Abstract
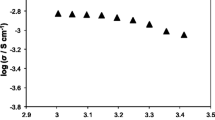
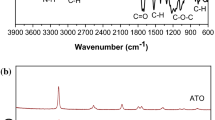
Gel polymer electrolytes are one of the candidates for solid electrolytes to solve safety issues and improve the energy density of solid-state lithium batteries. Gel polymer electrolyte has high ionic conductivity at room temperature (~ 10−3 S cm−1), but its mechanical properties are poor. Herein, we prepared a series of composite gel polymer electrolytes by N-methyl-N-propylpiperidinium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide, poly(vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene), LiTFSI, and various inorganic fillers. The addition of 5 wt% TiO2 can not only increase the ionic conductivity of gel polymer electrolytes but also improve the mechanical properties of gel polymer electrolytes. Besides, as a semiconductor, the TiO2 has safety risk when uses in composite gel polymer electrolyte. TiO2-ILGPE safety is investigated by cyclic voltammetry and battery performance. Additionally, TiO2-ILGPE displays a perfect flame-retarding ability, and TiO2 would not be reduced by the lithium metal anode.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yi TF, Pan JJ, Wei TT, Li Y, Cao G (2020) NiCo2S4-based nanocomposites for energy storage in supercapacitors and batteries. Nano Today 33:100894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2020.100894
Yi TF, Mei J, Peng PP, Luo S (2019) Facile synthesis of polypyrrole-modified Li5Cr7Ti6O25 with improved rate performance as negative electrode material for Li-ion batteries. Compos Part B Eng 167:566–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.03.032
Yi TF, Wei TT, Li Y, He YB, Wang ZB (2020) Efforts on enhancing the Li-ion diffusion coefficient and electronic conductivity of titanate-based anode materials for advanced Li-ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater 26:165–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2019.12.042
Rosero-Navarro NC, Kinoshita T, Miura A, Higuchi M, Tadanaga K (2017) Effect of the binder content on the electrochemical performance of composite cathode using Li6PS5Cl precursor solution in an all-solid-state lithium battery. Ionics (Kiel) 23:1619–1624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2106-x
Pan XN, Hou J, Liu L, Yang PX, Zhang JQ, An MZ, Li N (2017) A piperidinium-based ester-functionalized ionic liquid as electrolytes in Li/LiFePO4 batteries. Ionics (Kiel) 23:3151–3161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2104-z
Kato Y, Hori S, Saito T, Suzuki K, Hirayama M, Mitsui A, Yonemura M, Iba H, Kanno R (2016) High-power all-solid-state batteries using sulfide superionic conductors. Nat Energy 1:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/nenergy.2016.30
Navarra MA, Manzi J, Lombardo L, Panero S, Scrosati B (2011) Ionic liquid-based membranes as electrolytes for advanced lithium polymer batteries. ChemSusChem 4:125–130. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201000254
Lian PJ, Zhao BS, Zhang LQ, Xu N, Wu MT, Gao XP (2019) Inorganic sulfide solid electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium secondary batteries. J Mater Chem A 7:20540–20557. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ta04555d
Thangadurai V, Weppner W (2006) Recent progress in solid oxide and lithium ion conducting electrolytes research. Ionics (Kiel) 12:81–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-006-0013-7
Richards WD, Miara LJ, Wang Y, Kim JC, Ceder G (2016) Interface stability in solid-state batteries. Chem Mater 28:266–273. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b04082
Luo W, Gong Y, Zhu Y, Li Y, Yao Y, Zhang Y, Fu KK, Pastel G, Lin CF, Mo Y, Wachsman ED, Hu L (2017) Reducing interfacial resistance between garnet-structured solid-state electrolyte and Li-metal anode by a germanium layer. Adv Mater 29:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201606042
Wang L, Liu D, Huang T, Geng Z, Yu A (2020) Reducing interfacial resistance of a Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 solid electrolyte/electrode interface by polymer interlayer protection. RSC Adv 10:10038–10045. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra00829j
Weppner W (2003) Engineering of solid state ionic devices. Ionics (Kiel) 9:444–464. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02376599
Ulaganathan M, Rajendran S (2010) Preparation and characterizations of PVAc/P(VdF-HFP)-based polymer blend electrolytes. Ionics (Kiel) 16:515–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-009-0415-4
Yang P, Liu L, Li L, Hou J, Xu YP, Ren X, An MZ, Li N (2014) Gel polymer electrolyte based on polyvinylidenefluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene and ionic liquid for lithium ion battery. Electrochim Acta 115:454–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.10.202
Kim K, Park S, Choi S, Lee H (2006) Ionic liquid – polymer gel electrolytes based on morpholinium salt and PVdF ( HFP ) copolymer. J Power Sources 155:385–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2005.05.018
Chaudoy V, Ghamouss F, Luais E, Tran-Van F (2016) Cross-linked polymer electrolytes for Li-based batteries: from solid to gel electrolytes. Ind Eng Chem Res 55:9925–9933. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b02287
Zhang MY, Li MX, Chang Z, Wang YF, Gao J, Zhu YS, Wu YP, Huang W (2017) A Sandwich PVDF/HEC/PVDF gel polymer electrolyte for lithium ion battery. Electrochim Acta 245:752–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.05.154
Jayathilaka PARD, Dissanayake MAKL, Albinsson I, Mellander BE (2003) Dielectric relaxation, ionic conductivity and thermal studies of the gel polymer electrolyte system PAN/EC/PC/LiTFSI. Solid State Ionics 156:179–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(02)00616-1
Yang L, Wang Z, Feng Y, Tan R, Zuo Y, Gao R, Zhao Y, Han L, Wang Z, Pan F (2017) Flexible composite solid electrolyte facilitating highly stable “soft contacting” Li–electrolyte interface for solid state lithium-ion batteries. Adv Energy Mater 7:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201701437
Choudhary S, Sengwa RJ (2017) Effects of different inorganic nanoparticles on the structural, dielectric and ion transportation properties of polymers blend based nanocomposite solid polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 247:924–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.07.051
Quartarone E, Mustarelli P, Magistris A (1998) PEO-based composite polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 110:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-2738(98)00114-3
Monroe C, Newman J (2005) The impact of elastic deformation on deposition kinetics at lithium/polymer interfaces. J Electrochem Soc 152:A396. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1850854
Lopez J, Mackanic DG, Cui Y, Bao Z (2019) Designing polymers for advanced battery chemistries. Nat Rev Mater 4:312–330. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-019-0103-6
Tambelli CC, Bloise AC, Rosário AV, Pereira EC, Magon CJ, Donoso JP (2007) Characterisation of PEO–Al2O3 composite polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 47:1677–1682
Liu W, Liu N, Sun J, Hsu PC, Li Y, Lee HW, Cui Y (2015) Ionic conductivity enhancement of polymer electrolytes with ceramic nanowire fillers. Nano Lett 15:2740–2745. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b00600
Chee SC, Heng YA, Lian TL, et al. (2018) Effect of Al2O3 in poly(methyl methacrylate) composite polymer electrolytes. 3rd International Conference on the Science and Engineering of Materials 2017.
Mohamad AA, Mohamed NS, Yahya MZA, et al. (2003) Ionic conductivity studies of poly(vinyl alcohol) alkaline solid polymer electrolyte and its use in nickel–zinc cells. Solid State Ionics 156(1-2):171–177
Yang Z, Peng H, Wang W, Liu T (2010) Crystallization behavior of poly(ε-caprolactone)/layered double hydroxide nanocomposites. J Appl Polym Sci 116:2658–2667. https://doi.org/10.1002/app
Hu J, Wang W, Zhou B, Feng Y, Xie X, Xue Z (2019) Poly(ethylene oxide)-based composite polymer electrolytes embedding with ionic bond modified nanoparticles for all-solid-state lithium-ion battery. J Memb Sci 575:200–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2019.01.025
Zhao B, Lu X, Wang Q, Yang J, Zhao J, Zhou H (2020) Enhancing the ionic conductivity in a composite polymer electrolyte with ceramic nanoparticles anchored to charged polymer brushes. Chinese Chem Lett 31:831–835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2019.06.009
Hu XL, Hou GM, Zhang MQ, Rong MZ, Ruan WH, Giannelis EP (2012) A new nanocomposite polymer electrolyte based on poly(vinyl alcohol) incorporating hypergrafted nano-silica. J Mater Chem 22:18961–18967. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm33156j
Pan X, Liu T, Kautz DJ, Mu L, Tian C, Long TE, Yang P, Lin F (2018) High-performance N-methyl-N-propylpiperidinium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide/poly(vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene) gel polymer electrolytes for lithium metal batteries. J Power Sources 403:127–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.09.080
Choi BK, Shin KH (1996) Effects of SiC fillers on the electrical and mechanical properties of (PEO)16LiClO4 electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 86–88:303–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2738(96)00134-8
Köster TKJ, van Wüllen L (2010) Cation-anion coordination, ion mobility and the effect of Al2O3 addition in PEO based polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 181:489–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2010.02.005
Gadjourova Z, Andreev YG, Tunstall DP, Bruce PG (2001) Ionic conductivity in crystalline polymer electrolytes. Nature 412:520–523. https://doi.org/10.1038/35087538
Angulakshmi N, Nahm KS, Swaminathan V et al (2012) Nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Polym Process Charact 394:55–65. https://doi.org/10.1201/b13105
Mohamad AA, Mohamed NS, Yahya MZA, et al (2003) Ionic conductivity studies of poly ( vinyl alcohol ) alkaline solid polymer electrolyte and its use in nickel – zinc cells. 156:171–177
Gorecki W, Donoso P, Berthier C et al (1988) NMR, DSC and conductivity study of the polymer solid electrolytes P(EO) (LiCp+1F2p+3SO3)x. Solid State Ionics 28–30:1018–1022. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2738(88)90323-2
Funding
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21878061). X.P. and Q.H. acknowledge the support from China Scholarship Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P.Y., X.P., and Q.H. designed the experiments. X.P. and Q.H. performed preparation, materials characterization, and electrochemical measurements. L.L, J.Z., and M.A. participated in the scientific discussion. X.P. and Q.H. analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript with assistance from coauthors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 815 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, X., Hou, Q., Liu, L. et al. Semiconductor TiO2 ceramic filler for safety-improved composite ionic liquid gel polymer electrolytes. Ionics 27, 2045–2051 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-020-03850-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-020-03850-9