Abstract
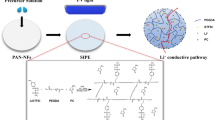
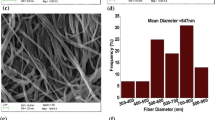
Solid-state battery has been considered as ultimate form of lithium-ion batteries due to high safety and extreme temperature tolerance, but the solid-state electrolyte fails to meet the requirements which are often suffered from low ionic conductivity, weak mechanical properties, and poor interfacial contact with the electrode simultaneously. In this paper, we report preparation of a new polymer cross-linking PVDF nanofibrous-based quasi solid-state electrolyte (P-PVDF) by in situ polymerization of melamine and epoxy-ended amino-terminated polyoxypropylene with LiPF6-based liquid electrolyte in framework of PVDF nanofiber. The polymer cross-linking PVDF nanofiber not only improves mechanical strength for polymer electrolyte but also contributes to the one-off formation of a homogenous solid electrolyte interface to suppressing dendrite lithium. The ether-dominated polymer chains provide ionic transportation channel induced high ionic conductivity (1.35 mS/cm). In comparison with liquid electrolyte, the P-PVDF polymer electrolyte exhibits significantly enhanced rate behavior with retention rate of 75% (61% for the liquid elelctrolyte) at 8 °C, cycling stability of 92% initial capacities (80% for liquid electrolyte) after 200 cycles.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Han JH, Liu P, Ito Y, Guo XW, Hirata A, Fujita T, Chen MW (2018) Bilayered nanoporous graphene/molybdenum oxide for high rate lithium ion batteries. Nano Energy 45:273–279
Scrosati B, Garche J (2010) Lithium batteries: status, prospects and future. J Power Sources 195:2419–2430
Wang B, Ryu J, Choi S, Song G, Hong D, Hwang C, Chen X, Wang B, Li W, Song HK, Park S, Ruoff RS (2018) Folding graphene film yields high areal energy storage in lithium-ion batteries. ACS Nano 12:1739–1746
Dumn B, Kamath H, Tarascon JM (2011) Electrical energy storage for the grid: a battery of choices. Science 334:928–935
Lee H, Yanilmaz M, Toprakci O, Fu K, Zhang X (2014) A review of recent developments in membrane separators for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Energy Environ Sci 7:232
Kong L, Peng HJ, Huang JQ, Zhang Q (2017) Review of nanostructure current collectors in lithium-sulfur batteries. Nano Res 10:4027–4054
Chen L, Shaw LL (2014) Recent advances in lithium–sulfur batteries. J Power Sources 267:770–783
Woo H, Wi S, Kim J, Lee S, Hwang T, Kang J, Kim J, Park K, Gil B, Nam S, Park B (2018) Complementary surface modification by disordered carbon and reduced graphene oxide on SnO2 hollow spheres as an anode for Li-ion battery. Carbon 129:342–348
Zhang J, Liu Z, Kong Q, Zhang C, Pang S, Yue L, Wang X, Yao J, Cui G (2013) Renewable and superior thermal-resistant cellulose-based composite nonwoven as lithium-ion battery separator. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:128–134
Liu T, An QF, Wang XS, Zhao Q, Zhu BK, Gao CJ (2014) Preparation and properties of PEC nanocomposite membranes with carboxymethyl cellulose and modified silica. Carbohydr Polym 106:403–409
Li H, Wang Z, Chen L, Huang X (2009) Research on advanced materials for Li-ion batteries. Adv Mater 21:4593–4607
Balke N, Jesse S, Morozovska A, Eliseev E, Chung D, Kim Y, Adamczyk L, Garcia R, Dudney N, Kalinin S (2010) Nanoscale mapping of ion diffusion in a lithium-ion battery cathode. Nat Nanotechnol 5:749
Huang X (2010) Separator technologies for lithium-ion batteries. J Solid State Electr 15:649–662
Zhu B, Liu X, Li N, Yang C, Ji T, Yan K, Chi H, Zhang X, Sun F, Sun D, Chi C, Wang X, Wang Y, Chen L, Yao L (2019) Three-dimensional porous graphene microsphere for high-performance anode of lithium ion batteries. Surf Coat Tech 360:232–237
Liao H, Hong H, Zhang H, Li Z (2016) Preparation of hydrophilic polyethylene/methylcellulose blend microporous membranes for separator of lithium-ion batteries. J Membrane Sci 498:147–157
Liao H, Zhang H, Hong H, Li Z, Qin G, Zhu H, Lin Y (2016) Novel cellulose aerogel coated on polypropylene separator as gel polymer electrolyte with high ionic conductivity for lithium-ion batteries. J Membrane Sci 514:332–339
Etacheri V, Marom R, Elazari R, Salitra G, Aurbach D (2011) Challenges in the devellopment of advanced Li-ion batteries: a review. Energy Environ Sci 4:3243
Rollins HW, Harrup MK, Dufek EJ, Jamison DK, Sazhin SV, Gering KL, Daubaras DL (2014) Fluorinated phosphazene co-solvents for improved thermal and safety performance in lithium-ion batteries electrolyte. J Power Sources 263:66–74
Xiao W, Wang Z, Miao C, Yan X (2016) Preparation of Si/Ti mesoporous melecular sieve and its application in P (VDF-HFP)-based composite polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 216:467–474
Bachman JC, Muy S, Grimaud A, Chang HH, Pour N, Lux SF, Paschos O, Maglia F, Lupart S, Lamp P, Giordano L, Shao-Horn Y (2016) Inorganic solid-state electrolyte for lithium batteries: mechanisms and properties governing ion conduction. Chem Rev 116:140–162
Li G, Gao Y, He X (2017) Organosulfide-plasticized solid-electrolyte interphase layer enables stable lithium metal anodes for long-cycle lithium-sulfur batteries. Nat Commun 8:850
Larcher D, Tarascon JM (2015) Towards greener and more sustainable batteries for electrical energy storage. Nat Chem 7:19–29
Watanable M, Thomas ML, Passerini S (2017) Ionic-liquid based polymer electrolyte liquids to energy storage and conversion materials and devices. Chem Rev 117:7190–7239
Zhao Q, Xie R, Luo F, Faraj Y, Liu Z, Ju XJ, Wang W, Chu LY (2018) Preparation of high strength poly (vinylidene fluoride) porous membrane with cellular structure via vapor-induced phase separation. J Membrane Sci 549:151–164
Xia Y, Liang YF, Xie D, Wang XL, Zhang SZ, Xia XH, Gu CD, Tu JP (2019) A poly (vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene) based three-dimensional network gel polymer electrolyte for solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries. Chem Eng J 358:1047–1053
Zhu Y, Wang F, Liu L, Xiao S, Chang Z, Wu Y (2013) Composite of a nonwoven fabric with poly (vinylidene fluoride) as a gel membrane of high safety for lithium ion battery. Energy Environ Sci 6:618–624
Liao H, Zhang H, Qin G, Li Z, Li L, Hong H (2017) A macro-porous graphene oxide-based membrane as a separator with enhanced thermal stability for high-safety lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv 7:22112–22120
Kim YB, Tran-Phu T, Kim M, Jung DW, Yi GR, Park JH (2015) Facilitated ion diffusion in multiscale porous particles: application in battery separators. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:4511–4517
Ryou MH, Lee YM, Park JK, Choi JW (2011) Mussel-inspired polydopamine-treated polyethylene separators for high-power li-ion batteries. Adv Mater 23:3066–3070
Fang L-F, Shi J-L, Zhu B-K, Zhu L-P (2013) Facile introduction of polyether chains onto polypropylene separators and its application in lithium ion batteries. J Membrane Sci 448:143–150
Liao H, Chen H, Zhou F, Zhang Z, Chen H (2019) Dendrite-free lithium deposition induced by mechanical strong sponge-supported unique 3D cross-linking polymer electrolyte for lithium metal batteries. J Power Sources 435:226748
Eo S-M, Cha E, Kim D-W (2009) Effect of an inorganic additive on the cycling performances of lithium-ion polymer cells assembled with polymer-coated separators. J Power Sources 189:766–770
Kim JY, Lim DY (2010) Surface-modified membrane as a separator for lithium-ion polymer battery. Energies 3:866–885
Park J-H, Cho J-H, Park W, Ryoo D, Yoon S-J, Kim JH, Jeong YU, Lee S-Y (2010) Close-packed SiO2/poly (methyl methacrylate) binary nanoparticles-coated polyethylene separators for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 195:8306–8310
Zhou D, Shanmukaraj D, Tkacheva A, Armand M, Wang G (2019) Polymer electrolytes for lithium-based batteries: advances and prospects. Chem 5:2326–2352
Zhou D, Tkacheva A, Tang X, Sun B, Shanmukaraj D, Li P, Zhang F, Armand M, Wang G (2019) Stable conversion chemistry-based lithium metal batteries enabled by hierarchical multifunctional polymer electrolytes with near-single ion conduction. Angew Chem Int Ed 58:6001–6006
Funding
This work are supported by the link projects of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11602082), Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 2019JJ50136) and the scientific research fundation of Hunan Provincial Education Department (No. 19C0596 and 19C596).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 663 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, F., Liao, H. & Zhang, Z. Mechanical strong polymer cross-linking PVDF nanofiber electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries. Ionics 26, 3893–3900 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-020-03549-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-020-03549-x