Abstract
Purpose
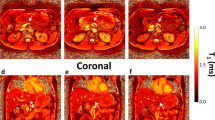
To evaluate the influence of fat deposition on T1 relaxation time of pancreatic parenchyma using dual-flip-angle T1 mapping with and without fat suppression.
Methods
Forty-five patients who underwent abdominal MR imaging including T1 mapping with dual-flip-angle method on 3T MRI were included. We measured T1 relaxation time of pancreatic parenchyma on the T1 map images with and without fat suppression. T1 relaxation time of bone marrow was also measured as a reference organ with abundant fat deposition. Fat signal fraction (FSF) was also measured at the same location as T1 map images. Then, the correlation between T1 relaxation time and FSF was assessed.
Results
T1 relaxation times of pancreatic parenchyma and bone marrow on the T1 map images without fat suppression showed significantly negative correlation with FSF (pancreas, r = − 0.394, P = 0.007; bone marrow, r = − 0.550, P < 0.001), while there were no significant correlations between them on the T1 map images with fat suppression. On the T1 map images without fat suppression, T1 relaxation times of pancreatic parenchyma as well as bone marrow in patients with FSF ≥ 10% were significantly shorter than those in patients with FSF < 10% (pancreas, P = 0.041; bone marrow, P = 0.005). Conversely, on the T1 map images with fat suppression, no significant differences in T1 relaxation times were found between two groups.
Conclusion
T1 relaxation time of the pancreas on T1 mapping was influenced by the presence of fat deposition. Therefore, fat suppression technique in T1 mapping will be essential for evaluating T1 relaxation time of pancreatic parenchyma.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cassinotto C, Feldis M, Vergniol J, Mouries A, Cochet H, Lapuyade B et al (2015) MR relaxometry in chronic liver diseases: comparison of T1 mapping, T2 mapping, and diffusion-weighted imaging for assessing cirrhosis diagnosis and severity. Eur J Radiol 84(8):1459–1465
Haimerl M, Verloh N, Zeman F, Fellner C, Muller-Wille R, Schreyer AG et al (2013) Assessment of clinical signs of liver cirrhosis using T1 mapping on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced 3T MRI. PLoS ONE 8(12):e85658
Ding Y, Rao SX, Meng T, Chen C, Li R, Zeng MS (2014) Usefulness of T1 mapping on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MR imaging in assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur Radiol 24(4):959–966
Hueper K, Peperhove M, Rong S, Gerstenberg J, Mengel M, Meier M et al (2014) T1-mapping for assessment of ischemia-induced acute kidney injury and prediction of chronic kidney disease in mice. Eur Radiol 24(9):2252–2260
Dass S, Suttie JJ, Piechnik SK, Ferreira VM, Holloway CJ, Banerjee R et al (2012) Myocardial tissue characterization using magnetic resonance noncontrast T1 mapping in hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 5(6):726–733
Schelbert EB, Messroghli DR (2016) State of the art: clinical applications of cardiac T1 mapping. Radiology 278(3):658–676
Bulluck H, Maestrini V, Rosmini S, Abdel-Gadir A, Treibel TA, Castelletti S et al (2015) Myocardial T1 mapping. Circ J Off Jpn Circ Soc 79(3):487–494
Kim KA, Park MS, Kim IS, Kiefer B, Chung WS, Kim MJ et al (2012) Quantitative evaluation of liver cirrhosis using T1 relaxation time with 3 tesla MRI before and after oxygen inhalation. J Magn Reson Imaging 36(2):405–410
Hoad CL, Palaniyappan N, Kaye P, Chernova Y, James MW, Costigan C et al (2015) A study of T(1) relaxation time as a measure of liver fibrosis and the influence of confounding histological factors. NMR Biomed 28(6):706–714
Mathur A, Marine M, Lu D, Swartz-Basile DA, Saxena R, Zyromski NJ et al (2007) Nonalcoholic fatty pancreas disease. HPB Off J Int Hepato Pancreato Biliary Assoc 9(4):312–318
Tirkes T, Lin C, Fogel EL, Sherman SS, Wang Q, Sandrasegaran K (2017) T1 mapping for diagnosis of mild chronic pancreatitis. J Magn Reson Imaging 45(4):1171–1176
Wang M, Gao F, Wang X, Liu Y, Ji R, Cang L et al (2018) Magnetic resonance elastography and T1 mapping for early diagnosis and classification of chronic pancreatitis. J Magn Reson Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.26008
Paajanen H, Brasch RC, Dean PB (1988) Experimental acute pancreatitis: MR relaxation time studies using gadolinium-DTPA. Magn Reson Med 6(1):63–73
Yoon JH, Lee JM, Lee KB, Kim SW, Kang MJ, Jang JY et al (2016) Pancreatic steatosis and fibrosis: quantitative assessment with preoperative multiparametric MR imaging. Radiology 279(1):140–150
Erturk SM (2009) Chronic pancreatitis and diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology 252(1):316
Yasokawa K, Ito K, Kanki A, Yamamoto A, Torigoe T, Sato T et al (2018) Evaluation of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency by cine-dynamic MRCP using spatially selective inversion-recovery (IR) pulse: correlation with severity of chronic pancreatitis based on morphological changes of pancreatic duct. Magn Reson Imaging 48:70–73
Schlaudraff E, Wagner HJ, Klose KJ, Heverhagen JT (2008) Prospective evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy of secretin-enhanced magnetic resonance cholangiopancreaticography in suspected chronic pancreatitis. Magn Reson Imaging 26(10):1367–1373
Balci NC, Smith A, Momtahen AJ, Alkaade S, Fattahi R, Tariq S et al (2010) MRI and S-MRCP findings in patients with suspected chronic pancreatitis: correlation with endoscopic pancreatic function testing (ePFT). J Magn Reson Imaging 31(3):601–606
Wang HZ, Riederer SJ, Lee JN (1987) Optimizing the precision in T1 relaxation estimation using limited flip angles. Magn Reson Med 5(5):399–416
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors. Institutional review board approval for retrospective publication of data was obtained, and patients’ informed consent was waived.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent was waived.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Higashi, M., Tanabe, M., Okada, M. et al. Influence of fat deposition on T1 mapping of the pancreas: evaluation by dual-flip-angle MR imaging with and without fat suppression. Radiol med 125, 1–6 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-019-01087-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-019-01087-9