Abstract
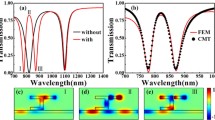
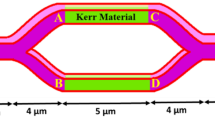
In this study, the signal processing in three-port and four-port plasmonic coupler devices by coherently controlling the phases and amplitudes of launched surface plasmons is investigated by finite-difference time-domain method (FDTD) simulation. This device is composed of two metal-dielectric-metal waveguides with a strip cavity imbedded in the shared metal layer. Interference between the plasmonic signals of two input ports is caused by the tunneling effect of surface plasmons in the strip cavity. The functions of signal modulation, recovery, filtering, and plasmon-induced transparency (PIT) of the proposed devices are proposed and demonstrated. The all-optical logic gates based on the proposed devices are also designed and verified.





Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Bruck R, Muskens OL (2013) Plasmonic nanoantennas as integrated coherent perfect absorbers on SOI waveguides for modulators and all-optical switches. Opt Express 21(23):27652–27661. doi:10.1364/OE.21.027652
Fang X, Tseng ML, Ou J-Y, MacDonald KF, Tsai DP, Zheludev NI (2014) Ultrafast all-optical switching via coherent modulation of metamaterial absorption. Appl Phys Lett 104:141102. doi:10.1063/1.4870635
Zhang J, MacDonald KF, Zheludev NI (2012) Controlling light-with-light without nonlinearity. Light: Sci & Appl 1:e18. doi:10.1038/lsa.2012.18
Fang X, MacDonald KF, Zheludev NI (2015) Controlling light with light using coherent metadevices: all-optical transistor, summator and invertor. Light Sci Appl 4:e292. doi:10.1038/lsa.2015.65
Pannipitiya A, Rukhlenko ID, Premaratne M, Hattori HT, Agrawal GP (2010) Improved transmission model for metal-dielectric-metal plasmonic waveguides with stub structure. Opt Express 18(6):6191–6204. doi:10.1364/OE.18.006191
Veronis G, Yu Z, Kocabas SE, Miller DAB, Brongersma ML, Fan S (2009) Metal-dielectric-metal plasmonic waveguide devices for manipulating light at the nanoscale. Chin Opt Lett 7(4):302–308. doi:10.3788/COL20090704.0302
Wang B, Wang GP (2005) Plasmon Bragg reflectors and nanocavities on flat metallic surfaces. Appl Phys Lett 87:013107. doi:10.1063/1/1954880
Fang M, Shi F, Chen Y (2016) Unidirectional all-optical absorption switch based on optical Tamm state in nonlinear plasmonic waveguide. Plasmonics 11:197–203. doi:10.1007/s11468-015-0042-z
Kang Z, Wang GP (2008) Coupled metal gap waveguides as plasmonic wavelength sorters. Opt Express 16(11):7680–7685. doi:10.1364/OE.16.007680
Mahigir A, Dastmalchi P, Shin W, Fan S, Veronis G (2015) Plasmonic coaxial waveguide-cavity devices. Opt Express 23(16):20549–20562. doi:10.1364/OE.23.020549
Chen Z, Song X, Duan G, Wang L, Yu L (2015) Multiple Fano resonances control in MIM side-coupled cavities systems. IEEE Photo J 7(3):2701009. doi:10.1109/JPHOT.2015.2433012
Mei X, Huang X, Tao J, Zhu J, Zhu Y, Jin X (2010) A wavelength demultiplexing structure based on plasmonic MDM side-coupled cavities. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 27(12):2707–2713. doi:10.1364/JOSAB.27.002707
Tao J, Huang XG, Zhu JH (2010) A wavelength demultiplexing structure based on metal-dielectric-metal plasmonic nano-capillary resonators. Opt Express 18(11):11111–11116. doi:10.1364/OE.18.011111
He Z, Li H, Zhan S, Li B, Chen Z, Xu H (2015) Tunable multi-switching in plasmonic waveguide with Kerr nonlinear resonator. Sci Rep 5:15837. doi:10.1038/srep15837
Shiu RC, Lan YC, Guo GY (2014) Optical multiple bistability in metal-insulator-metal plasmonic waveguides side-coupled with twin racetrack resonators. J Opt Soc Am B 31(11):2581–2586. doi:10.1364/JOSAB.31.002581
Lee PH, Lan YC (2010) Plasmonic waveguide filters based on tunneling and cavity effects. Plasmonics 5:417–422. doi:10.1007/sll468-010-9159-2
Melikyan A, Alloatt L, Muslija A, Hillerkuss D, Schindler PC, Li J, Palmer R, Korn D, Muehlbrandt S, Thourhout DV, Chen B, Dinu R, Sommer M, Koos C, Kohl M, Freude W, Leuthold J (2014) High-speed plasmonic phase modulators. Nature Photon 8:229–233. doi:10.1038/nphoton.2014.9
Yu F, Yao D, Knoll W (2004) Oligonucleotide hybridization studied by a surface plasmon diffraction sensor (SPDS). Nucleic Acids Res 32(9):e75. doi:10.1093/nar/gnh067
Wu D, Fang N, Sun C, Zhang X (2003) Terahertz plasmonic high pass filter. Appl Phys Lett 83:201–203. doi:10.1063/1.1591083
Kekatpure RD, Barnard ES, Cai W, Brongersma ML (2010) Phase-coupled plasmon-induced transparency. PRL 104:243902. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett. 104.243902
Liu N, Langguth L, Weiss T, Kastel J, Fleischhauer M, Pfau T, Giessen H (2009) Plasmonic analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency at the Drude damping limit. Nature Mater 8:758–762. doi:10.103 8/nmat2495
Yaramadi M, Moravvej-Farshi MK, Yousefi L (2015) Subwavelength grapheme-based plasmonic THz switches and logic gates. IEEE Trans THz Sci Technol 5(5):725–731
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6(12):4370–4379
Nieter C, Cary JR (2004) VORPAL: a versatile plasma simulation code. J Comput Phys 196:448–473
Acknowledgement
The authors acknowledge financial support from the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (Grant No. 104-2112-M-006-005-MY3). They are also grateful to the National Center for High-Performance Computing, Taiwan, for its support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, HH., Cheng, B.H. & Lan, YC. Coherent-Controlled All-Optical Devices Based on Plasmonic Resonant Tunneling Waveguides. Plasmonics 12, 2005–2011 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0474-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0474-0