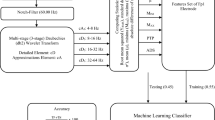
Abstract
Chaos is often described as the limited development of nonlinear dynamic systems that create intricate and non-repetitive patterns. In this study, we questioned how chaotic electronic signals can be transformed into sound stimuli and explored their impact on brain activity using Electroencephalography (EEG). Our experiment involved 31 participants exposed to sounds generated from three processes from electronic implementations: signals from chaotic attractors, periodic limit cycles,and aleatory distributions. Our goal was to analyze characteristics and EEG signals to uncover the complex relationship between chaotic auditory stimuli and cognitive processes. Interestingly the chaotic stimuli caused a reduction in synchronization in the delta (\(\delta\)) and theta (\(\theta\)) frequency bands. We observed differences of up to 30 and 40%, primarily concentrated in the brain’s frontal areas. This desynchronization in \(\delta\) and \(\theta\) bands, seen in individuals, has implications for regulating irregular \(\theta\) power in certain neural disorders. On the other hand, exposure to signals had mostly minimal effects on EEG readings. This research significantly contributes to our understanding of how the brain responds to stimuli derived from electronic systems. It sheds light on applications for modulating activity. Examining unpredictable sounds offers an understanding of the unique impacts of chaotic auditory inputs on brain activity, opening possibilities for further investigations at the crossroads of chaos theory, acoustics, and neuroscience.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azarnoosh M, Nasrabadi AM, Mohammadi MR, Firoozabadi M (2011) Investigation of mental fatigue through EEG signal processing based on nonlinear analysis: symbolic dynamics. Chaos Solitons Fractals 44(12):1054–1062
Barrio R, Blesa F, Serrano S (2009) Qualitative analysis of the Rössler equations: bifurcations of limit cycles and chaotic attractors. Phys D Nonlinear Phenomena 238(13):1087–1100
Buzsaki G (2006) Rhythms of the brain. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Cao B, Gu H, Ma K (2022) Complex dynamics of hair bundle of auditory nervous system (I): spontaneous oscillations and two cases of steady states. Cognit Neurodyn 16(4):917–940
Cao B, Gu H, Wang R (2022) Complex dynamics of hair bundle of auditory nervous system (II): forced oscillations related to two cases of steady state. Cognit Neurodyn, pp 1–26
Chen G, Ueta T (1999) Yet another chaotic attractor. Int J Bifurc Chaos 9(07):1465–1466
Delorme A, Makeig S (2004) EEGLAB: an open-source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics, including independent component analysis. J Neurosci Methods 134(1):9–21
Devaney R (1986) An introduction to chaotic dynamical systems. Benjamin/Cummings
Farrugia N, Benoit CE, Schwartze M, Pell M, Obrig H, Dalla Bella S, Kotz S (2014) Auditory cueing in Parkinson’s disease: effects on temporal processing and spontaneous theta oscillations. Proc Soc Behav Sci 126:104–105
Faure P, Korn H (2001) Is there chaos in the brain? I. Concepts of nonlinear dynamics and methods of investigation. Comptes Rendus de lAcadémie des Sciences-Series III-Sciences de la Vie, 324(9):773–793
Galadí JA, Torres JJ, Marro J (2020) Emergence and interpretation of oscillatory behaviour similar to brain waves and rhythms. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 83:105093
Gálvez G, Recuero M, Canuet L, Del-Pozo F (2018) Short-term effects of binaural beats on eeg power, functional connectivity, cognition, gait and anxiety in Parkinson’s disease. Int J Neural Syst 28(05):1750055
Garcia-Argibay M, Santed MA, Reales JM (2019) Binaural auditory beats affect long-term memory. Psychol Res 83(6):1124–1136
Glass L, Mackey MC (1988) From clocks to chaos: the rhythms of life. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Horowitz P, Hill W (2015) The art of electronics, p. 559 (3rd ed.). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Jinghua X, Zeng-Rong L, Ren L (1994) The measures of sequence complexity for EEG studies. Chaos Solitons Fractals 4(11):2111–2119
Kardou, CA, Shaw PB (2014) Evaluation of smartphone sound measurement applications. J Acoust Soc Am, 135(4);EL186–EL192
Karkare S, Saha G, Bhattacharya J (2009) Investigating long-range correlation properties in EEG during complex cognitive tasks. Chaos Solitons Fractals 42(4):2067–2073
Kleiner M, Brainard D, Pelli D, Ingling A, Murray R, Broussard C (2007) What’s new in Psychtoolbox-3. Perception 36(14):1
Korn H, Faure P (2003) Is there chaos in the brain? II. Experimental evidence and related models. Comptes rendus biologies, 326(9):787–840
Lane JD, Kasian SJ, Owens JE, Marsh GR (1998) Binaural auditory beats affect vigilance performance and mood. Physiol Behav 63(2):249–252
Larsson PG, Kostov H (2005) Lower frequency variability in the alpha activity in EEG among patients with epilepsy. Clin Neurophys 116(11):2701–2706
Lin, H., Wang, C., Yu, F., Hong, Q., Xu, C, Sun Y (2023) A triple-memristor hopfield neural network with space multi-structure attractors and space initial-offset behaviors. IEEE Trans Comput Aided Des Integrated Circuits Syst
Lin H, Wang C, Yu F, Sun J, Du S, Deng Z, Deng Q (2023) A review of chaotic systems based on memristive Hopfield neural networks. Mathematics 11(6):1369
Liu Q, Balsters JH, Baechinger M, Van der Groen O, Wenderoth N, Mantini D (2015) Estimating a neutral reference for electroencephalographic recordings: the importance of using a high-density montage and a realistic head model. J Neural Eng 12(5):056012
Lorenz EN, Haman K (1996) The essence of chaos. Pure Appl Geophys 147(3):598–599
Maity AK, Pratihar R, Mitra A, Dey S, Agrawal V, Sanyal S, Ghosh D (2015) Multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis of alpha and theta EEG rhythms with musical stimuli. Chaos Solitons Fractals 81:52–67
Montoya JL, Landi N, Kober H, Worhunsky PD, Rutherford HJV, Mencl WE, Mayes LC, Potenza MN (2012) Regional brain responses in nulliparous women to emotional infant stimuli. PLOS ONE 7(5):e36270
Nazaré TE, Nepomuceno EG, Martins SAM, Butusov DN (2020) A note on the reproducibility of chaos simulation. Entropy 22(9):953
Niedermeyer E, da Silva FL (Eds.) (2005) Electroencephalography: basic principles, clinical applications, and related fields. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Ontanon-Garcia LJ, Lozoya-Ponce RE (2017) Analog Electronic Implementation of Unstable Dissipative Systems of Type I with Multi-Scrolls Displaced Along Space. Int J Bifurc Chaos 27(06):1750093
Ontanon-Garcia LJ, Campos-Canton E, Femat R (2016) Analog electronic implementation of a class of hybrid dissipative dynamical systems. Int J Bifurc Chaos 26(01):1650018
Orponen P (1997) A survey of continuous-time computation theory. In: Advances in algorithms, languages, and complexity (pp 209–224). Springer, Boston, MA
Pamul a, H., Kasprzak, C., Klaczynski, M. (2016) Nuisance assessment of different annoying sounds based on psychoacoustic metrics and electroencephalography. Diagnostyka, 17
Pavlov AN, Grishina DS, Runnova AE, Maksimenko VA, Pavlova ON, Shchukovsky NV, Kurths J (2019) Recognition of electroencephalographic patterns related to human movements or mental intentions with multiresolution analysis. Chaos Solitons Fractals 126:230–235
Perko L (2013) Differential equations and dynamical systems (Vol. 7). Springer Science & Business Media
Rana, F. S., Pape, D., & Service, E (2022) The effect of increasing acoustic and linguistic complexity on auditory processing: an EEG study. Brain Res 1327:77–90
Rodrigues PG, Stefano Filho CA, Attux R, Castellano G, Soriano DC (2019) Space-time recurrences for functional connectivity evaluation and feature extraction in motor imagery brain-computer interfaces. Med Biol Eng Comput 57(8):1709–1725
Rössler OE (1976) An equation for continuous chaos. Phys Lett A 57(5):397–398
Salas P (2018) Análisis y diseño de sistemas caóticos clásicos con base en filtros pasa-bajas. Doctoral Dissertation. http://fc.uaslp.mx/pca/tesis/2018Doctorado/SalasCastroPablo-Doctorad o201837.pdf
Salas-Castro P, Delgado-Aranda F, Tristán-Hernández E, Martínez-Montejano RC, Murguía JS, Campos-Cantón I (2018) Application of dynamical system theory in LC harmonic oscillator circuits: a complement tool to the Barkhausen criterion. Int J Electrical Eng Educ 55(3):258–272
Sanyal S, Nag S, Banerjee A, Sengupta R, Ghosh D (2019) Music of brain and music on the brain: a novel EEG sonification approach. Cognit Neurodyn 13:13–31
Sarbadhikari SN, Chakrabarty K (2001) Chaos in the brain: a short review alluding to epilepsy, depression, exercise and lateralization. Med Eng Phys 23(7):447–457
Schnupp J, Nelken I, King A (2011) Auditory neuroscience: making sense of sound. MIT Press
Spiousas I, Etchemendy PE, Eguia MC, Calcagno ER, Abregú E, & Vergara RO (2017). Sound spectrum influences auditory distance perception of sound sources located in a room environment. Front Psychol, 8
Stam KJ, Tavy DL, Jelles B, Achtereekte HA, Slaets JP, Keunen RW (1994) Non-linear dynamical analysis of multichannel EEG: clinical applications in dementia and Parkinson’s disease. Brain Topogr 7:141–150
Strogatz SH (2001) Nonlinear dynamics and chaos: with applications to physics. Perseus Books, Biology and Chemistry
Tong Q, Kong J, Xu J (1996) A note on analyzing schizophrenic EEG with complexity measure. Chaos Solitons Fractals 7(3):371–375
Tristán-Hernández E, Pavón-García I, Campos-Cantón I, Ontañón-García LJ, Kolosovas-Machuca ES (2017) Influence of background noise produced in university facilities on the brain waves associated with attention of students and employees. Perception 46(9):1105–1117
Weiss H, Weiss V (2003) The golden mean as clock cycle of brain waves. Chaos Solitons Fractals 18(4):643–652
Welch PD (1967) The use of Fast Fourier Transform for the estimation of power spectra: A method based on time averaging over short, modified periodograms (PDF). IEEE Trans Audio Electroacoust, AU-15(2):70–73,
Wolf A (2021) Wolf Lyapunov exponent estimation from a time series. (https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/48084-wolf-lyapunov-exponent-estimation-from-a-time-series), MATLAB Central File Exchange. Retrieved January 14, 2021
Wolf A, Swift JB, Swinney HL, Vastano JA (1985) Determining Lyapunov exponents from a time series. Phys D Nonlinear Phenomena 16(3):285–317
Wolpaw J, Wolpaw EW. (Eds.). (2012) Brain-computer interfaces: principles and practice. OUP USA
Yao W, Wang C, Sun Y, Gong S, Lin H (2023) Event-triggered control for robust exponential synchronization of inertial memristive neural networks under parameter disturbance. Neural Netw 164:67–80
Yu, S., Lü, J., Tang, W. K. S., & Chen, G. (2006). A general multiscroll Lorenz system family and its realization via digital signal processors. Chaos Interdiscip J Nonlinear Sci, 16(3):033126
Yu F, Shen H, Yu Q, Kong X, Sharma PK, Cai S (2022) Privacy protection of medical data based on multi-scroll memristive Hopfield neural network. IEEE Trans Netw Sci Eng 10(2):845–858
Acknowledgements
Gerardo Acosta would like to thank Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología for the mixed scholarship for master’s degree studies (number 462043). E. Guevara acknowledges support from Cátedras CONAHCYT program project No. 528. Luis Javier Ontanon acknowledges COPOCYT for the financial support of project number DG-522/2023 with title "Predicción y seguimiento de trayectorias de sistemas dinámicos mediante redes neuronales artificiales recurrentes y su aplicación en vehículos autónomos”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Acosta Martínez, G., Guevara, E., Kolosovas-Machuca, E.S. et al. Sonification of electronic dynamical systems: Spectral characteristics and sound evaluation using EEG features. Cogn Neurodyn (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-024-10112-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-024-10112-1