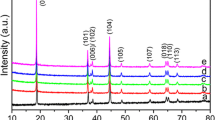
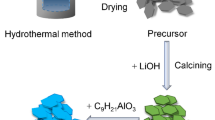
Abstract
LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 materials with different crystal surface proportions are synthesized by graphite-assisted calcination method. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) reveals homogeneous microsized polyhedral morphology with different proportions of exposed {100} and {111} surfaces. The most highlighted result is that LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 with appropriate proportion exposed {100} and {111} surfaces can achieve both high power and long lifetime simultaneously. The LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 with appropriate proportion exposed {100} and {111} surfaces can provide a large capacity of 74.8 mAh g−1 even at a discharge rate as high as 20 C. Besides, the capacity retentions of the LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 with appropriate proportion exposed {100} and {111} surfaces are found to be 93.33% at 1 C after 100 cycles. These results represent the experimental evidence for lattice-plane anisotropy in LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 crystals. Moreover, the LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 with appropriate proportion exposed {100} and {111} surface structure is beneficial for obtaining high volumetric energy density and excellent processability in practical applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yi T-F, Li Y-M, Li X-Y, Pan JJ, Zhang Q, Zhu YR (2017) Enhanced electrochemical property of FePO4-coated LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 as cathode materials for Li-ion battery. Sci Bull 62:1004–1010
Yi TF, Mei J, Zhu YR (2016) Key strategies for enhancing the cycling stability and rate capacity of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 as high-voltage cathode materials for high power lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 316:85–105
Yi TF, Chen B, Zhu YR, Li XY, Zhu RS (2014) Enhanced rate performance of molybdenum-doped spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials for lithium ion battery. J Power Sources 247:778–785
Xie Y, Zhu YR, Zhu RS et al (2012) High rate micron-sized niobium-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 as ultra high power positive-electrode material for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 12:59–65
Sun W, Li Y, Liu Y, Guo Q, Luo S, Yang J, Zheng C, Xie K (2018) Hierarchical waxberry-like LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 as an advanced cathode material for lithium-ion batteries with superior rate capability and long-term cyclability. J Mater Chem A 6:14155–14161
Sun W, Li Y, Xie K, Luo S, Bai G, Tan X, Zheng C (2018) Constructing hierarchical urchin-like LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 hollow spheres with exposed {111} facets as advanced cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Nano Energy 54:175–183
Li B, Xing L, Xu M, Lin H, Li W (2013) New solution to instability of spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 as cathode for lithium ion battery at elevated temperature. Electrochem Commun 34:48–51
Lin M, Ben L, Sun Y, Wang H, Yang Z, Gu L, Yu X, Yang XQ, Zhao H, Yu R, Armand M, Huang X (2015) Insight into the atomic structure of high-voltage spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material in the first cycle. Chem Mater 27:292–303
Risthaus T, Wang J, Friesen A, Wilken A, Berghus D, Winter M, Li J (2015) Synthesis of spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 with secondary plate morphology as cathode material for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 293:137–142
Li W, Song B, Manthiram A (2017) High-voltage positive electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Chem Soc Rev 46:3006–3059
Sha O, Qiao Z, Wang S, Tang Z, Wang H, Zhang X, Xu Q (2013) Improvement of cycle stability at elevated temperature and high rate for LiNi0.5 − xCuxMn1.5O4 cathode material after Cu substitution. Mater Res Bull 48:1606–1611
Jang M, Jung H, Scrosati B et al (2012) Improved Co-substituted, LiNi0.5 − xCo2xMn1.5 − xO4 lithium ion battery cathode materials. J Power Sources 220:354–359
Wang J, Nie P, Xu G et al (2018) High-voltage LiNi0.45Cr0.1Mn1.45O4 cathode with superlong cycle performance for wide temperature lithium-ion batteries. Adv Funct Mater 28:1704808.1704801–1704808.1704809
Arrebola JC, Caballero A, Hernán L, Morales J (2010) Re-examining the effect of ZnO on nanosized 5.0 V LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel: an effective procedure for enhancing its rate capability at room and high temperatures. J Power Sources 195:4278–4284
Ma F, Geng F, Yuan A, Xu J (2017) Facile synthesis and characterization of a SnO2-modified LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 high-voltage cathode material with superior electrochemical performance for lithium ion batteries. Phys Chem Chem Phys 19:9983–9991
Liu D, Trottier J, Charest P, Fréchette J, Guerfi A, Mauger A, Julien CM, Zaghib K (2012) Effect of nano LiFePO4 coating on LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 5 V cathode for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 204:127–132
Sclar H, Haik O, Menachem T, Grinblat J, Leifer N, Meitav A, Luski S, Aurbach D (2012) The Effect of ZnO and MgO coatings by a sono-chemical method, on the stability of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 as a cathode material for 5 V Li-ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc 159:A228–A237
Cho J-H, Park J-H, Lee M-H, Song HK, Lee SY (2012) A polymer electrolyte-skinned active material strategy toward high-voltage lithium ion batteries: a polyimide-coated LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel cathode material case. Energy Environ Sci 5:7124–7131
Yang T, Zhang N, Lang Y, Sun K (2011) Enhanced rate performance of carbon-coated LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 56:4058–4064
Wu WW, Xiang HF, Zhong GB, Su W, Tang W, Zhang Y, Yu Y, Chen CH (2014) Ordered LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 hollow microspheres as high-rate 5 V cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 119:206–213
Cabana J, Zheng H, Shukla AK, Kim C, Battaglia VS, Kunduraci M (2011) Comparison of the performance of LiNi1/2Mn3/2O4 with different microstructures. J Electrochem Soc 158:A997–A1004
Hai B, Shukla AK, Duncan H, Chen G (2013) The effect of particle surface facets on the kinetic properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials. J Mater Chem A 1:759–769
Wei G, Lu X, Ke F et al (2010) Crystal habit-tuned nanoplate material of Li[Li1/3-2x/3NixMn2/3-x/3]O2 for high-rate performance lithium-ion batteries. Adv Mater 22:4364–4367
Ju X, Huang H, He W, Zheng H, Deng P, Li S, Qu B, Wang T (2018) Surfactant-assisted synthesis of high energy {010} facets beneficial to Li-ion transport kinetics with layered LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:6312–6320
Chen Z, Zhao R, Li A, Hu H, Liang G, Lan W, Cao Z, Chen H (2015) Polyhedral ordered LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel with excellent electrochemical properties in extreme conditions. J Power Sources 274:265–273
Wei WU, Xing Q, Guo J et al (2017) Influence of cerium doping on structure and electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials. J Rare Earths 035:887–895
Talyosef Y, Markovsky B, Salitra G, Aurbach D, Kim HJ, Choi S (2005) The study of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 5-V cathodes for Li-ion batteries. J Power Sources 146:664–669
Wang L, Li H, Huang X, Baudrin E (2011) A comparative study of Fd-3 m and P4332 “LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4”. Solid State Ionics 193:32–38
Amin R, Belharouk I (2017) Part I: Electronic and ionic transport properties of the ordered and disordered LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel cathode. J Power Sources 348:311–317
Amin R, Belharouak I (2017) Part-II: Exchange current density and ionic diffusivity studies on the ordered and disordered spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode. J Power Sources 348:318–325
Zhou X, Chen M, Xiang M, Bai H, Guo J (2013) Solid-state combustion synthesis of spinel LiMn2O4 using glucose as a fuel. Ceram Int 39:4783–4789
Deng Y, Zhou Y, Shi Z, Zhou X, Quan X, Chen G (2013) Porous LiMn2O4 microspheres as durable high power cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 1:8170–8177
Theissmann R, Fendrich M, Zinetullin R et al (2008) Crystallographic reorientation and nanoparticle coalescence. Phys Rev B 78:602–611
Zhang J, Huang F, Lin Z (2010) Progress of nanocrystalline growth kinetics based on oriented attachment. Nanoscale 2:18–34
Xiao J, Chen X, Sushko PV, Sushko ML, Kovarik L, Feng J, Deng Z, Zheng J, Graff GL, Nie Z, Choi D, Liu J, Zhang JG, Whittingham MS (2012) High-performance LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel controlled by Mn3+ concentration and site disorder. Adv Mater 24:2109–2116
Liu H, Wang J, Zhang X, Zhou D, Qi X, Qiu B, Fang J, Kloepsch R, Schumacher G, Liu Z, Li J (2016) Morphological evolution of high-voltage spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries: the critical effects of surface orientations and particle size. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:4661–4675
Benedek R, Thackeray MM (2011) Simulation of the surface structure of lithium manganese oxide spinel. Phys Rev B 83:173–184
Kim JS, Kim K, Cho W, Shin WH, Kanno R, Choi JW (2012) A truncated manganese spinel cathode for excellent power and lifetime in lithium-ion batteries. Nano Lett 12:6358–6365
Kim JH, Myung ST, Yoon CS et al (2004) Comparative study of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4-δ and LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathodes having two crystallographic structures: Fd3m and P4332. Cheminform 35:906–914
Zhang N, Ai L, Mao L, Feng Y, Xie Y, Wang S, Liang Y, Cui X, Li S (2019) Understanding the role of Mg-doped on core-shell structured layered oxide LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2. Electrochim Acta 319:822–831
Liu GQ, Kuo HT, Liu RS, Shen CH, Shy DS, Xing XK, Chen JM (2010) Study of electrochemical properties of coating ZrO2 on LiCoO2. J Alloys Compd 496:512–516
Liu H, Li C, Zhang HP, Fu LJ, Wu YP, Wu HQ (2006) Kinetic study on LiFePO4/C nanocomposites synthesized by solid state technique. J Power Sources 159:717–720
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.21766017, 51962019), the High Value Patent Conversion Implementation Project (No. 18ZC1LA014), and the Lanzhou University of Technology Hongliu First-class Discipline Construction Program
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Y., Tuo, K., Wang, P. et al. Appropriate proportion truncated octahedron LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 with excellent electrochemical properties for lithium-ion batteries prepared by graphite-assisted calcination method. Ionics 26, 6003–6012 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-020-03786-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-020-03786-0