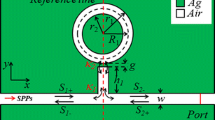
Abstract
A plasmonic waveguide system composed of metal-insulator-metal (MIM) stub coupled with circular cavity resonator was proposed to produce ultra sharp Fano resonances, which resulted from the coupling between the ultra narrow discrete resonances and the ultra broad spectrum of the plasmonic circular cavity and stub resonator, respectively. The spectral line shapes of the Fano resonances can be easily adjusted by changing the structure parameters. And the transmittance of the system can sharply decrease from peak (“on state”) to valley (“off state”) with wavelength shifts of only about 8 nm. Due to the sharp phase change of the ultra asymmetric Fano resonance, a maximum group index of about 180 can be realized. Also, the ultra sharp spectrum contributes to a highly efficient plasmonic refractive index sensor, which can yield a linear sensitivity of 1277 nm/RIU and figure of merit of about 2.1 × 104. The proposed structure may have potential applications in nanoscale filter, slow light, and refractive index sensor.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yanchuk BL, Zheludev NI, Maier SA, Halas NJ, Nordlander P, Giessen H, Chong CT (2010) The Fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials the Fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials. Nat Mater 9:707–715
Ye J, Wen FF, Sobhani H, Lassiter JB, Van Dorpe P, Nordlander P, Halas NJ (2012) Plasmonic nanoclusters: near field properties of the Fano resonance interrogated with SERS. Nano Lett 12:1660–1667
Liu SD, Yang Z, Liu RP, Li XY (2011) High sensitivity localized surface plasmon resonance sensing using a double split NanoRing cavity. J Phys Chem C 115:24469–24477
Verellen N, Van Dorpe P, Huang C, Lodewijks K, Vandenbosch GAE, Lagae L, Moshchalkov VV (2011) Plasmon line shaping using nanocrosses for high sensitivity localized surface plasmon resonance sensing. Nano Lett 11:391–397
Hao F, Sonnefraud Y, Van Dorpe P, Maier SA, Halas NJ, Nordlander P (2008) Symmetry breaking in plasmonic nanocavities: subradiant LSPR sensing and a tunable Fano resonance. Nano Lett 8:3983–3988
Chen JX, Wang P, Chen CC, Lu YH, Ming H, Zhan QW (2011) Plasmonic EIT-like switching in bright-dark-bright plasmon resonators. Opt Express 19:5970–5978
Liu N, Weiss T, Mesch M, Langguth L, Eigenthaler U, Hirscher M, Sonnichsen C, Giessen H (2010) Planar metamaterial analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency for plasmonic sensing. Nano Lett 10:1103–1107
Zhang J, Xiao S, Jeppesen C, Kristensen A, Mortensen NA (2010) Electromagnetically induced transparency in metamaterials at near-infrared frequency. Opt Express 18:17187–17192
Liu N, Langguth L, Thomas W, Kästel J, Fleischhauer M, Pfau T, Giessen H (2009) Plasmonic analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency at the Drude damping limit. Nat Mater 8:758–762
Zhang S, Genov DA, Wang Y, Liu M, Zhang X (2008) Plasmon-induced transparency in metamaterials. Phys Rev Lett 101:47401
Zhang Y, Jia TQ, Zhang HM, Xu ZZ (2012) Fano resonances in disk-ring plasmonic nanostructure: strong interaction between bright dipolar and dark multipolar mode. Opt Lett 37:4919–4921
Niu L, Zhang JB, Fu YH, Kulkarni S, Lukyanchuk B (2011) Fano resonance in dual-disk ring plasmonic nanostructures. Opt Express 19:22974–22981
Habteyes TG, Dhuey S, Cabrini S, Schuck PJ, Leone SR (2011) Theta-shaped plasmonic nanostructures: bringing “dark” multipole plasmon resonances into action via conductive coupling. Nano Lett 11:1819–1825
Wu DJ, Jiang SM, Liu XJ (2012) Fano-like resonances in asymmetric homodimer of gold elliptical nanowires. J Phys Chem C 116:13745–13748
Pena-Rodríguez O, Pal U, Campoy-Quiles M, Rodríguez-Fernandez L, Garriga M, Alonso MI (2011) Enhanced Fano resonance in asymmetrical Au:Ag heterodimers. J Phys Chem C 115:6410–6414
Shafiei F, Monticone F, Le KQ, Liu X, Hartsfield T, Alu A, Li X (2013) Subwavelength plasmonic metamolecule exhibiting magnetic-based optical Fano resonance. Nat Nanotechnol 8:95–99
Lassiter JB, Sobhani H, Knight MW, Mielczarek WS, Nordlander P, Halas NJ (2012) Designing and deconstructing the Fano lineshape in plasmonic nanoclusters. Nano Lett 12:1058–1062
Chen Z, Yu L, Wang LL, Duan GY, Zhao YF, Xiao JH (2015) A refractive index nanosensor based on Fano resonance in the plasmonic waveguide system. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 27:1695–1698
Qi JW, Chen ZQ, Chen J, Li YD, Qiang W, Xu JJ, Sun Q (2014) Independently tunable double Fano resonances in asymmetric MIM waveguide structure. Opt Express 22:14688–14695
Chen Z, Yu L, Wang LL, Duan GY, Zhao YF, Xiao JH (2015) Sharp asymmetric line shapes in a plasmonic waveguide system and its application in nanosensor. J Lightwave Technol 33:3250–3253
Cui YD, Zeng C (2013) All-optical EIT-like phenomenon in plasmonic stub waveguide with ring resonator. Opt Commun 297:190–193
Wen KH, Hu YH, Chen L, Zhou JY, Lei L, Guo Z (2015) Fano resonance with ultra-high figure of merits based on plasmonic metal-insulator-metal waveguide. Plasmonics 10:27–32
Wen KH, Hu YH, Chen L, Zhou JY, Lei L, Meng ZM (2015) Single/dual Fano resonance based on plasmonic metal-dielectric-metal waveguide. Plasmonics. doi:10.1007/s11468-015-0056-6
Han Z, Bozhevolnyi SI (2011) Plasmon-induced transparency with detuned ultracompact Fabry-Perot resonators in integrated plasmonic devices. Opt Express 19:3251–3257
Yun BF, Hu GH, Cong JW, Cui YP (2014) Plasmonic induced transparency in metal-insulator-metal waveguide by a stub coupled with F-P resonator. Mater Res Exp 1:036201
Chen JJ, Li Z, Zou YJ, Deng ZL, Xiao JH, Gong QH (2013) Coupled-resonator-induced Fano resonances for plasmonic sensing with ultra-high figure of merits. Plasmonics 8:1627–1631
Lu H, Liu XM, Mao D, Gong YK, Wang GX (2011) Induced transparency in nanoscale plasmonic resonator systems. Opt Lett 36:3233–3235
Chen JJ, Sun CW, Gong QH (2014) Fano resonances in a single defect nanocavity coupled with a plasmonic waveguide. Opt Lett 39:52–55
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China under Grant No.11374048 and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Binfeng, Y., Ruohu, Z., Guohua, H. et al. Ultra Sharp Fano Resonances Induced by Coupling between Plasmonic Stub and Circular Cavity Resonators. Plasmonics 11, 1157–1162 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0154-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0154-5