Abstract
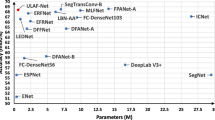
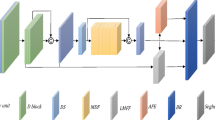
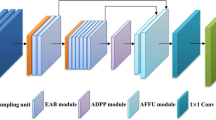
In recent years, the performance of real-time semantic segmentation has increasingly become a research focus for real-time applications such as autonomous driving. Although large deep models have excellent segmentation results, their inference speed is slow and the models are complex, which makes them difficult to deploy in practice. To address these problems, a lightweight network with efficient multi-scale feature aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation (EMFANet) is proposed in this paper, which employs the encoder–decoder framework with efficient channel attention mechanism. In EMFANet, the effective symmetric attention residual unit (SARU) is presented to rapidly obtain large amounts of multi-scale contextual information. The lightweight multi-scale information aggregation unit (MIAU) is presented for efficient fusion of multi-scale features. Experimental results on the Cityscapes test set show that EMFANet can obtain 72.1% mean intersection over union (mIoU) and 143 FPS with only 1.03 M parameters. It also has competitive segmentation capability on the low-resolution Camvid test set with a fast inference speed of 357 FPS. EMFANet achieves an outstanding performance balance between segmentation accuracy, inference speed and model size.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Li, G., Liu, Z., Zhang, X., Lin, W.: Lightweight salient object detection in optical remote-sensing images via semantic matching and edge alignment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 61, 1–11 (2023)
Shelhamer, E., Long, J., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(4), 640–651 (2017)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2015), pp. 1–14 (2015)
Zhao, H., Shi, J., Qi, X., Wang, X., Jia, J.: Pyramid scene parsing network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2881–2890 (2017)
Chen, L.-C., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F., Adam, H. Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. arXiv preprint (2017). arXiv:1706.05587
Cordts, M., Omran, M., Ramos, S., Rehfeld, T., Enzweiler, M., Benenson, R., Franke, U., Roth, S., Schiele, B.: The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3213–3223 (2016)
Badrinarayanan, V., Kendall, A., Cipolla, R.: Segnet: a deep convolutional encoder–decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(12), 2481–2495 (2017)
Paszke, A., Chaurasia, A., Kim, S., Culurciello, E. Enet: A Deep Neural Network Architecture for Real-time Semantic Segmentation. arXiv preprint (2016). arXiv:1606.02147
Sachin, M., Mohammad, R., Anat, C., Linda, S., Hannaneh, H.: Espnet: efficient spatial pyramid of dilated convolutions for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 552–568 (2018)
Romera, E., Alvarez, J.M., Bergasa, L.M., Arroyo, R.: Erfnet: efficient residual factorized convnet for real-time semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 19(1), 263–272 (2017)
Wang, Y., Cui, Z., Li, Y.: Distribution-consistent modal recovering for incomplete multimodal learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 22025–22034 (2023)
Yu, C., Wang, J., Peng, C., Gao, C., Yu, G., Sang, N.: Bisenet: bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 325–341 (2018)
Changqian, Y., Gao, C., Wang, J., Gang, Y., Shen, C., Sang, N.: Bisenet v2: bilateral network with guided aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vision 129, 3051–3068 (2021)
Li, H., Xiong, P., Fan, H., Sun, J.: Dfanet: deep feature aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9522–9531 (2019)
Howard, A.G., Zhu, M., Chen, B., Kalenichenko, D., Wang, W., Weyand, T., Andreetto, M., Adam, H.: Mobilenets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv preprint (2017). arXiv:1704.04861
Han, K., Wang, Y., Tian, Q., Guo, J., Xu, C., Xu, C.: Ghostnet: more features from cheap operations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1580–1589 (2020)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, October 5–9, 2015, Proceedings, Part III, vol. 18, pp. 234–241. Springer (2015)
Wang, Q., Wu, B., Zhu, P, Li, P., Zuo, W., Hu, Q.: Eca-net: efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 11534–11542 (2020)
Huang, Z., Wang, X., Huang, L., Huang, C., Wei, Y., Liu, W.: Ccnet: criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 603–612 (2019)
Cao, Y., Xu, J., Lin, S., Wei, F., Hu, H.: Gcnet: non-local networks meet squeeze-excitation networks and beyond. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (2019)
Zhong, Z, Lin, Z.Q., Bidart, R., Hu, X., Daya, I.B., Li, Z., Zheng, W.-S., Li, J., Wong, A.: Squeeze-and-attention networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 13065–13074 (2020)
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.-Y., Kweon, I.S..: Cbam: convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 3–19 (2018)
Lu, T., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Wei, L., Wang, Z., Jiang, J.: Face hallucination via split-attention in split-attention network. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 5501–5509 (2021)
Wang, Y., Tao, L., Zhang, Y., Wang, Z., Jiang, J., Xiong, Z.: Faceformer: aggregating global and local representation for face hallucination. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 33(6), 2533–2545 (2023)
Wang, Y., Lu, T., Yao, Y., Zhang, Y., Xiong, Z.: Learning to hallucinate face in the dark. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 26, 2314–2326 (2023)
Li, G., Han, C., Liu, Z.: No-service rail surface defect segmentation via normalized attention and dual-scale interaction. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 72, 1–10 (2023)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7132–7141 (2018)
Li, G., Wang, Y., Liu, Z., Zhang, X., Zeng, D.: Rgb-t semantic segmentation with location, activation, and sharpening. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 33(3), 1223–1235 (2023)
Chen, L.-C., Papandreou, G., Kokkinos, I., Murphy, K., Yuille, A.L.: Deeplab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40(4), 834–848 (2018)
Yan, H., Zhang, C., Wu, M.: Lawin Transformer: Improving Semantic Segmentation Transformer with Multi-scale Representations via Large Window Attention. arXiv preprint (2022) arXiv:2201.01615
Wang, Y., Li, G., Liu, Z.: Sgfnet: semantic-guided fusion network for rgb-thermal semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 33(12), 7737–7748 (2023)
Liu, W., Rabinovich, A., Berg, A.C.: Parsenet: Looking Wider to See Better. arXiv preprint (2015) arXiv:1506.04579
Yu, C., Wang, J., Peng, C., Gao, C., Yu, G., Sang, N.: Learning a discriminative feature network for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1857–1866 (2018)
Wang, Y., Zhou, Q., Liu, J., Xiong, J., Gao, G., Wu, X., Latecki, L.J.: Lednet: a lightweight encoder-decoder network for real-time semantic segmentation. In: 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 1860–1864. IEEE (2019)
Gao, G., Guoan, X., Yi, Y., Xie, J., Yang, J., Yue, D.: Mscfnet: a lightweight network with multi-scale context fusion for real-time semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 23(12), 25489–25499 (2021)
Gao, G., Guoan, X., Li, J., Yi, Y., Huimin, L., Yang, J.: Fbsnet: a fast bilateral symmetrical network for real-time semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 25, 3273–3283 (2023)
Si, H., Zhang, Z., Lv, F., Yu, G., Lu, F.: Real-Time Semantic Segmentation via Multiply Spatial Fusion Network. arXiv preprint (2019). arXiv:1911.07217
Xu, Q., Ma, Y., Wu, J., Long, C.: Faster bisenet: a faster bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation. In: 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–8. IEEE (2021)
Wang, X., Liu, R., Dong, J., Zhang, Q., Zhou, D.: Lightweight real-time image semantic segmentation network based on multi-resolution hybrid attention mechanism. Wirel. Commun. Mobile Comput. 1–10, 2022 (2022)
Singha, T., Pham, D.-S., Krishna, A.: A real-time semantic segmentation model using iteratively shared features in multiple sub-encoders. Pattern Recogn. 140, 109557 (2023)
Zhang, X., Zhou, X., Lin, M., Sun, J.: Shufflenet: an extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6848–6856 (2018)
Emara, T., El Munim, H.E.A., Abbas, H.M.: Liteseg: a novel lightweight convnet for semantic segmentation. In: 2019 Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), pp. 1–7. IEEE (2019)
Xuegang, H., Gong, J.: Larfnet: lightweight asymmetric refining fusion network for real-time semantic segmentation. Comput. Graph. 109, 55–64 (2022)
Wang, P., Li, L., Pan, F., Wang, L.: Lightweight bilateral network for real-time semantic segmentation. J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inf. 27(4), 673–682 (2023)
Mazhar, S., Atif, N., Bhuyan, M.K., Ahamed, S.R.: Block attention network: a lightweight deep network for real-time semantic segmentation of road scenes in resource-constrained devices. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 126, 107086 (2023)
Dou, Z., Ye, D., Wang, B.: Autosegedge: searching for the edge device real-time semantic segmentation based on multi-task learning. Image Vis. Comput. 136, 104719 (2023)
Mengxu, L., Zhenxue Chen, Q.M., Jonathan, W., Wang, N., Rong, X., Yan, X.: Frnet: factorized and regular blocks network for semantic segmentation in road scene. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 23(4), 3522–3530 (2020)
Singha, T., Pham, D.S., Krishna, A.: Sdbnet: lightweight real-time semantic segmentation using short-term dense bottleneck. In: 2022 International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), pp 1–8 (2022)
Hao, S., Zhou, Y., Guo, Y., Hong, R., Cheng, J., Wang, M.: Real-time semantic segmentation via spatial-detail guided context propagation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 33, 1752–1764 (2022)
Wan, Q., Huang, Z., Lu, J., Yu, G. Zhang, L.: Seaformer: squeeze-enhanced axial transformer for mobile semantic segmentation. In: The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations (2023)
Fan, J., Wang, F., Chu, H., Xiao, H., Cheng, Y., Gao, B.: Mlfnet: multi-level fusion network for real-time semantic segmentation of autonomous driving. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 8(1), 756–767 (2023)
Mengxu, L., Chen, Z., Liu, C., Ma, S., Cai, L., Qin, H.: Mfnet: multi-feature fusion network for real-time semantic segmentation in road scenes. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 23(11), 20991–21003 (2022)
Nirkin, Y., Wolf, L., Hassner, T.: Hyperseg: patch-wise hypernetwork for real-time semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4061–4070 (2021)
Yang, Z., Hongshan, Y., Qiang, F., Sun, W., Jia, W., Sun, M., Mao, Z.-H.: Ndnet: narrow while deep network for real-time semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 22(9), 5508–5519 (2020)
Wang, K., Yang, J., Yuan, S., Li, M.: A lightweight network with attention decoder for real-time semantic segmentation. Vis. Comput. 38(7), 2329–2339 (2022)
Liu, J., Zhou, Q., Qiang, Y., Kang, B., Wu, X., Zheng, B.: Fddwnet: a lightweight convolutional neural network for real-time semantic segmentation. In: ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 2373–2377. IEEE (2020)
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project Number 62076044), and the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, China (Grant No. cstc2019jcyj-zdxm0011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XH: research direction, resources, formal analysis, project administration, writing—review and editing. YK: conceptualization, methodology, experiment, data collection and analysis, test, writing—original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Ke, Y. EMFANet: a lightweight network with efficient multi-scale feature aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation. J Real-Time Image Proc 21, 40 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-024-01421-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-024-01421-z