Abstract
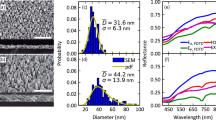
We report on the investigation of the localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) in periodical Au nanostructures. The arrays of Au nanoclusters and dimers were fabricated on Si and Si/SiO2 surfaces by electron beam lithography. Diameters and periods of nanoclusters with disk shape vary in the range of 30–150 and 130–200 nm, respectively. Because of the opaque nature of the substrates, optical reflection spectroscopy was chosen to probe the plasmonic properties of the metal nanostructures. From a comparison of experimental reflection spectra with those numerically simulated by the Finite Difference Time Domain (FDTD) method, we determined the model structural parameters of the plasmonic nanostructures. These parameters were further used for the calculation of absorptance spectra of the plasmonic structures for which absorptance in the substrate was subtracted. LSPR positions were determined from the maxima of the absorptance spectra.
This study reveals a strong dependence of the LSPR position on nanocluster size, distance between nanoclusters, as well as on the SiO2 layer thickness in the nanometer range. In the case of dimer arrays, the plasmon anisotropy in the dimers leads to a splitting of the LSPR plasmon into two modes with orthogonal polarizations.
The absorptance spectra reveal a transverse LSPR mode corresponding to the excitation of plasmons in nanoclusters induced by scattered fields from the neighboring ones.
This research provides a pathway for a fast and cost-effective determination of the LSPR position from optical reflection spectra. A broad field of potential applications of metal structures with well-controlled plasmonic properties includes surface-enhanced infrared absorption, photoluminescence, and Raman scattering as well as signal transmission in silicon photonics.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Monticone F, Alù A (2017) Metamaterial, plasmonic and nanophotonic devices. Rep Prog Phys 80:036401. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6633/aa518f
Guler U, Kildishev AV, Boltasseva A, Shalaev VM (2015) Plasmonics on the slope of enlightenment: the role of transition metal nitrides. Faraday Discuss 178:71–86. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4FD00208C
Mayer KM, Hafner JH, Antigen AÀ (2011) Localized surface plasmon resonance sensors. Chem Rev 111:3828–3857. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr100313v
Kabashin AV, Evans P, Pastkovsky S, Hendren W, Wurtz GA, Atkinson R, Pollard R, Podolskiy VA, Zayats AV (2009) Plasmonic nanorod metamaterials for biosensing. Nat Mater 8:867–871. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2546
Anker JN, Hall WP, Lyandres O, Shah NC, Zhao J, van Duyne RP (2008) Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat Mater 7:442–453. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2162
Stockman MI (2011) Nanoplasmonks: the physics behind the applications. Phys Today 64:39–44. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3554315
Gramotnev DK, Bozhevolnyi SI (2010) Plasmonics beyond the diffraction limit. Nat Photonics 4:83–91. https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2009.282
Ozbay E (2006) Plasmonics: merging photonics and electronics at nanoscale dimensions. Science 311:189–193. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1114849
Huang HJ, Hsiao C-N, Shiao M-H et al (2016) Rapid fabrication of three-dimensional gold dendritic nanoforests for visible light-enhanced methanol oxidation. Electrochim Acta 192:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.01.043
Chau YFC, Wang CK, Shen L, Lim CM, Chiang HP, Chao CTC, Huang HJ, Lin CT, Kumara NTRN, Voo NY (2017) Simultaneous realization of high sensing sensitivity and tunability in plasmonic nanostructures arrays. Sci Rep 7:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-17024-7
Campbell SA (2001) The science and engineering of microelectronic fabrication. Oxford University Press, New York
Dionne JA, Sweatlock LA, Sheldon MT, Alivisatos AP, Atwater HA (2010) Silicon-based plasmonics for on-chip photonics. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron 16:295–306. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTQE.2009.2034983
Li E-P, Chu H-S (2014) Plasmonic Nanoelectronics and sensing. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Bohren CF, Huffman DR (1983) Absorption and scattering of light by small particles. Wiley, New York
Langhammer C, Kasemo B, Zorić I (2007) Absorption and scattering of light by Pt, Pd, Ag, and Au nanodisks: absolute cross sections and branching ratios. J Chem Phys 126:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2734550
Zorić I, Kasemo B, Langhammer C, Zaaach M (2011) Gold, platinum, and aluminum nanodisk plasmons : material damping mechanisms. ACS Nano 5:2535–2546. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn102166t
Qin F, Cui X, Ruan Q, Lai Y, Wang J, Ma H, Lin HQ (2016) Role of shape in substrate-induced plasmonic shift and mode uncovering on gold nanocrystals. Nanoscale 8:17645–17657. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NR06387J
Leong K, Chen Y, Masiello DJ, Zin MT, Hnilova M, Ma H, Tamerler C, Sarikaya M, Ginger DS, Jen AKY (2010) Cooperative near-field surface plasmon enhanced quantum dot nanoarrays. Adv Funct Mater 20:2675–2682. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201000424
Sheremet E, Milekhin AG, Rodriguez RD, Weiss T, Nesterov M, Rodyakina EE, Gordan OD, Sveshnikova LL, Duda TA, Gridchin VA, Dzhagan VM, Hietschold M, Zahn DRT (2014) Surface- and tip-enhanced resonant Raman scattering from CdSe nanocrystals. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:21198–21203. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cp05087h
Gillibert R, Sarkar M, Bryche JF, Yasukuni R, Moreau J, Besbes M, Barbillon G, Bartenlian B, Canva M, Chapelle ML (2016) Directional surface enhanced Raman scattering on gold nano-gratings. Nanotechnology 27:115202. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/27/11/115202
Milekhin AG, Yeryukov NA, Sveshnikova LL, Duda TA, Rodyakina EE, Sheremet ES, Ludemann M, Gordan OD, Latyshev AV, Zahn DRT (2013) Surface enhanced Raman scattering by organic and inorganic semiconductors formed on laterally ordered arrays of Au nanoclusters. Thin Solid Films 543:35–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2013.03.070
Ovchinnikov V (2015) Reflection from irregular array of silver nanoparticles on multilayer substrate. Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Quantum, Nano/Bio, and Micro Technologies (ICQNM 2015), (ISBN: 978-1-61208-303-2), pp. 16–21
Gwyddion – free SPM (AFM, SNOM/NSOM, STM, MFM, …) data analysis software. http://gwyddion.net/
FDTD Solutions, Version 8.20.1731 (2018), Lumerical Inc. (Canada). https://www.lumerical.com/products/fdtd-solutions/
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6:4370–4379. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.6.4370
Johnson P, Christy R (1974) Optical constants of transition metals: Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, and Pd. Phys Rev B 9:5056–5070. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.9.5056
Aspnes DE, Studna AA (1983) Dielectric functions and optical parameters of Si, Ge, GaP, GaAs, GaSb, InP, InAs, and InSb from 1.5 to 6.0 eV. Phys Rev B 27:985–1009. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.27.985
Malitson IH (1965) Interspecimen comparison of the refractive index of fused silica. J Opt Soc Am 55:1205. https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSA.55.001205
Hu E-T, Liu X-X, Cai Q-Y, Yao Y, Zang KY, Yu KH, Wei W, Xu XX, Zheng YX, Wang SY, Zhang RJ, Chen LY (2017) Tunable optical properties of co-sputtered Ti-SiO2 nanocomposite thin films. Opt Mater Express 7:2387. https://doi.org/10.1364/OME.7.002387
Palmer JM (1995) Chapter 25 the measurement of transmission , absorption , emission , and reflection. In: Bass M (ed) Handbook of optics volume II devices, measurements , and properties. McGRAW-HILL, INC., p 25.1–25.25
Kreibig U, Vollmer M (1995) Optical properties of metal clusters. Springer, Berlin
Maier SA, Kik PG, Atwater HA, Meltzer S, Harel E, Koel BE, Requicha AAG (2003) Local detection of electromagnetic energy transport below the diffraction limit in metal nanoparticle plasmon waveguides. Nat Mater 2:229–232. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat852
Maier SA, Kik PG, Atwater HA (2002) Observation of coupled plasmon-polariton modes in Au nanoparticle chain waveguides of different lengths: estimation of waveguide loss. Appl Phys Lett 81:1714–1716. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1503870
Milekhin AG, Yeryukov NA, Sveshnikova LL, Duda TA, Rodyakina EE, Gridchin VA, Sheremet ES, Zahn DRT (2015) Combination of surface- and interference-enhanced Raman scattering by CuS nanocrystals on nanopatterned Au structures. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 6:749–754. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.6.77
Nicolas R, Lévêque G, Marae-Djouda J, Montay G, Madi Y, Plain J, Herro Z, Kazan M, Adam PM, Maurer T (2015) Plasmonic mode interferences and Fano resonances in metal-insulator- metal nanostructured interface. Sci Rep 5:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14419
Ruemmele JA, Hall WP, Ruvuna LK, Van Duyne RP (2013) A localized surface plasmon resonance imaging instrument for multiplexed biosensing. Anal Chem 85:4560–4566. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac400192f
Jain PK, El-Sayed MA (2010) Plasmonic coupling in noble metal nanostructures. Chem Phys Lett 487:153–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2010.01.062
Yang SC, Kobori H, He CL, Lin MH, Chen HY, Li C, Kanehara M, Teranishi T, Gwo S (2010) Plasmon hybridization in individual gold nanocrystal dimers: direct observation of bright and dark modes. Nano Lett 10:632–637. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl903693v
Krasnok AE, Maksymov IS, Denisyuk AI, Belov PA, Miroshnichenko AE, Simovskii CR, Kivshar YS (2013) Optical nanoantennas. Uspekhi Fiz Nauk 183:561–589. https://doi.org/10.3367/UFNr.0183.201306a.0561
Wei H, Xu H (2013) Hot spots in different metal nanostructures for plasmon-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nanoscale 5:10794. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nr02924g
Heeg S, Fernandez-Garcia R, Oikonomou A, Schedin F, Narula R, Maier SA, Vijayaraghavan A, Reich S (2013) Polarized plasmonic enhancement by Au nanostructures probed through raman scattering of suspended graphene. Nano Lett 13:301–308. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl3041542
Ahmed A, Gordon R (2012) Single molecule directivity enhanced Raman scattering using nanoantennas. Nano Lett 12:2625–2630. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl301029e
Wei XZ, Mulvaney P (2014) Optical properties of strongly coupled plasmonic nanoparticle clusters. In: Richardson NV, Holloway S (eds) Handbook of surface science. Volume 4. Modern Plasmonics Elsevier BV, pp 75–108
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Alexander Oreshonkov and Alexander Shakhramanyan for assistance with numerical simulations.
Funding
This work has been supported and funded by Volkswagen Foundation, MERGE project (TU Chemnitz), Russian Foundation for Basic Research (projects 18-02-00615_a, 18-29-20066_mk, and 19-52-12041 NNIO_a) and the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation. S.L.V. acknowledges RSF (grant no. 17-13-01412) for support of FT-IR measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anikin, K., Rodyakina, E., Veber, S. et al. Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance in Gold Nanocluster Arrays on Opaque Substrates. Plasmonics 14, 1527–1537 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-019-00949-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-019-00949-2