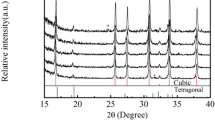
Abstract
Fast oxide-ion conductors La2Mo2-xWxO9 (x = 0–1) have been prepared using mechanochemical activation (MA) of starting oxides in a high-power planetary ball mill. Studies of La2Mo2-xWxO9 genesis and structural properties using thermal analysis, XRD, SEM, IR, and Raman spectroscopy have revealed that MA results in the formation of an amorphous precursor, while the cubic β-phase is formed after calcination at 700–900 °C. Due to a high dispersion of powders, high-density pellets of W-LAMOX ceramics have been obtained already after sintering at 950 °C. Their electrical conductivity measured by the impedance spectroscopy depends on the W concentration being sufficiently high (up to 5.6∙10−3 S/cm at 630 °C) at temperatures below 650 °C.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lacorre P, Goutenoire F, Bohnke O, Retoux R, Laligant Y (2000) Designing fast oxide-ion conductors based on La2Mo2O9. Nature 404:856–858
Georges S, Goutenoire F, Bohnke O, Steil MC, Skinner SJ, Wiemhufer HD, Lacorre P (2004) The LAMOX family of fast oxide-ion conductors: overview and recent results. J New Mat Electrochem Systems 7:51–57
Malavasi L, Fisher C.A J and Islam MS (2010) Oxide-ion and proton conducting electrolyte materials for clean energy applications: structural and mechanistic features. Chem Soc Rev 39:4370–4387
Jacquens J, Farrusseng D, Georges S, Viricelle JP, Gaudillere C, Corbel G, Lacorre P (2010) Tests for the use of La2Mo2O9-based oxides as multipurpose SOFC Core materials. Fuel Cells 10:433–439
Lo JC, Tsai DS, Chen YC, Le MV, Chung WH (2011) La2Mo2O9-based electrolyte: ion conductivity and anode-supported cell under single chamber conditions. J Am Ceram Soc 94:806–811
Malavasi L, Kim HJ, Billinge SJL, Proffen T, Tealdi C, Flor G (2007) Nature of the monoclinic to cubic phase transition in the fast oxygen ion conductor La2Mo2O9 (LAMOX). J Am Chem Soc 129:6903–6907
Tealdi C, Chiodelli G, Malavasi L, Flor G (2004) Effect of alkaline-doping on the properties of La2Mo2O9 fast oxygen ion conductor. J Mater Chem 14:3553–3557
Subasri R, Matusch D, Nafe H, Aldinger F (2004) Synthesis and characterization of (La1-xMx)2Mo2O9-δ; M = Ca2+, Sr2+ or Ba2+. J Eur Ceram Soc 24(1):129–137
Marrero-Lopez D, Perez-Coll D, Ruiz-Morales J, Canales-Vazquez J, Martin-Sedeno MC, Nunez P (2007) Synthesis and transport properties in La2−xAxMo2O9−δ (A = Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+, K+) series. Electrochim Acta 52:5219–5231
Georges S, Goutenoire F, Altorfer F, Sheptyakov D, Fauth F, Suard E, Lacorre P (2003) Thermal, structural and transport properties of the fast oxide-ion conductors La2-xRxMo2O9 (R = Nd, Gd, Y). Solid State Ionics 161:231–241
Tsai DS, Hsieh MJ, Tseng JC, Lee HY (2005) Ionic conductivities and phase transitions of lanthanide rare-earth substituted La2Mo2O9. J Eur Ceram Soc 25:481–487
Corbel G, Suard E, Lacorre P (2011) Structural key of the thermal expansion and the oxide ionic conduction in derivatives of La2Mo2O9: a temperature-controlled neutron diffraction study of β-La1.7Bi0.3Mo2O9. Chem Mater 23:1288–1298
Corbel G, Laligant Y, Goutenoire F, Suard E, Lacorre P (2005) Effects of partial substitution of Mo6+ by Cr6+ and W6+ on the crystal structure of the fast oxide-ion conductor structural effects of W6+. Chem Mater 17:4678–4684
Jin TY, Madhava Rao MV, Cheng CL, Tsai DS, Hung MH (2007) Structural stability and ion conductivity of the Dy and W substituted La2Mo2O9. Solid State Ionics 178:367–374
Georges S, Goutenoire F, Laligant Y, Lacorre P (2003) Reducibility of fast oxide-ion conductors La2-xRxMo2-yWyO9 (R ~ Nd, Gd). J Mater Chem 13:2317–2321
Georges S, Bohnke O, Goutenoire F, Laligant Y, Fouletier J, Lacorre P (2006) Effects of tungsten substitution on the transport properties and mechanism of fast oxide-ion conduction in La2Mo2O9. Solid State Ionics 177:1715–1720
Collado JA, Aranda MAG, Cabeza A, Olivera-Pastor P, Bruque S (2002) Synthesis, structures and thermal expansion of the La2Mo2−xWxO9 series. J Solid State Chem 167:80–85
Tealdi C, Chiodelli G, Flor G, Leonardi S (2010) Electrode stability and electrochemical performance of LAMOX electrolytes under fuel cell conditions. Solid State Ionics 181:1456–1461
Chiodelli G, Malavasi L (2013) Electrochemical open circuit voltage (OCV) characterization of SOFC materials. Ionics 19:1135–1144
Marrero-Lopez D, Canales-Vazquez J, Ruiz-Morales J, Irvine J, Nunez P (2005) Electrical conductivity and redox stability of La2Mo2 − xWxO9 materials. Electrochem Acta 50:4385–4395
Marrero-Lopez D, Canales-Vazquez J, Zhou W, Irvine JTS, Nunez P (2006) Structural studies on W6+ and Nd3+ substituted La2Mo2O9 materials. J Solid State Chem 179:278–288
Baque L, Vega-Castillo J, Georges S, Caneiro A, Djurado E (2013) Microstructural and electrical characterizations of tungsten-doped La2Mo2O9 prepared by spray pyrolysis. Ionics 19:1761–1774
Vega-Castillo JE, Ravell UK, Corbel G, Lacorrec P, Caneiro A (2014) Thermodynamic stability of La2Mo2−yWyO9, La2Mo2−yWyO8.96+0.02y and La7Mo7(2−y)/2W7y/2O30 (y = 0, 0.5 and 1.0). Dalton Trans 43:2661–2669
Haynes WM (ed) (2012-2013) CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. 93rd Edition CRC Press. https://books.google.ru/books
Rojac T, Kosec M (2010) High-energy ball milling. In: Sopicka-Lizer M (ed) Mechanochemical processing of nanopowders, Woodhead Publishing Limited, pp 111–141
Sepelak V, Duvel A, Wilkening M, Beckerb KD, Heitjans P (2013) Mechanochemical reactions and syntheses of oxide. Chem Soc Rev 42:7507–7520
Zyryanov VV (2008) Mechanochemical synthesis of complex oxides. Russ Chem Rev 77:105–135
Lacorre P, Retoux R (1997) First direct synthesis by high energy ball milling of a new lanthanum molybdate. J. Solid State Chem 132:443–446
Georges S, Goutenoire F, Lacorre P, Steil MC (2005) Sintering and electrical conductivity in fast oxide ion conductors La2−xRxMo2−yWyO9 (R: Nd, Gd, Y). J Eur Ceram Soc 25:3619–3627
Kharlamova T, Pavlova S, Sadykov V, Chaikina M, Kriger T, Lapina O, Khabibulin J, Uvarov N, Frade J, Argirusis C (2007) Low-temperature synthesis methods of doped apatite-type lanthanum silicates. J Chem Eng Jap 40:1187–1191
Salavati-Niasari M, Hosseinzadeh G, Davar F (2011) Synthesis of lanthanum hydroxide and lanthanum oxide nanoparticles by sonochemical method. J Alloys Compd 509:4098–4103
Bernal S, Djerdj I, Garnweitner G, Su DS, Niederberger M (2007) Morphology-controlled nonaqueous synthesis of anisotropic lanthanum hydroxide nanoparticles. J Solid State Chem 180:2154–2165
Le Van T, Che M, Tatibouet JM, Kermarec M (1993) Infrared study of the formation and stability of La2O2CO3 during oxidative coupling of methane on La2O3. J Catal 142:18–26
Adachi G, Imanaka N (1998) The binary rare earth oxides. Chem Rev 98:1479–1514
Bernal S, Botana FJ, Garcia R, Rodriguez-Izquierdo JM (1987) Behavior of rare earth sesquioxides exposed to atmospheric carbon dioxide and water. React Solids 423:23–40
Segun L, Figlaz M, Cavagnat R, Lassegues JC (1995) Infrared and Raman spectra of MO3 molybdenum trioxides and MO3⋅xH,O molybdenum trioxide hydrates. Spectr Acta A 51:1323–1344
Krishna G, Ravikumar RVSN, Vijaya Kumar T, Ephraim SD, Ranjith B, Pranoy M, Dola S (2016) Investigation and comparison of optical and Raman bands of mechanically synthesised MoO3 Nano powders. Materials Today: Proceedings 3:4–63
Ingham B, Chong SV, Tallon JL (2005) Layered tungsten oxide-based organic-inorganic hybrid materials: an infrared and Raman study. J Phys Chem B 109:4936–4940
Sungpanich J, Thongtem T, Thongtem S (2012) Large-scale synthesis of WO3 nanoplates by a microwave-hydrothermal method. Ceram Inter 38:1051–1055
Saraiva GD, Luz-Lima C, Freire PTC, Ramiro de Castro AJ, de Sousa PF, Melo EA, Silva JH, Mendes Filho J (2013) Vibrational and structural properties in the dihydrate sodium tungstate and in the dihydrate sodium molybdate crystals. J Mol Struc 1033:154–161
Mirgorodsky A, Colas M, Smirnov M, Merle-Mejean T, El-Mallawany R, Thomas P (2012) Structural peculiarities and Raman spectra of TeO2/WO3-based glasses: a fresh look at the problem. J Solid State Chem 190:45–51
McEvoy TM, Stevenson KJ (2005) Spatially-resolved imaging of inhomogeneous ion/charge transfer behavior in polymorphous MoO3. I Conductivity and Chemical Mapping using Conductive Probe AFM and Raman Microscopy Langmuir 21:3521–3528
Diaz-Droguetta DE, El Fara R, Fuenzalida VM, Cabrera AL (2012) In situ-Raman studies on thermally induced structural changes of porous MoO3 prepared in vapor phase under He and H2. Mater Chem Phys 134:631–638
Meng L, Han H, Zhou D, Xia Y, Wang Z, Meng J (2016) Synthesis and luminescence properties of three dimensional architectures of nanostructural WO3. Optik 127:3454–3458
Pless JD, Kim HS, Smit JP, Wang X, Stair PC, Poeppelmeier KR (2006) Structure of Mg2.56V1.12W0.88O8 and vibrational Raman spectra of Mg2.5VWO8 and Mg2.5VMoO8. Inorg Chem 45:514–520
Sellemi H, Coste S, Barre M, Retoux R, Ali AB, Lacorre P (2015) Synthesis by the polyol process and ionic conductivity of nanostructured La2Mo2O9 powders. J All Compd 653:422–433
del Viola C M, Sangra AM, Pedregosa JC (1993) Vibrational spectroscopic characterization of lanthanide molybdates. J Mat Sci 28:6587–6590
Hayward SA, Redfern SAT (2004) Thermodynamic nature of and spontaneous strain below the cubic–monoclinic phase transition in La2Mo2O9. J Phys Condens Matter 16:3571–3583
Ge L, Guo K, Guo L (2015) Sinterability, reducibility, and electrical conductivity of fast oxide-ion conductors La1.8R0.2MoWO9 (R = Pr, Nd, Gd and Y). Ceram Int 41:10208–10215
Lacorre P, Selmi A, Corbel G, Boulard B (2006) On the flexibility of the structural framework of cubic LAMOX compounds in relationship with their anionic conduction properties. Inorg Chem 45:627–635
Acknowledgments
Support by RSF (Russian Science Foundation) 16-13-00112 Project, Federal Agency of Scientific Organizations (V.45.3.8 Project) and the Russian Ministry of Education and Science is gratefully acknowledged. We are very much thankful to Dr. Kharlamova T. for assistance in samples preparation and Dr. Chesalov Y. for recording IR and Raman spectra.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavlova, S., Bespalko, Y., Krieger, T. et al. Genesis, structural, and transport properties of La2Mo2-xWxO9 prepared via mechanochemical activation. Ionics 23, 877–887 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1869-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1869-9