Abstract
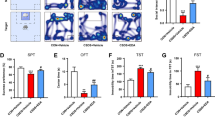
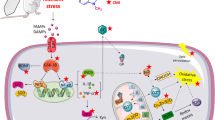
Depression is a major health problem in which oxidative stress and inflammation are inextricably connected in its pathophysiology. Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is an important anti-oxidant compound with anti-inflammatory and neuro-protective properties. This study was designed to investigate the hypothesis that CoQ10 by its anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory potentials can alleviate depressive- like behavior by restoring the balance of the tryptophan catabolites kynurenine/serotonin toward the serotonin pathway by down-regulation of hippocampal indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO-1). Depressive-like behavior was induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) protocol including food or water deprivation, cage tilting, reversed light cycle etc. Male Wistar rats were randomly divided into five groups; Control, CUMS, CUMS and CoQ10 (50,100 and 200 mg/kg/day i.p. respectively) groups. CoQ10 effects on different behavioral and biochemical tests were analyzed. CoQ10 showed significant antidepressant efficacy, as evidenced by significantly decreased stress induced changes to forced swimming challenge and open field test, as well as attenuating raised corticosterone level and adrenal glands weight. The anti-oxidant effect of CoQ10 was exhibited by its ability to significantly reduce hippocampal elevated malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal levels and elevate the reduced glutathione and catalase levels. CoQ10 significantly reduced different pro-inflammatory cytokines levels including interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-2, IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α. It suppressed hippocampal IDO-1 and subsequent production of kynurenine and enhanced the hippocampal contents of tryptophan and serotonin. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed that CoQ10 was able to attenuate the elevated microglial CD68 and elevate the astrocyte glial fibrillary acidic protein compared to CUMS group. CoQ10 exhibited antidepressant-like effects on rats exposed to CUMS. This could be attributed to its ability to reduce IDO-1 leading to shift the balance of the Kynurenine/ serotonin toward the serotonin pathway.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdollahzad H, Aghdashi MA, Jafarabadi MA, Alipour B (2015) Effects of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on inflammatory cytokines (TNF-a, IL-6) and oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Med Res 46(7):527–533. doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2015.08.006
Aboul-Fotouh S (2013a) Coenzyme Q10 displays antidepressant- like activity with reduction of hippocampal oxidative/nitrosative DNA damage in chronically stressed rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 104:105–112
Aboul-Fotouh S (2013b) Chronic treatment with coenzyme Q10 reverses restraint stress-induced anhedonia and enhances brain mitochondrial respiratory chain and creatine kinase activities in rats. Behav Pharmacol 24:552–560
Alcocer-Gómez E, Sánchez-Alcázar JA, Cordero MD (2014) Coenzyme q10 regulates serotonin levels and depressive symptoms in fibromyalgia patients: results of a small clinical trial. J Clin Psycho Pharmacol 34(2):277–278
Ambade A, Mandrekar P (2012) Oxidative stress and inflammation: essential partners in alcoholic liver disease. Int J Hepatol 2102 Article ID 853175, 9 pages
Anderson G, Maes M (2014) Oxidative/nitrosative stress and immuno-inflammatory pathways in depression: treatment implications. Curr Pharm Des 20:4126–4161
Beal MF (2002) Coenzyme Q10 as a possible treatment for neurodegenerative diseases. Free Radic Res 36:455–460
Bellac CL, Coimbra RS, Christen S, Leib SL (2006) Pneumococcal meningitis causes accumulation of neurotoxic kynurenine metabolites in brain regions prone to injury. Neurobiol Dis 24:395–402
Bowley MP, Drevets WC, Ngur D, Price JL (2002) Low glial numbers in the Amygdala in major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiatr 52:404–412
Britt SG, Chiu VW, Redpath GT et al (1992) Elimination of ascorbic acid-induced membrane lipid peroxidation and serotonin receptor loss by Trolox-C, a water soluble analogue of vitamin E. J Recept Res 12(2):181–200
Brydon L, Harrison NA, Walker C, Steptoe A, Critchley HD (2008) Peripheral inflammation is associated with altered substantia nigra activity and psychomotor slowing in humans. Biol Psychiatr (63):1022–9
Caspi A, Sugden K, Moffitt TE, Taylor A, Craig IW, Harrington H, McClay J, Mill J, Martin J, Braithwaite A, Poulton R (2003) Influence of life stress on depression: moderation by a polymorphismin the 5-HTT gene. Science 301:386–389
Corona AW, Fenn AM, Godbout JP (2012) Cognitive and behavioral consequences of impaired immunoregulation in aging. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 7(1):7–23. doi:10.1007/s11481-011-9313-4
Corona AW, Norden DM, Skendelas JP, Huang Y, O’Connor JC, Lawson M, Dantzer M, Kelley K, Godbout JP (2013) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibition attenuates lipopolysaccharide induced persistent microglial activation and depressive-like complications in fractalkine receptor (CX3CR1)-deficient mice. Brain Behav Immun 31:134–142. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2012.08.008
Czéh B, Simon M, Schmelting B, Hiemke C, Fuchs E (2006) Astroglial plasticity in the hippocampus is affected by chronic psychosocial stress and concomitant fluoxetine treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 31(8):1616–1626
Dahl J, Ormstad H, Aass HC, Malt UF, Bendz LT, Sandvik L, Brundin L, Reassen OA (2014) The plasma levels of various cytokines are increased during ongoing depression and are reduced to normal levels after recovery. Psycho Neur Endocrinol 45:77–86
Dantzer R, O’Connor JC, Freund GG, Johnson RW, Kelley KW (2008) From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 9(1):46–56. doi:10.1038/nrn2297
Dowlati Y, Herrmann N, Swardfager W, Liu H, Sham L, Reim EK, Lanctot KL (2010) A meta-analysis of cytokines in major depression. Biol Psychiatry 67:446–457
EEC Directive of (1986) COUNCIL DIRECTIVE of 24 November 1986 on the approximation of laws, regulations and administrative provisions of the Member States regarding the protection of animals used for experimental and other scientific purposes (86/609/EEC)
Forester BP, Zuo CS, Ravichandran C, Harper DG, Du F, Kim S, Cohen BM, Renshaw PF (2012) Coenzyme Q10 effects on creatine kinase activity and mood in geriatric bipolar depression. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 25(1):43–50
Hiles SA, Baker AL, de Malmanche T, Attia J (2012) A meta-analysis of differences in IL-6 and IL-10 between people with and without depression: exploring the causes of heterogeneity. Brain Behav Immun (26):1180–8
Hissin PJ, Hilf R (1973) A fluorometric method for the determination of oxidized and reduced glutathione in tissue. Anal Biochem 74:214–226. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(76)90326-2)
Jindal A, Mahesh R, Bhatt S (2013) Etazolate, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor reverses chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression-like behavior and brain oxidative damage. Pharmacol Biochem Behav (105C):63–70
Kim H, Chen L, Lim G, Sung B, Wang S, McCabe MF, Rusanescu G, Yang L, Tian Y, Mao J (2012) Brain indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase contributes to the comorbidity of pain and depression. J Clin Invest 122(8):2940–2954. doi:10.1172/JCI61884
Leonard B, Maes M (2012) Mechanistic explanations how cell-mediated immune activation, inflammation and oxidative and nitrosative stress pathways and their sequels and concomitants play a role in the pathophysiology of unipolar depression. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36(2):764–785
Lesser GL, Case D, Stark N, Williford S, Giguere J, Garino LA, Naughton MJ, Vitolins MZ, Lively MO, Shaw EG (2013) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of oral coenzyme Q10 to relieve self-reported treatment-related fatigue in newly diagnosed patients with breast cancer. J Support Oncol 11(1):31–42
Li LF, Yang J, Ma SP, Qu R (2013) Magnolol treatment reversed the glial pathology in an unpredictable chronic mild stress-induced rat model of depression. Eur J Pharmacol 711:42–49
Liu Y, Ho RC, Mak A (2012) Interleukin(IL)-6, tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF- alpha) and soluble interleukin-2 receptors (sIL-2R) are elevated in patients with Major depressive disorder: a meta-analysis and meta-regression. J Affect Disord 139:230–239
Liu Y, Jia G, Gou L, Sun L, Fu X, Lan N, Li S, Yin X (2013) Antidepressant-like effects of tea polyphenols on mouse model of chronic unpredictable mild stress. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 104:27–32
Liu B, Xu C, Wu X, Liu F, Du Y, Sun J, Tao J, Dong J (2015) Icariin exerts an antidepressant effect in an unpredictable chronic mild stress model of depression in rats and is associated with the regulation of hippocampal neuro inflammation. Neuroscience (294):193–205
Ma M, Ren Q, Zhang JC, Hashimoto K (2014) Effects of brilliant blue G on serum tumor necrosis factor-a levels and depression-like behavior in mice after lipopolysaccharide administration. Clin Psycho Pharmacol Neurosci (12):31–6
Maes M, Mihaylova I, Kubera M, Uytterhoeven M, Vrydags N, Bosmans E (2009) Lower plasma Coenzyme Q10 in depression: a marker for treatment resistance and chronic fatigue in depression and a risk factor to cardiovascular disorder in that illness. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 30(4):462–469
Maes M, Galecki P, Chang YS, Berk M (2011) A review on the oxidative and nitrosative stress (O&NS) pathways in major depression and their possible contribution to the (neuro)degenerative processes in that illness. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35(3):676–692
Mefford IN (1981) Application of high performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection to neurochemical analysis: measurement of catecholamines, serotonin and metabolites in rat brain. J Neurosci Methods 3:207–224
Miller AH (2008) Mechanisms of cytokine-induced behavioral changes: psychoneuroimmunology at the translational interface. Brain Behav Immun (23):149–1458
Miller AH (2009) Norman cousins lecture. Mechanisms of cytokine-induced behavioral changes: psychoneuroimmunology at the translational interface. Brain Behav Immun (23):149–158
Mohamed B, Aboul-Fotouh S, Ibrahim E, Shehata H, Mansour A, Yassin N, El-Eraky W, Abdel-Tawab AM (2013) Effects of pentoxifylline, 7-nitroindazole, and imipramine on tumor necrosis factor-α and indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase enzyme activity in the hippocampus and frontal cortex of chronic mild-stress-exposed rats. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 9:697–708
Moretti M, Colla A, de Oliveira Balen G, Dos Santos DB, Budni J, De Freitas AE, Farina M, Severo Rodrigues AL (2012) Ascorbic acid treatment, similarly to fluoxetine, reverses depressive-like behavior and brain oxidative damage induced by chronic unpredictable stress. J Psychiatr Res 46(3):331–340
Morris G, Anderson G, Berk M, Maes M (2013) Coenzyme Q10 depletion in medical and neuropsychiatric disorders: potential repercussions and therapeutic implications. Mol Neurobiol 48(3):883–903
Muller MB, Lucassen PJ, Yassouridis A, Hoogendijk WJ, Holsboer F, Swaab DF (2001) Neither major depression nor glucocorticoid treatment affects the cellular integrity of the human hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci 14:1603–1612
Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2010) Animal models of neuropsychiatric disorders. Nat Neurosci 13:1161–1169
Oxenkrug GF (2007) Genetic and hormonal regulation of tryptophan kynurenine metabolism: implications for vascular cognitive impairment, major depressive disorder and aging. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1122:35–49
Oxenkrug GF (2010) Metabolic syndrome, age-associated neuroendocrine disorders, and dysregulation of tryptophan-kynurenine metabolism. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1199:1–14
Porsolt RD, Bertin A, Jalfre M (1977) Behavioral despair in mice: a primary screening test for antidepressants. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 229:327–336
Raison CL, Capuron L, Miller AH (2006) Cytokines sing the blues: inflammation and the pathogenesis of depression. Trends Immunol (27):24–31
Rezin GT, Cardoso MR, Gonc, Alves CL, Scaini G, Fraga DB, Riegel RE (2008) Inhibition of mitochondrial respiratory chain in brain of rats subjected to an experimental model of depression. Neuro Chem Int (53):395–400
Scapagnini G, Davinelli S, Drago F, De Lorenzo A, Oriani G (2012) Antioxidants as antidepressants, fact or fiction? CNS Drugs 26(6):477–490
Schmelzer C, Lindner I, Rimbach G, Niklowitz P, Menke T, Döring F (2008) Functions of coenzyme Q10 in inflammation and gene expression. Bio Fact 1–4(32):179–183
Schwarzer E, Arese P, Skorokhod A (2015) Review article role of the lipo-peroxidation product 4-Hydroxynonenal in the pathogenesis of severe malaria anemia and malaria immuno depression. Oxidat Med Cell Long Article ID 638416, 11 pages
Takuma K, Baba A, Matsuda T (2004) Astrocyte apoptosis: implications for neuroprotection. Prog Neurobiol 72(2):111–127
Tarry-Adkins JL, Fernandez-Twinn DS, Hargreaves IP, Neergheen V, Aiken CE, Martin-Gronert MS, McConnell JM, Ozanne SE (2016) Coenzyme Q10 prevents hepatic fibrosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress in a male rat model of poor maternal nutrition and accelerated postnatal growth. Am J Clin Nutr 103:579–588
Tõnisaar M, Mällo T, Eller M, Häidkind R, Kõiv K, Harro J (2008) Rat behaviour after chronic variable stress and partial lesioning of 5-HT-ergic neurotransmission: effects of citalopram. Prog Neuro Psycho Pharmacol Biol Psychiatr 32:164–177
Tynan RJ, Beynon SB, Hinwood M, Johnson SJ, Nilsson M, Woods JJ, Walker FR (2013) Chronic stress-induced disruption of the astrocyte network is driven by structural atrophy and not loss of astrocytes. Acta Neuropathol 126:75–91. doi:10.1007/s00401-013-1102-0
Vaváková M, Ďuračková Z, Trebatická J (2015) Review article, markers of oxidative stress and neuroprogression in depression disorder. Oxidat Med Cellul Long Volume 2015, Article ID 898393, 12 pages
Wang Y, Cui XL, Liu YF, Gao F, Wei D, Li XW, Wang HN, Tan QR, Jiang W (2011) LPS inhibits the effects of fluoxetine on depression-like behavior and hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. Progr Neur Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatr 35:1831–1835
Wang N, Yu H, Shen X, Gao Z, Yang C, Yang J, Zhang G (2015) The rapid antidepressant effect of ketamine in rats is associated with down-regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the hippocampus. Ups J Med Sci 120:241–248
Willner P (1997) Validity, reliability and utility of the chronic mild stress model of depression: a 10-year review and evaluation. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 134:319–329
Willner P (2005) Chronic mild stress (CMS) revisited: consistency and behavioural neurobiological concordance in the effects of CMS. Neuropsychobiology 52:90–110
Wohleb ES, Franklin T, Iwata M, Duman RS (2016) Integrating neuroimmune systems in the neurobiology of depression. Nat Rev Neurosci. doi:10.1038/nrn.2016.69
World Health Organization (2015) Depression. Fact sheet N°369. October Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs369/en/. Accessed 23 October 2015
Xu Y, Wang C, Klabnik J, O’Donnell JM (2014) Novel therapeutic targets in depression and anxiety: antioxidants as a candidate treatment. Curr Neuro Pharmacol 12(2):108–119
Yirmiya R, Rimmerman N, Reshef R (2015) Depression as a microglial disease. Trends Neurosci 38(10):637–658. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2015.08.001
Zhu X, Jing L, Chen C, Shao M, Fan O, Diao J, Liu YL, Lv Z, Sun X (2015) Danzhi- Xiaoyao San ameliorates depressive-like behavior by shifting toward serotonin via the down regulation of hippocampal indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. J Ethno Pharmacol 160:86–93
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to express thanks to Dr. Walaa Baher, lecturer of histology, Ain Shams University for her help in the immunohistochemistry analysis part of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures were done following the European community guidelines for care and use of experimental animals (EEC Directive of 1986).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abuelezz, S.A., Hendawy, N. & Magdy, Y. Targeting Oxidative Stress, Cytokines and Serotonin Interactions Via Indoleamine 2, 3 Dioxygenase by Coenzyme Q10: Role in Suppressing Depressive Like Behavior in Rats. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 12, 277–291 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-016-9712-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-016-9712-7