Abstract
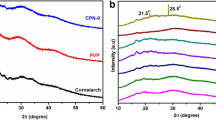
Biocompatible solid polymer blend electrolytes have been formed by cornstarch and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) with the incorporation of ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) via solution casting technique. XRD and FTIR analysis were used to study the complexation and structural properties of solid polymer electrolytes. From the electrical impedance study, it is confirmed that 60 wt.% NH4NO3 system attains the higher conductivity value of 6.81 × 10–5 Scm−1 at 303 K and 1.85 × 10–4 Scm−1 at 358 K. Wagner’s dc polarization technique has confirmed the higher cation diffusion coefficient (D+) and ionic mobility (μ+) than anion which proves that NH4NO3-based polymer blend electrolyte is a proton conductor. In order to improve the conductivity, 10 wt.% ethylene glycol (EG) is added to the higher conducting polymer blend electrolyte, and the conductivity of 2.08 × 10–4 Scm−1 is obtained at 303 K. Electrochemical cells have fabricated by using the higher conducting polymer blend electrolyte and plasticizer added electrolyte, and the open circuit voltage of 1.23 V and 1.36 V has obtained, respectively.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Der WuI, Chang FC (2007) Determination of the interaction within polyester-based solid polymer electrolyte using FTIR spectroscopy. Polymer (Guildf) 48:989–996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2006.12.045
Rao M, Geng X, Liao Y et al (2012) Preparation and performance of gel polymer electrolyte based on electrospun polymer membrane and ionic liquid for lithium ion battery. J Memb Sci 399–400:37–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEMSCI.2012.01.021
Fuzlin AF, Bakri NA, Sahraoui B, Samsudin AS (2019) Study on the effect of lithium nitrate in ionic conduction properties based alginate biopolymer electrolytes. Mater Res Express 7:015902. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/AB57BB
Jothi MA, Vanitha D, Bahadur SA, Nallamuthu N (2021) Promising biodegradable polymer blend electrolytes based on cornstarch:PVP for electrochemical cell applications. Bull Mater Sci 44:65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-021-02350-4
Anandha Jothi M, Vanitha D, Nallamuthu N et al (2020) Investigations of lithium ion conducting polymer blend electrolytes using biodegradable cornstarch and PVP. Phys B Condens Matter 580https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2019.411940
Yao P, Yu H, Ding Z et al (2019) Review on Polymer-Based Composite Electrolytes for Lithium Batteries. Front Chem 0:522. https://doi.org/10.3389/FCHEM.2019.00522
Kadir MFZ, Majid SR, Arof AK (2010) Plasticized chitosan–PVA blend polymer electrolyte based proton battery. Electrochim Acta 55:1475–1482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2009.05.011
Mohamad SA, Yahya R, Ibrahim ZA, Arof AK (2007) Photovoltaic activity in a ZnTe/PEO–chitosan blend electrolyte junction. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 91:1194–1198. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOLMAT.2007.04.002
Woo HJ, Majid SR, Arof AK (2013) Effect of ethylene carbonate on proton conducting polymer electrolyte based on poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL). Solid State Ionics 252:102–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SSI.2013.07.005
Aziz NA, Majid SR, Arof AK (2012) Synthesis and characterizations of phthaloyl chitosan-based polymer electrolytes. J Non Cryst Solids 358:1581–1590. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JNONCRYSOL.2012.04.019
Alavi S, Thompson DL (2002) Theoretical study of proton transfer in ammonium nitrate clusters. J Chem Phys 117:2599. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1489995
Ramesh S, Shanti R, Morris E (2012) Studies on the thermal behavior of CS:LiTFSI:[Amim] Cl polymer electrolytes exerted by different [Amim] Cl content. Solid State Sci 14:182–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2011.11.022
Hodge RM, Edward GH, Simon GP (1996) Water absorption and states of water in semicrystalline poly(vinyl alcohol) films. Polymer (Guildf) 37:1371–1376. https://doi.org/10.1016/0032-3861(96)81134-7
Rolland J, Poggi E, Vlad A, Gohy JF (2015) Single-ion diblock copolymers for solid-state polymer electrolytes. Polymer (Guildf) 68:344–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.POLYMER.2015.04.056
Long L, Wang S, Xiao M, Meng Y (2016) Polymer electrolytes for lithium polymer batteries. J Mater Chem A 4:10038–10069. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA02621D
Kumar PP (2006) Yashonath S (2006) Ionic conduction in the solid state. J Chem Sci 1181(118):135–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02708775
Rani MSA, Rudhziah S, Ahmad A, Mohamed NS (2014) Biopolymer Electrolyte Based on Derivatives of Cellulose from Kenaf Bast Fiber. Polym 2014, Vol 6, Pages 2371–2385 6:2371–2385. https://doi.org/10.3390/POLYM6092371
Samsudin AS, Isa MIN (2012) Structural and ionic transport study on CMC doped NH4Br: A new types of Biopolymer Electrolytes. J Appl Sci 12:174–179. https://doi.org/10.3923/JAS.2012.174.179
Hofmann A, Schulz M, Hanemann T (2013) Gel electrolytes based on ionic liquids for advanced lithium polymer batteries. Electrochim Acta. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.10.144
Jinisha B, KM A, Manoj M, et al (2017) Development of a novel type of solid polymer electrolyte for solid state lithium battery applications based on lithium enriched poly (ethylene oxide) (PEO)/poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) (PVP) blend polymer. Electrochim Acta 235:210–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.03.118
Ramesh S, Liew CW, Arof AK (2011) Ion conducting corn starch biopolymer electrolytes doped with ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate. J Non Cryst Solids 357:3654–3660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2011.06.030
Hema M, Selvasekerapandian S, Hirankumar G et al (2009) Structural and thermal studies of PVA:NH4I. J Phys Chem Solids 70:1098–1103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2009.06.005
AbouEl-Enein SA, El-Saied FA, Kasher TI, El-Wardany AH (2007) Synthesis and characterization of iron(III), manganese(II), cobalt(II), nickel(II), copper(II) and zinc(II) complexes of salicylidene-N-anilinoacetohydrazone (H2L1) and 2-hydroxy-1-naphthylidene-N-anilinoacetohydrazone (H2L2). Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 67:737–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SAA.2006.07.052
Trivedi MK, Branton A, Trivedi D et al (2015) Spectroscopic Characterization of Disodium Hydrogen Orthophosphate and Sodium Nitrate after Biofield Treatment. J Chromatogr Sep Tech 6:5. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7064.1000282
Abdelrazek EM, Elashmawi IS, El-khodary A, Yassin A (2010) Structural, optical, thermal and electrical studies on PVA/PVP blends filled with lithium bromide. Curr Appl Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2009.08.005
Arof AK, Amirudin S, Yusof SZ, Noor IM (2014) A method based on impedance spectroscopy to determine transport properties of polymer electrolytes. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:1856–1867. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CP53830C
Huang Y, Ma X, Wang S et al (2012) Determination of the interaction using FTIR within the components of GPE based on the synthesized grafted polymer. Ionics (Kiel) 18:167–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-011-0616-5
Mariappan CR, Govindaraj G (2002) Ac conductivity, dielectric studies and conductivity scaling of NASICON materials. Mater Sci Eng B Solid-State Mater Adv Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5107(02)00083-1
Winie T, Arof AK (2006) Transport properties of hexanoyl chitosan-based gel electrolyte. Ionics (Kiel). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-006-0026-2
Sundaramahalingam K, Muthuvinayagam M, Nallamuthu N (2019) AC Impedance Analysis of Lithium Ion Based PEO:PVP Solid Polymer Blend Electrolytes. Polym Sci - Ser A 61:565–576. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965545X19050171
Aziz SB (2016) Occurrence of electrical percolation threshold and observation of phase transition in chitosan (1−x) :AgI x (0.05 ≤ x ≤ 0.2)-based ion-conducting solid polymer composites. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0235-0
Woo HJ, Majid SR, Arof AK (2012) Dielectric properties and morphology of polymer electrolyte based on poly(ɛ-caprolactone) and ammonium thiocyanate. Mater Chem Phys 134:755–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATCHEMPHYS.2012.03.064
Buraidah MH, Teo LP, Majid SR, Arof AK (2009) Ionic conductivity by correlated barrier hopping in NH4I doped chitosan solid electrolyte. Phys B Condens Matter. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2008.12.027
Bresser D, Lyonnard S, Iojoiu C et al (2019) Decoupling segmental relaxation and ionic conductivity for lithium-ion polymer electrolytes. Mol Syst Des Eng 4:779–792. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9ME00038K
Tu Z, Kambe Y, Lu Y, Archer LA (2014) Nanoporous polymer-ceramic composite electrolytes for lithium metal batteries. Adv Energy Mater 4. https://doi.org/10.1002/AENM.201300654
Zhu Y, Xiao S, Shi Y et al (2013) A trilayer poly(vinylidene fluoride)/polyborate/poly(vinylidene fluoride) gel polymer electrolyte with good performance for lithium ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 1:7790–7797. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA00167A
Mishra R, Rao KJ (1998) Electrical conductivity studies of poly(ethyleneoxide)-poly(vinylalcohol) blends. Solid State Ionics 106:113–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-2738(97)00493-1
Yusof YM, Shukur MF, Illias HA, Kadir MFZ (2014) Conductivity and electrical properties of corn starch-chitosan blend biopolymer electrolyte incorporated with ammonium iodide. Phys Scr 89. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-8949/89/03/035701
Verma ML (2017) Sahu HD (2017) Study on ionic conductivity and dielectric properties of PEO-based solid nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. Ionics 239(23):2339–2350. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11581-017-2063-4
Jayanthi S (2014) Sundaresan B (2014) Effect of ultrasonic irradiation and TiO 2 on the determination of electrical and dielectric properties of PEO–P(VdF-HFP)–LiClO 4 -based nanocomposite polymer blend electrolytes. Ionics 213(21):705–717. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11581-014-1230-0
Teoh KH, Lim C-S, Ramesh S (2014) Lithium ion conduction in corn starch based solid polymer electrolytes. Measurement 48:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEASUREMENT.2013.10.040
Nicholson RS (2002) Theory and Application of Cyclic Voltammetry for Measurement of Electrode Reaction Kinetics. Anal Chem 37:1351–1355. https://doi.org/10.1021/AC60230A016
Bond AM, Feldberg SW (1998) Analysis of simulated reversible cyclic voltammetric responses for a charged redox species in the absence of added electrolyte. J Phys Chem B 102:9966–9974. https://doi.org/10.1021/JP9828437
and SHD, McCreery* RL (1999) Control of Catechol and Hydroquinone Electron-Transfer Kinetics on Native and Modified Glassy Carbon Electrodes. Anal Chem 71:4594–4602. https://doi.org/10.1021/AC990399D
Rao CVS, Ravi M, Raja V, et al (2012) Preparation and characterization of PVP-based polymer electrolytes for solid-state battery applications. Iran Polym J (English Ed. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-012-0058-6
Subba RC, Sharma A, Narasimha Rao VV (2003) Conductivity and discharge characteristics of polyblend (PVP + PVA + KIO3) electrolyte. J Power Sources 114:338–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-7753(02)00582-7
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Kalasalingam Academy of Research and Education for providing the technical and financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anandha Jothi M, Vanitha D, Sundaramahalingam K et al. Cornstarch/polyvinylpyrrolidone based proton conducting biocompatible polymer blend electrolyte for long life battery. Ionics 28, 1809–1822 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-022-04446-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-022-04446-1