Abstract
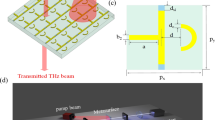
In this paper, we demonstrated a low-loss and high-transmission analogy of electromagnetically induced transparency based on all-dieletric metasurface. The metamaterial unit cell structure is composed of two mutually perpendicular silicon nanoscale bars. Under the joint effects of the neighboring meta-atoms’ coherent interaction and significant low absorption loss, the transmission and the Q-factor can reach up to 93 % and 139, respectively. Moreover, we use the coupled harmonic oscillator model to analyze the near field interaction between the two elements in the electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) metamaterial unit cell qualitatively and the effects of parameters on EIT. The figure-of-merit of 42 and the group delay of 0.65 ps are obtained. These characteristics make the metamaterial structure with potential to apply for ultrafast switches, sensor, and slow-light devices.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eberly J (1998) Area theorem rederived. Opt Express 2(5):173–176. doi:10.1364/OE.2.000173
Harris SE (1997) Electromagnetically induced transparency. Phys Today 50(7):36. doi:10.1063/1.881806
Vafapour Z, Zakery A (2015) New approach of plasmonically induced reflectance in a planar metamaterial for plasmonic sensing applications. Plasmonics 11(2):609–618. doi:10.1007/s11468-015-0077-1
Vafapour Z, Zakery A (2015) New regime of plasmonically induced transparency. Plasmonics 10(6):1809–1815. doi:10.1007/s11468-015-9992-4
Gu J, Singh R, Liu X, Zhang X, Ma Y, Zhang S, Maier SA, Tian Z, Azad AK, Chen HT, Taylor AJ, Han J, Zhang W (2012) Active control of electromagnetically induced transparency analogue in terahertz metamaterials. Nat Commun 3:1151. doi:10.1038/ncomms2153
Papasimakis N, Fu YH, Fedotov VA, Prosvirnin SL, Tsai DP, Zheludev NI (2009) Metamaterial with polarization and direction insensitive resonant transmission response mimicking electromagnetically induced transparency. Appl Phys Lett 94(21):211902. doi:10.1063/1.3138868
Li H-m, Liu S-b, Liu S-y, Wang S-y, Zhang H-f, Bian B-r, Kong X-k (2015) Electromagnetically induced transparency with large delay-bandwidth product induced by magnetic resonance near field coupling to electric resonance. Appl Phys Lett 106:114101. doi:10.1063/1.4915313
Shao J, Li J, Li J, Wang Y-K, Dong Z-G, Chen P, Wu R-X, Zhai Y (2013) Analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency by doubly degenerate modes in a U-shaped metamaterial. Appl Phys Lett 102(3):034106. doi:10.1063/1.4789432
Tassin P, Zhang L, Zhao R, Jain A, Koschny T, Soukoulis CM (2012) Electromagnetically induced transparency and absorption in metamaterials: the radiating two-oscillator model and its experimental confirmation. Phys Rev Lett 109:187401. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.109.187401
Safavi-Naeini AH, Mayer Alegre TP, Chan J, Eichenfield M, Winger M, Lin Q, Hill JT, Chang DE, Painter O (2011) Electromagnetically induced transparency and slow light with optomechanics. Nature 472(7341):69–73. doi:10.1038/nature09933
Zhang J, Xiao S, Jeppesen C, Kristensen A, Mortensen NA (2010) Electromagnetically induced transparency in metamaterials at near-infrared frequency. Opt Express 18(16):17187–17192. doi:10.1364/OE.18.017187
Li H-m, Liu S-b, Liu S-y, Wang S-y, Ding G-w, Yang H, Yu Z-y, Zhang H-f (2015) Low-loss metamaterial electromagnetically induced transparency based on electric toroidal dipolar response. Appl Phys Lett 106(8):083511. doi:10.1063/1.4913888
Sun Y, Tong Y-w, Xue C-h, Ding Y-q, Li Y-h, Jiang H, Chen H (2013) Electromagnetic diode based on nonlinear electromagnetically induced transparency in metamaterials. Appl Phys Lett 103(9):091904. doi:10.1063/1.4819854
Zhu L, Meng FY, Fu JH, Wu Q, Hua J (2012) An approach to configure low-loss and full transmission metamaterial based on electromagnetically induced transparency. IEEE Trans Magn 48(11):4285–4288. doi:10.1109/TMAG.2012.2200661
Luk’yanchuk B, Zheludev NI, Maier SA, Halas NJ, Nordlander P, Giessen H, Chong CT (2010) The Fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials. Nat Mater 9(9):707–715
Boltasseva A, Atwater HA (2011) Materials science. Low-loss plasmonic metamaterials. Science 331(6015):290–291. doi:10.1126/science.1198258
Yang Y, Wang W, Moitra P, Kravchenko II, Briggs DP, Valentine J (2014) Dielectric meta-reflectarray for broadband linear polarization conversion and optical vortex generation. Nano Lett 14(3):1394–1399. doi:10.1021/nl4044482
Moitra P, Yang Y, Anderson Z, Kravchenko II, Briggs DP, Valentine J (2013) Realization of an all-dielectric zero-index optical metamaterial. Nat Photonics 7(10):791–795. doi:10.1038/nphoton.2013.214
Zhang S, Genov DA, Wang Y, Liu M, Zhang X (2008) Plasmon-induced transparency in metamaterials. Phys Rev Lett 101(4):047401. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.101.047401
Fan SH, Suh W, Joannopoulos JD (2003) Temporal coupled-mode theory for the Fano resonance in optical resonators. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis 20(3):569–572. doi:10.1364/josaa.20.000569
Yang Y, Kravchenko II, Briggs DP, Valentine J (2014) All-dielectric metasurface analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency. Nat Commun 5:5753. doi:10.1038/ncomms6753
Wang J, Fan C, He J, Ding P, Liang E, Xue Q (2013) Double Fano resonances due to interplay of electric and magnetic plasmon modes in planar plasmonic structure with high sensing sensitivity. Opt Express 21(2):2236–2244. doi:10.1364/OE.21.002236
Anker JN, Hall WP, Lyandres O, Shah NC, Zhao J, Van Duyne RP (2008) Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat Mater 7(6):442–453
Li BX, Li HJ, Zeng LL, Zhan SP, He ZH, Chen ZQ, Xu H (2015) High-sensitivity sensing based on plasmon-induced transparency. IEEE Photonics J 7(5):1–7. doi:10.1109/jphot.2015.2483202
Zhang S, Bao K, Halas NJ, Xu H, Nordlander P (2011) Substrate-induced Fano resonances of a plasmonic nanocube: a route to increased-sensitivity localized surface plasmon resonance sensors revealed. Nano Lett 11(4):1657–1663. doi:10.1021/nl200135r
Liu N, Weiss T, Mesch M, Langguth L, Eigenthaler U, Hirscher M, Sönnichsen C, Giessen H (2010) Planar metamaterial analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency for plasmonic sensing. Nano Lett 10(4):1103–1107. doi:10.1021/nl902621d
Lu H, Liu X, Mao D (2012) Plasmonic analog of electromagnetically induced transparency in multi-nanoresonator-coupled waveguide systems. Phys Rev A 85(5):053803
Wu J, Jin B, Wan J, Liang L, Zhang Y, Jia T, Cao C, Kang L, Xu W, Chen J, Wu P (2011) Superconducting terahertz metamaterials mimicking electromagnetically induced transparency. Appl Phys Lett 99(16):161113. doi:10.1063/1.3653242
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant Nos. 61275059, 11374107, and 61475049.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhongchao Wei and Xianping Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Z., Li, X., Zhong, N. et al. Analogue Electromagnetically Induced Transparency Based on Low-loss Metamaterial and its Application in Nanosensor and Slow-light Device. Plasmonics 12, 641–647 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0309-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0309-z