Abstract
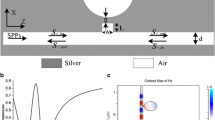
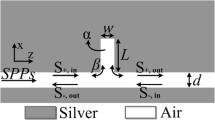
We have numerically investigated an analog of electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) in a metal-dielectric-metal (MDM) waveguide bend. The geometry consists of two asymmetrical stubs extending parallel to an arm of a straight MDM waveguide bend. Finite-difference time-domain simulations show that a transparent window is located at 1550 nm, which is the phenomenon of plasmonic-induced transparency (PIT). Signal wavelength is assumed to be 820 nm. The velocity of the plasmonic mode can be largely slowed down while propagating along the MDM bends. Multiple-peak plasmon-induced transparency can be realized by cascading multiple cavities with different lengths and suitable cavity-cavity separations. Large group index up to 73 can be obtained at the PIT window. Our proposed configuration may thus be applied to storing and stopping light in plasmonic waveguide bends. In addition, the relationship between the transmission characteristics and the geometric parameters including the radius of the nano-ring, the coupling distance, and the deviation length between the stub and the nano-ring is studied in a step further. The velocity of the plasmonic mode can be largely slowed down while propagating along the MDM bends. For indirect coupling, formation of transparency window is determined by resonance detuning, but, evolution of transparency is mainly attributed to the change of the coupling distance. Theoretical results may provide a guideline for control of light in highly integrated optical circuits. The characteristics of our plasmonic system indicate a significant potential application in integrated optical circuits such as optical storage, ultrafast plasmonic switch, highly performance filter, and slow light devices.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atwater HA (2007) The promise of plasmonics. Sci Am Mag 296(4):56–63
Anker JN, Hall WP, Lyandres O, Shah NC, Zhao J, Duyne RPV (2008) Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat Mater 7:442–453
Kaatuzian H, Photonics, 3rd printing (AKU Press, 2017), Vol 2, in Persian
Min Q, Chen C, Berini P, Gordon R (2010) Long range surface plasmons on asymmetric suspended thin film structures for biosensing applications. Opt Express 18:19009–19019
Jenkins FA, White HE (1981) “Fundamentals of Optics,” 4th Edition, McGraw-Hill
Fedyanin DY, Krasavin AV, Arsenin AV, Zayats AV (2012) Surface plasmon polariton amplification upon electrical injection in highly integrated plasmonic circuits. Nano Lett 12:2459–2463
Maier SA (2007) Plasmonics: fundamentals and applications. Springer, Berlin
Liu N, Langguth L, Weiss T, Kästel J, Fleischhauer M, Pfau T, Giessen H (2009) Plasmonic analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency at the Drude damping limit. Nat Mater 8(9):758–762
Han Z (2010) Ultracompact plasmonic racetrack resonators in metal-insulator-metal waveguides. Photonics Nanostruct Fundam Appl 8(3):172–176
Zhang Y, Darmawan S, Tobing LYM, Mei T, Zhang DH (2011) Coupled resonator-induced transparency in ring-bus-ring Mach-Zehnder interferometer. J Opt Soc Am B 28(1):28–36
Zhu S, Lo GQ, Kwong DL (2012) Components for silicon plasmonic nanocircuits based on horizontal Cu-SiO2-Si-SiO2-Cu nanoplasmonic waveguides. Opt Exp 20(6):5867–5881
Zhanghua H, Bozhevolnyi SI (2011) Plasmon-induced transparency with detuned ultracompact Fabry-Perot resonators in integrated plasmonic devices. Opt Express 19(4):3251
Xu Y, Zhang J, Song G (2013) Slow surface plasmons in plasmonic grating wave guide. IEEE Photon Technol Let 25(5):410–413
Yang X, Hu X, Chai Z, Lu C, Yang H, Gong Q (2014) Tunable ultracompact chip-integrated multichannel filter based on plasmon-induced transparencies. Appl Phys Lett 104(22):221114–1–221114-5
Hassani Keleshtery M, Kaatuzian H, Mir A (2016) Analysis and investigation of slow light based on plasmonic induced transparency in metal-dielectric-metal ring resonator in a waveguide system with different geometrical designs. Opt Photon J 6(8B):177–184
Wang Y, Wang J, Liu C, Luo Q, Zhang W, Gao S (2013) Plasmonic-induced transparency in metal–dielectric–metal waveguide bends. Appl Phys Express 6:082201
Zhou QZ, He P, Xu J, Zhuang X, Li Y, Pan A (2014) Gradient index plasmonic ring resonator with high extinction ratio. Opt Commun 312:280–283
Dupuis N, Lee BG, Rylyakov AV, Kuchta DM, Baks CW, Orcutt JS, Gill DM, Green WMJ, Schow CL (2015) Design and fabrication of low-insertion-loss and low-crosstalk broadband 2 × 2 Mach–Zehnder silicon photonic switches. J Lightw Technol 33(17):3597–3606
Abdul-Wahab S, Ahmed A, Marikar F (2011) The environmental impact of gold mines: pollution by heavy metals. Cent Eur J Eng 2(2):304–313
Kelly PE (2014) “Properties of materials,” CRC Press, Taylor and Fransis is an imprint of Group, International Standard Book Number: 13:978–1–4822-0624-1
Smith WF, Hashemi J “Foundation of materials science and engineering,” 4th edition. McGraw-Hill. P. 509. ISBN0–07–295358-6
Chien F-T, Chen C-W, Lee T-C, Wang C-L, Cheng C-H, Kang T-K, Chiu H-C (2013) A novel self-aligned double-channel polysilicon thin-film transistor. IEEE Trans Electron Dev 60(2):799–804
Lu Q, Zou C-L, Chen D, Zhou P, Wu G (2014) Extreme light confinement and low loss in triangle hybrid plasmonic waveguide. Opt Commun 319:141–146
Keshavarz Moazzam M, Kaatuzian H (2015) Design and investigation of N-type metal/insulator/semiconductor/metal structure two-port electro-plasmonic addressed routing switch. Appl Opt 54(20):6199–6207
Wang G, Zhang W, Gong Y, Liang J (2015) Tunable slow light based on plasmon-induced transparency in dual-stub-coupled waveguide. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 27(1)
Eftekharian A, Atikian H, Majedi AH (2013) Plasmonic superconducting nanowire single photon detector. Opt Exp 21(3):3043–3054
Nielsen MP, Ashfar A, Cadien K, Elezzabi AY (2013) Plasmonic materials for metal-insulator-semiconductor-insulator-metal nanoplasmonic waveguides on silicon-on-insulator platform. Opt Mater 36:294–298
Zhan S, Li H, Cao G, He Z, Li B, Yang H (2014) Slow light based on plasmonic-induced transparency in dual-ring resonator-coupled MDM waveguide system. J Phys D Appl Phys 47(20):205101
Han X, Wang T, Li X, Liu B, He Y, Tang J (2015) Dynamically tunable slow light based on plasmon induced transparency in disk resonators coupled MDM waveguide system. J Phys D: Appl Phys 48(10pp):235102
Mote RG, Chu H-S, Bai P, Li E-P (2012) Compact and efficient coupler to interface hybrid dielectric-loaded plasmonic waveguide with silicon photonic slab waveguide. Opt Commun 285:3709–3713
Sorger VJ, Ye Z, Oulton RF, Wang Y, Bartal G, Yin X, Zhang X (2011) Experimental demonstration of low-loss optical waveguiding at deep sub-wavelength scales. Nat Commun doi: 10.1038, ncomms 1315, pp
Hassani Keleshtery M, Kaatuzian H, Mir A, Zandi A (2017) Method proposing a slow light ring resonator with a metal-dielectric-metal waveguide system based on plasmonic induced transparency. Appl Opt 56(15):6199–6207
Hassan Kaatuzian, Ahmad Naseri Taheri (2015) Application of nano-scale plasmonic structures in design of stub filters-A step towards realization of plasmonic switches. INTECH, Book Chapter, Chapter 4, doi:https://doi.org/10.5772/59877
Taheri AN, Kaatuzian H (2014) Design and simulation of a nanoscale electro-plasmonic 1 × 2 switch based on metal-insulator-metal stub filter. Appl Opt 53(28):6546–6553
Melikyan A, Lindenmann N, Walheim S, Leufke PM, Ulrich S, Ye J, Vincze P, Hahn H, Schimmel T, Koos C, Freude W, Leuthold J (2011) Surface plasmon polariton absorption modulator. Opt Exp 19(9):8855–8869
Hu M, Wang F, Liang R, Zhou S, Xiao L (2015) Plasmonic-induced transparency based on plasmonic asymmetric dual side-coupled cavities. Elsevier Phys Lett A 379:581–584
Zhan Sh, Li H, Cao G, He Z, Li B, Yang H (2014) Slow light based on plasmon-induced transparency in dual-ring resonator-coupled MDM waveguide system. J Phys D: Appl Phys. 47 205101 (6pp)
Liu S-D, Yang Z, Liu R-P, Li X-Y (2011) Plasmonic-induced optical transparency in the near-infrared and visible range with double split nanoring cavity. Opt Express 19(16):15363
Lu Y, Rhee JY, Jang WH, Lee YP (2010) Active manipulation of plasmonic electromagnetically-induced transparency based on magnetic plasmon resonance. Opt Express 18(20):20912–20917
Olivieri A, Chen C, Hassan S, Lisicka-Skrzek E, Tait RN, Berini P (2015) Plasmonic nanostructured metal−oxide−semiconductor reflection modulators. Nano Lett 15:2304–2311
Li Z, Ma Y, Huang R, Singh R, Gu J, Tian Z, Han J, Zhang W (2011) Manipulating the plasmon-induced transparency in terahertz metamaterials. Opt Express 19(9):8912
Zhu S, Lo GQ, Kwong DL (2011) Electro-absorption modulation in horizontal metal-insulator-silicon-insulator-metal nanoplasmonic slot waveguides. Appl Phys Lett 99(1–3):151114
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express thanks to their colleagues in Photonic Research Laboratory (PRL), at Electrical Engineering Dept. of Amirkabir University of Technology (AUT) for their friendly support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keleshtery, M.H., Mir, A. & Kaatuzian, H. Investigating the Characteristics of a Double Circular Ring Resonators Slow Light Device Based on the Plasmonics-Induced Transparency Coupled with Metal-Dielectric-Metal Waveguide System. Plasmonics 13, 1523–1534 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0660-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0660-8