Abstract
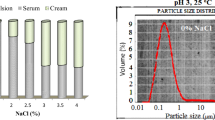
Rambutan seed protein untreated (No-US) and treated (US) with high intensity ultrasonication (~ 320 W 20 min) had been characterized. LC-MS/MS analysis revealed that molecular sizes of proteins identified in rambutan seed protein were in a range of 4.1 to 318.9 kDa. US protein had higher fractions of small molecular weight proteins than No-US protein, suggesting US disrupted polypeptide structures into smaller units. No-US protein and US protein displayed similar band patterns on SDS PAGE gels. The surface hydrophobicity, the denaturation temperature, and the enthalpy of heat denaturation of No-US protein and US protein were not significantly different. The applied ultrasonication was suggested to not have a strong effect on the protein tertiary conformation. Rambutan seed protein had a relatively high amount of hydrophobic amino acids of 40.2% promoted strong intra-hydrophobic interaction. Emulsions prepared by US protein had lesser bridging flocculation and higher creaming stability than prepared by No-US protein.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
None.
References
O.A. Higuera-Barraza, C.L. Del Toro-Sanchez, S. Ruiz-Cruz, E. Márquez-Ríos, Ultrason Sonochem. 31, 558 (2016)
J.A. Téllez-Morales, B. Hernández-Santo, J. Rodríguez-Miranda, Ultrason Sonochem. 61, 104787 (2020)
H. Hu, E.C.Y. Li-Chan, L. Wan, M. Tian, S. Pan, Food Hydrocoll. 32(2), 303 (2013)
H. Hu, J. Wu, E.C.Y. Li-Chan, L. Zhu, F. Zhang, X. Xu, G. Fan, L. Wang, X. Huang, S. Pan, Food Hydrocoll. 30(2), 647 (2013)
L. Jiang, J. Wang, Y. Li, Z. Wang, J. Liang, R. Wang, Y. Chen, W. Ma, B. Qi, M. Zhang, Food Res. Int. 62, 595 (2014)
S. Li, X. Yang, Y. Zhang, H. Ma, W. Qu, X. Ye, R. Muatasim, A.O. Oladejo, Ultrason Sonochem. 31, 85 (2016)
X. Sui, S. Bi, B. Qi, Z. Wang, M. Zhang, Y. Li, L. Jiang, Food Hydrocoll. 63, 727 (2017)
Q.-T. Zhang, Z.-C. Tu, H. Xiao, H. Wang, X.-Q. Huang, G.-X. Liu, C.-M. Liu, Y. Shi, L.-L. Fan, D.-R. Lin, Food Bioprod Process 92(1), 30 (2014)
R. Galindo-Luján, L. Pont, Z. Minic, M.V. Berezovski, V. Sanz-Nebot, F. Benavente, Food Chem. 363, 130250 (2021)
A. Tahmasian, J.A. Broadbent, A. Juhász, M. Nye-Wood, T.T. Le, U. Bose, M.L. Colgrave, Food Chem. 367, 130722 (2022)
N.A. Evaristus, W.N. Wan Abdullah, C.-Y. Gan, Peptides 102, 61 (2018)
J. Chandrapala, B. Zisu, M. Palmer, S. Kentish, M. Ashokkumar, Ultrason Sonochem. 18(5), 951 (2011)
L.L. Gao, Y.Q. Li, Z.S. Wang, G.J. Sun, X.M. Qi, H.Z. Mo, Food Chem. 240, 980 (2018)
Y. Deng, L. Huang, C. Zhang, P. Xie, J. Cheng, X. Wang, S. Li, Food Chem. 283, 539 (2019)
W. Xia, W.K. Siu, L.M.C. Sagis, Food Hydrocoll. 120, 106962 (2021)
A.R. Jambrak, T.J. Mason, V. Lelas, G. Krešić, LWT - Food Sci. Technol. 43(2), 254 (2010)
A.R. Jambrak, T.J. Mason, V. Lelas, L. Paniwnyk, Z. Herceg, J. Food. Eng. 121, 15 (2014)
J.A. Resendiz-Vazquez, J.A. Ulloa, J.E. Urías-Silvas, P.U. Bautista-Rosales, J.C. Ramírez-Ramírez, P. Rosas-Ulloa, L. González-Torres, Ultrason Sonochem. 37, 436 (2017)
J. O’Sullivan, B. Murray, C. Flynn, I. Norton, Food Hydrocoll. 53, 141 (2016)
K. Nishinari, Y. Fang, S. Guo, G.O. Phillips, Food Hydrocoll. 39, 301 (2014)
C.-H. Tang, X.-Y. Wang, X.-Q. Yang, L. Li, J. Food Eng. 92(4), 432 (2009)
F. Liu, C.-H. Tang, J. Agric, Food Chem. 61(37), 8888 (2013)
Z. Cui, Y. Chen, X. Kong, C. Zhang, Y. Hua, J. Agric. Food Chem. 62(7), 1634 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This research project was financial supported by Agricultural Research Development Agency (Public Organization) of Thailand or “ARDA” (CRP6405030700). Rambutan seeds in this study were kindly donated by Malee Group Public Company Limited and Universal Food Public Company Limited. Soy protein isolate was kindly donated by Rama Production Co. Ltd. (Bangkok, Thailand). Chemical analysis and some experimental work were performed at Central Instrument Facility (Faculty of Science, Mahidol University, Bangkok), Scientific and Technological Research Equipment Centre Chulalongkorn University (Bangkok), Proteomics Services Center (Faculty of Medical Technology, Mahidol University, Bangkok), National Metal and Materials Technology Center (National Science and Technology Center, Pathum Thani), Department of Science Service (Division of Engineering Materials, Bangkok), and Office of Scientific Instrument and Testing (Prince of Songkla University, Songkhla). The author would like to thank Associate Professor Dr. Kanitha Tananuwong for the valuable discussion on the LC-MS/MS technique.
Funding
This study was funded by Agricultural Research Development Agency (Public Organization) of Thailand or “ARDA” (CRP6405030700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Suwimon Ariyaprakai: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing-Original Draft, Writing – Review & Editing, Project administration, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
The LC-MS/MS analysis data showing names, molecular weight, and relative amounts of all proteins identified in US rambutan seed protein and in No-US rambutan seed protein. (DOCX 28.9 KB)
Supplementary Material 2
The image of SDS PAGE gel from Fig. 2 labled by SpotID. The corresponding table showing molecular weight band, band intensity, and band volume at each SpotID area of US rambutan seed protein and No-US rambutan seed protein. (DOCX 182 KB)
Supplementary Material 3
The DSC thermogram of (a) US rambutan seed protein and (b) No-US rambutan seed protein obtained by a heating rate of 5 °C/min. The graphs within the heating range of 70 °C to 100 °C were shown.(DOCX 35.3 KB)
Supplementary Material 4
The drawing pictures showing (a) emulsions stabilized by US rambutan seed protiens without bridging flocculaiton and (b) emulsions stabilized by No-US rambutan seed protiens with bridging flocculaiton.(DOCX 1.45 MB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ariyaprakai, S. Effects of High Intensity Ultrasonication on Molecular Characteristics and Emulsifying Properties of Rambutan Seed Protein. Food Biophysics 19, 230–242 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-023-09815-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-023-09815-5