Abstract
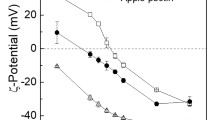
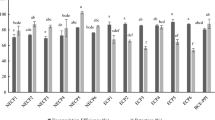
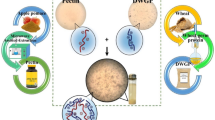
There is an increasing interest in the food industry to use potato protein as an alternative plant protein. However, its bitter taste often limits the utilization in novel foods and beverages. Coacervation is a promising technique to mask bitterness of certain food compounds. In the present study, we aimed to reduce the degree of bitterness of potato protein by generating protein-pectin complexes based on coacervation. Potato protein isolate and pectins derived from various origins having different degree of esterification (DE) were initially mixed under acidic conditions to promote the formation of complexes. Single and complex biopolymers were then characterized in terms of surface charge, solubility, rheological and sensorial properties as a function of protein pectin ratio, pectin source, and the degree of esterification, respectively. The protein-pectin ratio and degree of esterification of pectins substantially influenced the interaction behaviour and phase separation of the protein-pectin mixtures. The bitterness score decreased with increasing surface charge and pectin concentration. Bitterness was strongly reduced for complexes formed with high DE citrus pectin at a protein pectin ratio 0.33. The complexes generated at this ratio were relatively stable based on visual observation and microscopic images. Our results might have significant implications for the utilization of potato proteins in beverage applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Nesterenko, I. Alric, F. Silvestre, V. Durrieu, Ind. Crop. Prod. 42, 469–479 (2013)
S. Liu, C. Elmer, N.H. Low, M.T. Nickerson, Food Res. Int. 43(2), 489–495 (2010)
S. Sethi, S.K. Tyagi, R.K. Anurag, J. Food Sci. Technol. 53(9), 3408–3423 (2016)
M. Yavuz and B. Özçelik, Academic Food Journal/Akademik GIDA 14 (4) (2016)
A. Görgüç, P. Özer, F.M. Yılmaz, J. Food Compos. Anal. 87, 103424 (2020)
E. Sipos and L. Foster, in Dietary Proteins (AOCS Publishing, 1992), pp. 243–282
V.R. Young, P.L. Pellett, The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 59(5), 1203S–1212S (1994)
A. Tarrega, M.O. Ramírez-Sucre, J.F. Vélez-Ruiz, E. Costell, J. Food Eng. 109(3), 467–474 (2012)
I. Siro, E. Kapolna, B. Kápolna, A. Lugasi, Appetite 51(3), 456–467 (2008)
D. Asker, J. Weiss, D.J. McClements, J. Agric. Food Chem. 59(3), 1041–1049 (2011)
N.J. Gaudette, G.J. Pickering, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 53(5), 464–481 (2013)
D. Sun-Waterhouse, S.S. Wadhwa, Food Bioprocess Technol. 6(3), 607–627 (2013)
B. Zeeb, M. Yavuz-Düzgun, J. Dreher, et al., Food & Function 9(4), 2261–2269 (2018)
A.S. Sivam, D. Sun-Waterhouse, C.O. Perera, G.I.N. Waterhouse, Food Res. Int. 50(2), 574–585 (2013)
M. Friedman, J. Agric. Food Chem. 44(1), 6–29 (1996)
R.L. Jackman, R.Y. Yada, J. Food Sci. 53(5), 1427–1432 (1988)
M.S. Kaldy, Econ. Bot. 26(2), 142–144 (1972)
A.C. Kapoor, S.L. Desborough, P.H. Li, Potato Res. 18(3), 469–478 (1975)
L. Stounbjerg, C. Vestergaard, B. Andreasen, R. Ipsen, Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 566, 104–112 (2019)
S. Løkra, K.O. Strætkvern, Food 3(1), 88–95 (2009)
H.A. Schols, A.G.J. Voragen, Carbohydr. Res. 256(1), 83–95 (1994)
W.G.T. Willats, P. Knox, J.D. Mikkelsen, Trends Food Sci. Technol. 17(3), 97–104 (2006)
H. Salminen, J. Weiss, Food Biophysics 9(1), 29–38 (2014)
P.J.H. Daas, K. Meyer-Hansen, H.A. Schols, G.A. De Ruiter, A.G.J. Voragen, Carbohydr. Res. 318(1–4), 135–145 (1999)
M. Maniruzzaman, J.S. Boateng, M. Bonnefille, A. Aranyos, J.C. Mitchell, D. Douroumis, Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 80(2), 433–442 (2012)
D. Douroumis, Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery 4(4), 417–426 (2007)
M. Pein, M. Preis, C. Eckert, F.E. Kiene, Int. J. Pharm. 465(1–2), 239–254 (2014)
C. Morr, B. German, J. Kinsella, et al., J. Food Sci. 50(6), 1715–1718 (1985)
M.M. Bradford, Anal. Biochem. 72(1), 248–254 (1976)
W. H. Gardner, Handbook of Food Additives, 225–270 (1972)
M. Meilgaard, G. Civille, B. Carr, Sensory Evaluation Techniques. 4th ed. (CRC Press, New York, 2007), pp. 105–128
M. Meilgaard, G. Civille, B. Carr, Sensory Evaluation Techniques, 4th edn. (CRC Press, New York, 2007)
C.-H. Tang, X. Sun, Food Hydrocoll. 25(3), 315–324 (2011)
Y. Du, F. Chen, Y. Zhang, C. Rempel, M.R. Thompson, Q. Liu, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 132(44) (2015)
S.-W. Yin, J.-C. Chen, S.-D. Sun, C.H. Tang, X.Q. Yang, Q.B. Wen, J.R. Qi, Food Chem. 128(2), 420–426 (2011)
D.J. McClements, Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 9(5), 305–313 (2004)
R. Townend, R.J. Winterbottom, S.N. Timasheff, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 82(12), 3161–3168 (1960)
Y. Yang, M.E. Leser, A.A. Sher, D.J. McClements, Food Hydrocoll. 30(2), 589–596 (2013)
A. Krzeminski, K.A. Prell, J. Weiss, J. Hinrichs, Food Hydrocoll. 35, 332–340 (2014)
X. Wang, Q. Chen, X. Lü, Food Hydrocoll. 38, 129–137 (2014)
R. Lutz, A. Aserin, L. Wicker, N. Garti, Food Hydrocoll. 23(3), 786–794 (2009)
S. Turgeon, C. Schmitt, C. Sanchez, Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 12(4–5), 166–178 (2007)
F. Weinbreck, R. De Vries, P. Schrooyen, C. De Kruif, Biomacromolecules 4(2), 293–303 (2003)
B. Zeeb, C. Stenger, J. Hinrichs and J. Weiss, Food Structure 10, 10–20 (2016)
C. Stenger, B. Zeeb, J. Hinrichs, J. Weiss, J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 38(9), 1258–1265 (2017)
K. Protte, C. Bollow, A. Sonne, O. Menéndez-Aguirre, J. Weiss, J. Hinrichs, Food Biophysics 11(3), 226–234 (2016)
Y.P. Timilsena, T.O. Akanbi, N. Khalid, B. Adhikari, C.J. Barrow, International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 121, 1276–1286 (2019)
A. Ye, International Journal of Food Science & Technology 43(3), 406–415 (2008)
C. Sanchez, G. Mekhloufi, C. Schmitt, et al., Langmuir 18(26), 10323–10333 (2002)
Y. Kim, L. Wicker, Food Hydrocolloids 25(3), 419–425 (2011)
U. Einhorn-Stoll, T. Salazar, B. Jaafar, H. Kunzek, Nahrung-Food 45(5), 332–337 (2001)
T. Nordmark and G. R. Ziegler, Food Hydrocolloids 14(6), 579–590 (2000)
E. Hans-Ulrich, M. Frank and N. Karl, in Handbook of Food Science, Technology, and Engineering - 4 Volume Set (CRC Press, 2005)
Y.A. Antonov, M. Celus, C. Kyomugasho, M. Hendrickx, P. Moldenaers, R. Cardinaels, Food Hydrocoll. 94, 268–278 (2019)
D. Powell, E. Morris, M. Gidley, D. Rees, Journal of Molecular Biology 155(4), 517–531 (1982)
R. Kohn, O. Markovič, E. Machová, Collect. Czechoslov. Chem. Commun. 48(3), 790–797 (1983)
J. Thibault, M. Rinaudo, Biopolymers: Original Research on Biomolecules 24(11), 2131–2143 (1985)
M.-C. Ralet, V. Dronnet, H.C. Buchholt, J.-F. Thibault, Carbohydrate Research 336(2), 117–125 (2001)
C. Löfgren, S. Guillotin, H. Evenbratt, H. Schols, A.-M. Hermansson, Biomacromolecules 6(2), 646–652 (2005)
G. Limberg, R. Körner, H.C. Buchholt, T.M. Christensen, P. Roepstorff, J.D. Mikkelsen, Carbohydr. Res. 327(3), 293–307 (2000)
C. Rolin, Pectins and their Manipulation, 222–241 (2002)
B.L. Sperber, H.A. Schols, M.A.C. Stuart, W. Norde, A.G. Voragen, Food Hydrocolloids 23(3), 765–772 (2009)
S. Warnakulasuriya, P.K. Pillai, A.K. Stone, M.T. Nickerson, Food Chemistry 264, 180–188 (2018)
B. Zeeb, L. Mi-Yeon, M. Gibis, J. Weiss, Food Hydrocolloids 74, 53–61 (2018)
M. Buchweitz, M. Speth, D. Kammerer, R. Carle, Food Chemistry 139(1–4), 1168–1178 (2013)
A.T. Nasseri, J.-F. Thibault, M.-C. Ralet, Tree Sci. Biotechnol 2, 60–70 (2008)
C.M. Renard, M.-J. Crépeau, J.-F. Thibault, Carbohydr. Res. 275(1), 155–165 (1995)
N. Funasaki, I. Uratsuji, T. Okuno, S. Hirota, S. Neya, Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 54(8), 1155–1161 (2006)
Y. Miyanaga, A. Tanigake, T. Nakamura, et al., International Journal of Pharmaceutics 248(1–2), 207–218 (2002)
K. Kurihara, Y. Katsuragi, I. Matsuoka, M. Kashiwayanagi, T. Kumazawa, T. Shoji, Physiology & Behavior 56(6), 1125–1132 (1994)
T. Kumazawa, M. Kashiwayanagi, K. Kurihara, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research 888(1), 62–69 (1986)
E. Guichard, S. Issanchou, A. Descourvieres, P. Etievant, J. Food Sci. 56(6), 1621–1627 (1991)
J.P. Ley, Chemosens. Percept. 1(1), 58–77 (2008)
Acknowledgements
We thank Döhler GmbH (Darmstadt, Germany) and Herbstreith & Fox KG (Neuenbürg, Germany) for generously providing us with biopolymer samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yavuz-Düzgün, M., Zeeb, B., Dreher, J. et al. The Impact of Esterification Degree and Source of Pectins on Complex Coacervation as a Tool to Mask the Bitterness of Potato Protein Isolates. Food Biophysics 15, 376–385 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-020-09631-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-020-09631-1