Abstract
Purpose
Automatic retinal fundus image quality analysis is one of the most essential preliminary stages in automatic computer-aided retinal disease diagnosis system, which allows good-quality fundus images for accurate disease prediction through localization and segmentation of retinal regions. This paper presents new feature extraction methods using full-reference and no-reference image quality metrics for image quality classification.
Methods
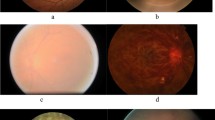
Basic image features, reference and no-reference features are extracted from the fundus image and applied through different classification techniques to determine the image quality for further diagnosis. In this paper, human-made categorization including good and non-good-quality fundus image classification is constructed by considering major features of retinal fundus images are illumination, clarity, image intensity, contrast and region visibility. The proposed system presented fundus image quality classification by automatic extraction of features from fundus images through image processing techniques and automatic classification of image quality through different classification algorithm.
Results
This system was thoroughly investigated on 2674 retinal fundus images from publically available datasets, namely MESSIDOR, Drishti-GS1, DRIVE, HRF, DRIONS-DB, DIARETDB0, DIARETDB1, IDRiD, INSPIRE-AVR, CHASE-DB1, ONHSD, DRIMDB and e-ophtha-EX with better performance results in terms of sensitivity, accuracy, precision and F1 score of 99.36%, 96.79%, 96.29% and 97.79%, respectively.
Conclusion
The proposed system results were compared to the existing state-of-the-art approaches and outperform existing methods for image quality assessment representing the efficiency and robustness of our system is most suitable for automatic image analysis during retinal disease diagnosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shen Z, Fu H, Shen J, Shao L (2021) Modeling and enhancing low-quality retinal fundus images. IEEE Trans Med Imag 40:996–1006. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2020.3043495
Bhatkalkar B, Joshi A, Prabhu S, Bhandary S (2020) Automated fundus image quality assessment and segmentation of optic disc using convolutional neural networks. Int J Electric Comput Eng 10:816–827
Dai P, Sheng H, Zhang J, Li L, Wu J, Fan M (2016) Retinal fundus image enhancement using the normalized convolution and noise removing. Int J Biomed Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5075612
Jiménez-García J, Romero-Oraá R, García M, López-Gálvez MI, Hornero R (2019) Combination of global features for the automatic quality assessment of retinal images. Entropy 21:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21030311
Muddamsetty SM, Moeslund TB (2020) Multi-level quality assessment of retinal fundus images using deep convolution neural networks. In: 16th international joint conference on computer vision theory and applications (VISAPP-2021). SCITEPRESS Digital Library
Sevik U, Köse C, Berber T, Erdöl H (2014) Identification of suitable fundus images using automated quality assessment methods. J Biomed Opt 19:046006. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.jbo.19.4.046006
Paulus J, Meier J, Bock R, Hornegger J, Michelson G (2010) Automated quality assessment of retinal fundus photos. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 5:557–564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-010-0479-7
Pires Dias JM, Oliveira CM, Da Silva CLA (2014) Retinal image quality assessment using generic image quality indicators. Inform Fusion 19:73–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2012.08.001
Shao F, Yang Y, Jiang Q, Jiang G, Ho Y (2017) Automated quality assessment of fundus images via analysis of illumination, naturalness and structure. IEEE Access 6:806–817. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2776126
Shen Y, Sheng B, Fang R, Li H, Dai L, Stolte S, Qin J, Jia W, Shen D (2020) Domain-invariant interpretable fundus image quality assessment. Med Image Anal 61:101654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2020.101654
Raj A, Shah NA, Tiwari AK, Martini MG (2020) Multivariate regression-based convolutional neural network model for fundus image quality assessment. IEEE Access 8:57810–57821. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2982588
Liu H, Zhang N, Jin S, Xu D, Gao W (2021) Small sample color fundus image quality assessment based on gcforest. Multimed Tools Appl 80:17441–17459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09362-y
Carmona Suárez EJ, Rincón Zamorano M, García-Feijoo J, Martínez-de-la-Casa JM, Servet MBMHM (2008) DRIONS-DB: digital retinal images for optic nerve segmentation database. http://www.ia.uned.es/~ejcarmona/DRIONS-DB.html
Sivaswamy J, Krishnadas SR, Joshi GD, Jain M, Ujjwal STA (2014) DRISHTI-GS: retinal image dataset for optic nerve head (ONH) segmentation IIIT. Hyderabad, India, pp 53–56
Decencière E, Zhang X, Cazuguel G, Lay B, Cochener B, Trone C, Gain P, Ordonez R, Massin P, Erginay A, Charton B, Klein J (2014) Feedback on a publicly distributed image database: the messidor database. Image Anal Stereol 33:231–234. https://doi.org/10.5566/ias.1155
Budai A, Bock R, Maier A, Hornegger JGM (2013) High-resolution fundus (HRF) image database. https://www5.cs.fau.de/research/data/fundus-images/
DRIVE: Digital retinal images for vessel extraction. https://drive.grand-challenge.org/
Niemeijer M, Xu X, Dumitrescu AV, Gupta P, van Ginneken B, Folk JCAM (2011) Automated measurement of the arteriolar-to-venular width ratio in digital color fundus photographs. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 30:1941–1950. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2011.2159619
Owen CG, Rudnicka AR, Mullen R, Barman SA, Monekosso D, Whincup PH, Ng J, Paterson C (2009) Retinal image analysis. https://blogs.kingston.ac.uk/retinal/chasedb1/
Kauppi T, Kalesnykiene V, Kamarainen J, Lensu L, Sorri I, Uusitalo H, Kalviainen H, Pietil J (2006) DIARETDB0 : evaluation database and methodology for diabetic retinopathy algorithms, pp 1–17
Kauppi T, Kalesnykiene V, Kamarainen J, Lensu L, Sorri I, Uusitalo H, Kalviainen H, Pietil J (2007) The DIARETDB1 diabetic retinopathy database and evaluation protocol. BMVC 2007 - Proceedings of the British machine vision conference 2007, pp 1–18 https://doi.org/10.5244/C.21.15
Lowell J, Hunter A, Steel D, Basu A, Ryder R, Fletcher E, Kennedy L (2004) Optic nerve head segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 23:256–264. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2003.823261
Decencière E, Cazuguel G, Zhang X, Thibault G, Klein JC, Meyer F, Marcotegui B, Quellec G, Lamard M, Danno R, Elie D, Massin P, Viktor Z, Erginay A, Laÿ B, Chabouis A (2013) TeleOphta: machine learning and image processing methods for teleophthalmology. Irbm 34:196–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irbm.2013.01.010
Porwal P, Pachade S, Kamble R, Kokare M, Deshmukh G, Sahasrabuddhe VFM (2018) Indian diabetic retinopathy image dataset (IDRiD). In: IEEE Dataport. https://ieee-dataport.org/open-access/indian-diabetic-retinopathy-image-dataset-idrid
Venkatanath N, Praneeth D, Maruthi Chandrasekhar B, Channappayya SSM (2015) Blind image quality evaluation using perception based features. In: In proceedings of the 21st National conference on communications (NCC). Piscataway, NJ, IEEE, pp 1–6
Mittal A, Soundararajan R, Bovik AC (2013) Making a “completely blind” image quality analyzer. IEEE Signal Process Lett 20:209–212. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2012.2227726
Mittal A, Anush KM, Alan CB (2011) Blind/referenceless image spatial quality evaluator. In: 2011 Conference record of the forty fifth asilomar conference on signals, systems and computers (ASILOMAR). IEEE, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, pp 723–727
Dos Santos JCM, Carrijo GA, de Fátima dos Santos Cardoso C, Ferreira JC, Sousa PM, Patrocínio AC (2020) Fundus image quality enhancement for blood vessel detection via a neural network using CLAHE and Wiener filter. Res Biomed Eng 36:107–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42600-020-00046-y
Fleming AD, Philip S, Goatman KA, Olson JA, Sharp PF (2006) Automated assessment of diabetic retinal image quality based on clarity and field definition. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47(3):1120–1125. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.05-1155
Saha SK, Fernando B, Cuadros J, Xiao D, Kanagasingam Y (2018) Automated quality assessment of colour fundus images for diabetic retinopathy screening in telemedicine. J Digital Imag 31:869–878. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-018-0084-9
Wang Z, Simoncelli E, Bovik AC (2003) Multi-scale structural similarity for image quality assessment. N Y 2:9–13. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACSSC.2003.1292216
Mittal A, Moorthy AK, Bovik AC (2012) No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain. IEEE Trans Image Process 21:4695–4708. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2012.2214050
Jacob SG, Ramani G (2011) Discovery of knowledge patterns in clinical data through data mining algorithms: multi-class categorization of breast tissue data. Int J Comput Appl 32:46–53
Ramani RG, Sivagami G (2019) Identification of bio-markers for breast cancer detection through data mining methods. Int J Recent Technol Eng 8:763–769
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
This work does not involve studies with human participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramani, R.G., Shanthamalar, J.J. Automated image quality appraisal through partial least squares discriminant analysis. Int J CARS 17, 1367–1377 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-022-02668-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-022-02668-2