Abstract
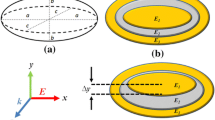
Surface plasmon resonances of an ellipsoid-ring nanostructure with spatial symmetry breaking have been investigated theoretically. In this plasmonic system, the multiple Fano resonances are enhanced and can be tuned effectively by rotating the nanoellipsoid in the cavity of the ring. It is demonstrated that such multiple Fano resonances result from the plasmon coupling between the bright mode of the nanoellipsoid and the dark mode of the nanoring. The dark octupolar and the bright octupolar Fano resonances can be excited by modifying the geometrical parameters of the nanostructure. The asymmetry also allows the generation of strong electric field enhancements in this nanostructure which can be applied in the surface-enhanced spectroscopy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes WL, Dereux A, Ebbesen TW (2003) Surface plasmon sub-wavelength optics. Nature 424:824–830
Gramotnev DK, Bozhevolnyi SI (2010) Plasmonics beyond the diffraction limit. Nat Photonics 4:83–91
Barrow SJ, Funston AM, Wei XZ, Mulvaney P (2013) DNA-directed self-assembly and optical properties of discrete 1D, 2D and 3D plasmonic structures. Nano Today 8:138–167
Bustos-Marún RA, Dente AD, Coronado EA, Pastawski HM (2014) Tailoring optical fields emitted by subwavelength nanometric sources. Plasmonics 9:925–934
Bustos-Marún RA, Coronado EA, Pastawski HM (2010) Buffering plasmons in nanoparticle waveguides at the virtual-localized transition. Phys Rev B 82:035434
Lee SJ, Guan ZQ, Xu HX, Moskovits M (2007) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and nanogeometry: the plasmonic origin of SERS. J Phys Chem C 111(49):17985–17988
Banholzer MJ, Millstone JE, Qin L, Mirkin CA (2008) Rationally designed nanostructures for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Chem Soc Rev 37:885
Fei L, Brandl DW, Urzhumov YA, Wang H, Kundu J, Halas NJ, Aizpurua J, Nordlander P (2008) Metallic nanoparticle arrays: a common substrate for both surface-enhanced Raman scattering and surface-enhanced infrared absorption. ACS Nano 2:707–718
Atwater HA, Polman A (2010) Plasmonics for improved photovoltaic devices. Nat Mater 9:205–213
Senyuk B, Evans JS, Ackerman PJ, Lee T, Manna P, Vigderman L, Zubarev ER, Lagemaat J, Smalyukh II (2012) Shape-dependent oriented trapping and scaffolding of plasmonic nanoparticles by topological defects for self-assembly of colloidal dimers in liquid crystals. Nano Lett 12:955–963
Zhang SP, Xu HX (2012) Optimizing substrate-mediated plasmon coupling toward high-performance plasmonic nanowire waveguides. ACS Nano 9:8128–8135
Cetin AE, Altug H (2012) Fano resonant ring/disk plasmonic nanocavities on conducting substrates for advanced biosensing. ACS Nano 11:9989–9995
Jain PK, Huang XH, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA (2007) Review of some interesting surface plasmon resonance-enhanced properties of noble metal nanoparticles and their applications to biosystems. Plasmonics 2:107–118
Thyagarajan K, Butet J, Martin OJF (2013) Augmenting second harmonic generation using Fano resonances in plasmonic systems. Nano Lett 13:1847–1851
Sheikholeslami SN, Garcia-Etxarri A, Dionne JA (2011) Controlling the interplay of electric and magnetic modes via Fano-like plasmon resonances. Nano Lett 11:3927–3934
Feng H, Sonnefraud Y, Dorpe PV, Maier SA, Halas NJ, Nordlander P (2008) Symmetry breaking in plasmonic nanocavities: subradiant LSPR sensing and a tunable Fano resonance. Nano Lett 11:3983–3988
Zaccaria RP, Angelis DF, Toma A, Razzari L, Alabastri A, Das G, Liberale C, Fabrizio ED (2012) Surface plasmon polariton compression through radially and linearly polarized source. Opt Lett 37:545–547
Sonnefraud Y, Verellen N, Sobhani H, Vandenbosch GAE, Moshchalkov VV, Dorpe PV, Nordlander P, Maier SA (2010) Experimental realization of subradiant, superradiant, and Fano resonances in ring/disk plasmonic nanocavities. ACS Nano 3:1664–1670
Habteyes TG, Dhuey S, Cabrini S, Schuck PJ, Leone SR (2011) Theta-shaped plasmonic nanostructures: bringing “dark” multipole plasmon resonances into action via conductive coupling. Nano Lett 11:1819–1825
Dregely D, Hentschel M, Giessen H (2011) Excitation and tuning of higher-order Fano resonances in plasmonic oligomer clusters. ACS Nano 5:8202–8211
Mirin NA, Bao K, Nordlander P (2009) Fano resonances in plasmonic nanoparticle aggregates. J Phys Chem A 113:4028–4034
Brown LV, Sobhani H, Lassiter JB, Nordlander P, Halas HJ (2010) Heterodimers: plasmonic properties of mismatched nanoparticle pairs. ACS Nano 4:819–832
Li ZP, Shegai T, Haran G, Xu HX (2009) Multiple-particle nanoantennas for enormous enhancement and polarization control of light emission. ACS Nano 3(3):637–642
Rahmani M, Lukiyanchuk B, Tahmasebi T, Lin Y, Liew T, Hong M (2012) Polarization-controlled spatial localization of near-field energy in planar symmetric coupled oligomers. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 107:23–30
Rahmani M, Lukiyanchuk B, Nguyen TTV, Tahmasebi T, Lin Y, Liew TYF, Hong MH (2011) Influence of symmetry breaking in pentamers on Fano resonance and near-field energy localization. Opt Mater Express 1:1409–1415
Brandl DW, Mirin NA, Nordlander P (2006) Plasmon modes of nanosphere trimers and quadrumers. J Phys Chem B 110:12302–12310
Li JN, Liu TZ, Zheng HR, Gao F, Dong J, Zhang ZL, Zhang ZY (2013) Plasmon resonances and strong electric field enhancements in side-by-side tangent nanospheroid homodimers. Opt Express 21(14):17176–17185
Chang WS, Lassiter JB, Swanglap P, Sobhani H, Khatua S, Nordlander P, Halas NJ, Link S (2012) A plasmonic Fano switch. Nano Lett 12:4977–4982
Fu YH, Zhang JB, Yu YF, Luk’yanchuk B (2012) Generating and manipulating higher order Fano resonances in dual-disk ring plasmonic nanostructures. ACS Nano 6:5130–5137
Liu TZ, Li JN, Gao F, Han QY, Liu SZ (2013) Generation and manipulation of higher order Fano resonances in plasmonic nanodisks with a built-in missing sectorial slice. Europhys Lett 104:47009
Li JN, Liu TZ, Zheng HR, Dong J, He EJ, Gao W, Han QY, Wang C, Wu YN (2014) Higher order Fano resonances and electric field enhancements in disk-ring plasmonic nanostructures with double symmetry breaking. Plasmonics 9(6):1439–1445
Amin M, Bağcı H (2012) Investigation of Fano resonances induced by higher order plasmon modes on a circular nano-disk with an elongated cavity. Progr Electromagn Res Lett 130:187–206
Abb M, Wang YD, Albella P, Albella P, Groot CH, Aizpurua J, Muskens OL (2012) Interference, coupling, and nonlinear control of high-order modes in single asymmetric nanoantennas. ACS Nano 7:6462–6470
Ho JF, Luk’yanchuk B, Zhang JB (2012) Tunable Fano resonances in silver silica silver multilayer nanoshells. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 107:133–137
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6(12):4370–4379
Halas NJ, Lal S, Link S, Chang WS, Natelson D, Hafner JH, Nordlander P (2012) A plethora of plasmonics from the laboratory for nanophotonics at Rice University. Adv Mater 24:4842–4877
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (GK201002038) and Natural Science Basis Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (program no. 2011JQ1014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, K., Huo, Y., Liu, T. et al. Manipulation of Electrical Field Enhancements and Fano Resonances in Nanoellipsoid/Ring Plasmonic Cavities. Plasmonics 10, 1041–1048 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-9899-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-9899-0