Metals: Ti, Ti6Al4V, and CoCrMo[J]. Biomaterials, 2004, 25(19): 4731–4739
Chen R, Zheng J, Nie P, et al. Two-step Anodization of Maltilayer TiO2 Nanotube and Its Photocatalytic Activity under UV Light[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2012, 27(5): 866–870
Frank MJ, Walter MS, Lyngstadaas SP, et al. Hydrogen Content in Titanium and a Titanium-zirconium Alloy After Acid Etching[J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2013, 33(3): 1282–1288
Vorobyev AY, Guo C. Femtosecond Laser Structuring of Titanium Implants[J]. Applied surface science, 2007, 253(17): 7272–7280
Reimers H, Gold J, Kasemo B, et al. Topographical and Surface Chemical Characterization of Nanosecond Pulsed-laser Micromachining of Titanium at 532-nm Wavelength[J]. Applied Physics A, 2003, 77(3-4): 491–498
Reddy S, Wasnik S, Guha A, et al. Evaluation of Nano-biphasic Calcium Phosphate Ceramics for Bone Tissue Engineering Applications: in vitro and Preliminary in vivo Studies[J]. Journal of Biomaterials Applications, 2013, 27(5): 565–575
Ho YH, Vora HD, Dahotre NB. Laser Surface Modification of AZ31B Mg Alloy for Bio-wettability[J]. Journal of Biomaterials Applications, 2015, 29(7): 915–928
Kurella A, Dahotre NB. Review Paper: Surface Modification for Bioimplants: the Role of Laser Surface Engineering[J]. Journal of Biomaterials Applications, 2005, 20(1): 5–50
Mendonça G, Mendonça DBS, Aragao FJL, et al. Advancing Dental Implant Surface Technology-from Micron-to Nanotopography[J]. Biomaterials, 2008, 29(28): 3822–3835
Buser D, Broggini N, Wieland M, et al. Enhanced Bone Apposition to a Chemically Modified SLA Titanium Surface[J]. Journal of Dental Research, 2004, 83(7): 529–533
Ellingsen JE, Johansson CB, Wennerberg A, et al. Improved Retention and Bone-tolmplant Contact with Fluoride-modified Titanium Implants[J]. The International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Implants, 2003, 19(5): 659–666
Liu H, Webster TJ. Mechanical Properties of Dispersed Ceramic Nanoparticles in Polymer Composites for Orthopedic Applications[J]. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 2010, 5: 299–313
Yao C, Slamovich EB, Webster TJ. Enhanced Osteoblast Functions on Anodized Titanium with Nanotube-like Structures[J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 2008, 85(1): 157–166
Mendonca G, Mendonça DBS, Simoes L G P, et al. The Effects of Implant Surface Nanoscale Features on Osteoblast-specific Gene Expression[J]. Biomaterials, 2009, 30(25): 4053–4062
Aparicio C, Padrós A, Gil FJ. In Vivo Evaluation of Micro-rough and Bioactive Titanium Dental Implants Using Histometry and Pull-out Tests[J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2011, 4(8): 1672–1682
Hallab NJ, Vermes C, Messina C, et al. Concentration-and Compositiondependent Effects of Metal Ions on Human MG-63 Osteoblasts[J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 2002, 60(3): 420–433
Tengvall P, Lundström I, Sjöqvist L, et al. Titanium-hydrogen Peroxide Interaction: Model Studies of the Influence of the Inflammatory Response on Titanium Implants[J]. Biomaterials, 1989, 10(3): 166–175
Li P, Ohtsuki C, Kokubo T, et al. The Role of Hydrated Silica, Titania, and Alumina in Inducing Apatite on Implants[J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 1994, 28(1): 7–15
Oh S H, Finones RR, Daraio C, et al. Growth of nano-scale Hydroxyapatite Using Chemically Treated Titanium Oxide Nanotubes[J]. Biomaterials, 2005, 26(24): 4938–4943
Dong LM, Wang C. Study on the Structure Analysis and Forming Mechanism of Bone-like Apatite. Journal of Functional Materials 2004, 35: 2397–2400 (Chinese)
Barrere F, Snel MME, van Blitterswijk C A, et al. Nano-scale Study of the Nucleation and Growth of Calcium Phosphate Coating on Titanium Implants[J]. Biomaterials, 2004, 25(14): 2901–2910
Jonášová L, Müller FA, Helebrant A, et al. Biomimetic Apatite Formation on Chemically Treated Titanium[J]. Biomaterials, 2004, 25(7): 1187–1194
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51175306 and 51575320), the Tai Shan Scholar Foundation (TS20130922), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2014JC020)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, R., Wan, Y., Ai, X. et al. Fabrication of micro/nano-textured titanium alloy implant surface and its influence on hydroxyapatite coatings. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 31, 440–445 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-016-1389-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-016-1389-5