Abstract
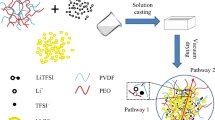
All-solid-state Li-ion batteries (ASSLBs) are promising systems to power electronic devices and electric vehicles for their high-energy density and safety. PEO-based composite electrolytes containing lithium salts and various fillers have been regarded as the most attractive solid electrolytes for ASSLBs due to their high interfacial compatibility with electrodes, high mechanical flexibility, and easy fabrication. For PEO/lithium salt/ceramic composite electrolytes, both “ceramic-in-polymer” and “polymer in ceramic” can be applied to solid-state batteries. “Ceramic-in-polymer” can provide high ionic conductivity but narrow electrochemical window; “polymer in ceramic” can provide wide electrochemical window but low ionic conductivity. In order to combine the high conductivity of “ceramic in polymer” with the wide electrochemical window of “polymer in ceramic,” we designed multilayer PEO/ Li6.4La3Zr1.4Ta0.6O12(LLZTO) composite electrolytes with low content of LLZTO (10wt %) in the inside layer and high content of LLZTO (40wt %) in the surface layer (PCEs-40–10-40) by a simple solution casting method. The PCEs-40–10-40 showed high ionic conductivity(4.61 × 10–4 \({\mathrm{S}\cdot \mathrm{cm}}^{-1}\)) and a wide electrochemical window(> 5.1 V) at 60 ℃. Compared with monolayer composite electrolytes, solid-state LiFePO4|Li batteries with multilayer composite electrolytes showed much better cycling stability (capacity retention of 98.8% after 200 cycles) at 0.5C and 60 ℃. This work shall give practical insights for the applications of PEO-based composite electrolytes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tarascon JM, Armand M (2001) Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 414:359–367. https://doi.org/10.1038/35104644
Nitta N, Wu F, Lee JT, Yushin G (2015) Li-ion battery materials: present and future. Mater Today 18:252–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2014.10.040
Liang L, Sun X, Zhang J et al (2019) Sur-/interfacial regulation in all-solid-state rechargeable Li-ion batteries based on inorganic solid-state electrolytes: advances and perspectives. Mater Horizons 6:871–910. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8mh01593g
Liang L, Sun X, Zhang J et al (2019) In situ synthesis of hierarchical core double-shell Ti-doped LiMnPO 4 @NaTi 2 (PO 4) 3 @C/3D graphene cathode with high-rate capability and long cycle life for lithium-ion batteries. Adv Energy Mater 9:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201802847
Janek J, Zeier WG (2016) A solid future for battery development. Nat Energy 1:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1038/nenergy.2016.141
Xu K (2014) Electrolytes and interphases in Li-ion batteries and beyond. Chem Rev 114:11503–11618. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500003w
Gao Z, Sun H, Fu L et al (2018) Promises, challenges, and recent progress of inorganic solid-state electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries. Adv Mater 30:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201705702
Ye F, Liao K, Ran R, Shao Z (2020) Recent advances in filler engineering of polymer electrolytes for solid-state Li-Ion batteries: a review. Energy Fuels 34:9189–9207
Takada K (2018) Progress in solid electrolytes toward realizing solid-state lithium batteries. J Power Sources 394:74–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.05.003
Zhou Q, Ma J, Dong S et al (2019) Intermolecular chemistry in solid polymer electrolytes for high-energy-density lithium batteries. Adv Mater 31:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201902029
Yan Y, Ju J, Dong S et al (2021) In situ polymerization permeated three-dimensional Li+-percolated porous oxide ceramic framework boosting All solid-state lithium metal battery. Adv Sci 8:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202003887
Lv Z, Zhou Q, Zhang S et al (2021) Cyano-reinforced in-situ polymer electrolyte enabling long-life cycling for high-voltage lithium metal batteries. Energy Storage Mater 37:215–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2021.01.017
Cui G (2020) Reasonable design of high-energy-density solid-state lithium-metal batteries. Matter 2:805–815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matt.2020.02.003
Nie K, Wang X, Qiu J et al (2020) Increasing poly(ethylene oxide) stability to 4.5 v by surface coating of the cathode. ACS Energy Lett 5:826–832. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsenergylett.9b02739
Zhang J, Zhao N, Zhang M et al (2016) Flexible and ion-conducting membrane electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries: dispersion of garnet nanoparticles in insulating polyethylene oxide. Nano Energy 28:447–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2016.09.002
Zhou W, Wang Z, Pu Y et al (2019) Double-layer polymer electrolyte for high-voltage all-solid-state rechargeable batteries. Adv Mater 31:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201805574
Chen L, Li Y, Li SP et al (2018) PEO/garnet composite electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries: from “ceramic-in-polymer” to “polymer-in-ceramic.” Nano Energy 46:176–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.12.037
Kimura K, Motomatsu J, Tominaga Y (2016) Correlation between solvation structure and Ion-conductive behavior of concentrated poly(ethylene carbonate)-based electrolytes. J Phys Chem C 120:12385–12391. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b03277
Qiu J, Liu X, Chen R et al (2020) Enabling stable cycling of 4.2 V high-voltage All-solid-state batteries with PEO-based solid electrolyte. Adv Funct Mater 30:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201909392
Li D, Chen L, Wang T, Fan LZ (2018) 3D fiber-network-reinforced bicontinuous composite solid electrolyte for dendrite-free lithium metal batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:7069–7078. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b18123
Zewde BW, Admassie S, Zimmermann J et al (2013) Enhanced lithium battery with polyethylene oxide-based electrolyte containing silane-Al2O3 ceramic filler. Chemsuschem 6:1400–1405. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201300296
Zhao Y, Huang Z, Chen S et al (2016) A promising PEO/LAGP hybrid electrolyte prepared by a simple method for all-solid-state lithium batteries. Solid State Ionics 295:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2016.07.013
Wan Z, Lei D, Yang W et al (2019) Low resistance–integrated all-solid-state battery achieved by Li7La3Zr2O12 nanowire upgrading polyethylene oxide (PEO) composite electrolyte and PEO cathode binder. Adv Funct Mater 29:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201805301
Funding
This study is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51772333).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, D., Huang, Y., He, M. et al. Multilayer PEO/LLZTO composite electrolyte enables high-performance solid-state Li-ion batteries. Ionics 27, 4127–4134 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-021-04176-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-021-04176-w