Abstract
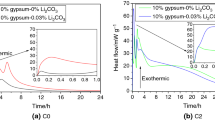
The influences of nano-TiO2 on the setting time, hydration process, hydration productsand morphology of sulphoaluminate cement were studied by Vicat apparatus, isothermal calorimetry, X-raydiffraction (XRD), thermal analysis and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The experimental results showthat the incorporation of nano-TiO2 can obviously promote the setting and hardening process of sulphoaluminatecement, and shorten the interval between the initial and final setting time, the hydration induction period ofsulphoaluminate cement is significantly shortened and the acceleration period begins immediately, but thehydration exothermic rate at hydration stationary phase is not obviously impacted. The nano-TiO2 additives haveinfluence on the formation rate and degree of crystallinity, but do not affect the type of hydration process. Thestructure of hydration products is compact at middle age, but their content and microstructure do not change.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sobolev K, GUTIÉ RREZ MF. How Nanotechnology can Change the Concrete World [J]. American Ceramic Society Bulletin, 2005, 84: 16–20
Ye Q, Zhang ZN, Kong DY, et al. Influence of Nano-SiO2 Addition on Properties of Hardened Cement Paste as Compared with Silica Fume [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2007, 21: 539–545
JO BW, KIM CH, TAE GH, et al. Characteristics of Cement Mortar with Nano-SiO2 Particles [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2007, 21: 1351–1355
LI H, ZHANG M.H, OU JP. Abrasion Resistance of Concrete Containing Nano-particles for Pavement [J]. Wear, 2006, 260: 1262–1266
Gaitero JJ, Campillo I, Guerrero A. Reduction of the Calcium Leaching Rate of Cement Paste by Addition of Silica Nanoparticles [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2008, 38: 1112–1118
Dolado J S, Campillo I, Erkiziae E, et al. Effect of Nanosilica Additions on Belite Cement Pastes Held in Sulfate Solutions [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2007, 90: 3973–3976
ZHANG M.H, LI H. Pore Structure and Chloride Permeability of Concrete Containing Nano-particles for Pavement [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2011, 25: 608–616
Lee BY, Kurtis KE. Influence of TiO2 Nanoparticles on Early C3S Hydration [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2010, 93: 3399–3405
Chen J, Kou SC, Poon CS. Hydration and Properties of Nano-TiO2 Blended Cement Composites [J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2012, 34: 642–649
Geng HN, Duan P, Chen W, et al. Carbonation of Sulphoaluminate Cement with Layered Double Hydroxides [J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2003, 29: 97–101
Peng JH, Lou ZH. Study on the Mechanism of Ettringite Formation [J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2000, 28: 511–515(in Chinese)
Ma HZ, Deng M. Effect of Alkali on Ettringite Crystallization and Solubility [J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Technology, 2007, 29: 37–40(in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (No.2014CFB874) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No.2013-YB-25)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, B., Li, H., Mei, J. et al. Effect of Nano-TiO2 addition on the hydration and hardening process of sulphoaluminate cement. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 30, 768–773 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-015-1225-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-015-1225-3