Abstract
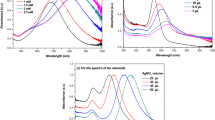
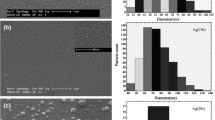
Glancing angle deposition is a powerful method for direct fabrication of nanostructures on various substrates. In this research, GLAD method has been used to fabricate Ag nanostructures with columnar morphology for refractive index sensing applications. The morphology and plasmonic properties of the nanostructures are controlled by changing deposition parameters such as glancing angle, speed of azimuthal rotation of the substrate, and the height of deposited nanostructures. The results show that increasing the deposition thickness from 200 to 500 nm leads to narrowing the plasmonic peak, which mainly relates to increment of the distance between larger nanostructures. By changing the glancing angle between 86° to 80°, the narrowest plasmonic peak corresponding to the greatest sensitivity has been obtained for the film deposited at the angle of 82°. Also, increment of the rotation speed of the samples leads to narrowing of the plasmonic peaks. By measuring the refractive index sensitivity (RIS) of the nanostructures, a best sensitivity of 154 nm/RIU has been obtained. Finally, we investigated the stability of Ag nanostructures in deionized water by introducing a new stabilizing technique in which a thin Au layer is coated on the Ag nanostructures. This technique has the merits of simultaneously protecting the Ag nanostructures against oxidation and keeping their refractive index sensitivity high enough for long time usages.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kreibig U, Vollmer M (1995) Optical Properties of Metal Clusters. Springer, Berline
Maier SA (2007) Plasmonics:fundamentals and applications. Springer, Berline
Hutter E, Fendler JH (2004) Exploitation of localized surface plasmon resonance. Adv Mater 16(19):1685–1706
Nader S and Ahmad M (2012) “Optical properties of Ag conic helical nanostructures,” Appl. Phys. Lett., vol. 100
Kelly KL, Coronado E, Zhao LL, Schatz GC (2003) The optical properties of metal nanoparticles: the influence of size, shape, and dielectric environment. J Phys Chem B 107:668–677
Ghosh SK, Pal T (2007) Interparticle coupling effect on the surface plasmon resonance of gold nanoparticles: from theory to applications. Chem Rev 107(11):4797–4862
Novo C, Funston AM, Pastoriza-Santos I, Liz-Marzán LM, Mulvaney P (2008) Influence of the medium refractive index on the optical properties of single gold triangular prisms on a substrate. J Phys Chem C 112(1):3–7
Petryayeva E, Krull UJ (2011) Localized surface plasmon resonance: nanostructures, bioassays and biosensing—a review. Anal Chim Acta 706(1):8–24
He Y, Fu J, Zhao Y (2014) Oblique angle deposition and its applications in plasmonics. Front Phys 9(1):47–59
Caoa J, Suna T, Grattana KTV (2014) Gold nanorod-based localized surface plasmon resonance biosensors: a review. Sens Actuators B 195:332–351
Aćimović SS et al (2014) LSPR chip for parallel, rapid, and sensitive detection of cancer markers in serum. Nano Lett 14(5):2636–2641
Rodríguez-Fortuño FJFJ et al (2011) Highly-sensitive chemical detection in the infrared regime using plasmonic gold nanocrosses. Appl Phys Lett 98:133118
Chen S, Svedendahl M, Käll M, Gunnarsson L, Dmitriev A (2009) Ultrahigh sensitivity made simple: nanoplasmonic label-free biosensing with an extremely low limit-of-detection for bacterial and cancer diagnostics. Nanotechnol 20(43):1–9
Bingham JM, Anker JN, Kreno LE, Van Duyne RP (2010) Gas sensing with high-resolution localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 132(49):17358–17359
Miller MM, Lazarides AA (2005) Sensitivity of metal nanoparticle surface plasmon resonance to the dielectric environment. J Phys Chem B 109(46):21556–21565
Martinsson E, Otte MA, Shahjamali MM, Sepulveda B, Aili D (2014) Substrate effect on the refractive index sensitivity of silver nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 118(42):24680–24687
Martinsson E et al (2014) Optimizing the refractive index sensitivity of plasmonically coupled gold nanoparticles. Plasmonics 9(4):773–780
Nath N, Chilkoti A (2004) Label-free biosensing by surface plasmon resonance of nanoparticles on glass: optimization of nanoparticle size. Anal Chem 76(18):5370–5378
Fujiwara K, Watarai H, Itoh H, Nakahama E, Ogawa N (2006) Measurement of antibody binding to protein immobilized on gold nanoparticles by localized surface plasmon spectroscopy. Anal Bioanal Chem 386(3):639–44
Haes AJ, Van Duyne RP (2002) A nanoscale optical biosensor: sensitivity and selectivity of an approach based on the localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy of triangular silver nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 124(35):10596–10604
Riboh JC, Haes AJ, McFarland AD, Yonzon CR, Van Duyne RP (2003) A nanoscale optical biosensor: real-time immunoassay in physiological buffer enabled by improved nanoparticle adhesion. J Phys Chem B 107(8):1772–1780
Gao D, Chen W, Mulchandani A, Schultz JS (2007) Detection of tumor markers based on extinction spectra of visible light passing through gold nanoholes. Appl Phys Lett 90:073901
Prikulis J, Hanarp P, Olofsson L, Sutherland D, Käll M (2004) Optical spectroscopy of nanometric holes in thin gold films. Nano Lett 4(6):1003–1007
Larsson EM, Alegret J, Käll M, Sutherland DS (2007) Sensing characteristics of NIR localized surface plasmon resonances in gold nanorings for application as ultrasensitive biosensors. Nano Lett 7(5):1256–1263
Aizpurua J et al (2003) Optical properties of gold nanorings. Phys Rev Lett 90(5):1–4
Hanarp P, Käll M, Sutherland DS (2003) Optical properties of short range ordered arrays of nanometer gold disks prepared by colloidal lithography. J Phys Chem B 107(24):5768–5772
Rindzevicius T, Alaverdyan Y, Käll M (2007) Long-range refractive index sensing using plasmonic nanostructures. J Phys Chem C 111(32):11806–11810
Tsai CY, Lu SP, Lin JW, Lee PT (2011) High sensitivity plasmonic index sensor using slablike gold nanoring arrays. Appl Phys Lett 98:153108
Nehru N, Yu L, Wei Y, Hastings JT (2014) Using U-shaped localized surface plasmon resonance sensors to compensate for nonspecific interactions. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 13(1):55–61
Barbillon G, Bijeon JL, Plain J, Royer P (2009) Sensitive detection of biological species through localized surface-plasmon resonance on gold nanodisks. Thin Solid Films 517(9):2997–3000
Hawkeye MM, Brett MJ (2007) Glancing angle deposition: fabrication, properties, and applications of micro- and nanostructured thin films. J Vac Sci Technol A 25(5):1317
Robbie K et al (2004) Ultrahigh vacuum glancing angle deposition system for thin films with controlled three-dimensional nanoscale structure. Rev Sci Instrum 75(4):1089
Sobhkhiz N, Moshaii A (2014) Silver conical helix broadband plasmonic nanoantenna. J Nanophoton 8(1):083078
Zhou Q, He Y, Abell J, Zhang Z, Zhao Y (2011) Optical properties and surface enhanced Raman scattering of L-shaped silver nanorod arrays. J Phys Chem C 115(29):14131–14140
Zhao Y-P, Chaney SB, Zhang ZY (2006) Absorbance spectra of aligned Ag nanorod arrays prepared by oblique angle deposition. J Appl Phys 100:063527
Fu J-X, Collins A, Zhao Y-P (2008) Optical properties and biosensor application of ultrathin silver films prepared by oblique. J Phys Chem C 112:16784–16791
Gish DA, Nsiah F, McDermott MT, Brett MJ (2007) Localized surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Anal Chem 79:4228–4232
Arai T, Kumar PKR, Rockstuhl C, Awazu K, Tominaga J (2007) An optical biosensor based on localized surface plasmon resonance of silver nanostructured films. J Opt A Pure Appl Opt 9:699–703
Kedem O, Tesler AB, Vaskevich A, Rubinstein I (2011) Sensitivity and optimization of localized surface plasmon resonance transducers. ACS Nano 5:748–760
Zheng YB, Juluri BK, Mao X, Walker TR, Huang TJ (2008) Systematic investigation of localized surface plasmon resonance of long-range ordered Au nanodisk arrays. J Appl Phys 103:014308
Mayer KM, Hafner JH (2011) Localized surface plasmon resonance sensors. Chem Rev 111:3828–3857
Knight MW, Wu Y, Lassiter B, Nordlander P, Halas NJ (2009) Substrates matter: influence of an adjacent dielectric on an individual plasmonic nanoparticle. Nano Lett 9:2188–2192
Dmitriev A et al (2008) Enhanced nanoplasmonic optical sensors with reduced substrate effect. Nano Lett 8:3893–3898
Garcia MA (2011) Surface plasmons in metallic nanoparticles: Fundamentals and applications. J Phys D Appl Phys 44:283001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 368 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbasian, S., Moshaii, A., Vayghan, N.S. et al. Ag Nanostructures Produced by Glancing Angle Deposition with Remarkable Refractive Index Sensitivity. Plasmonics 12, 631–640 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0308-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0308-0