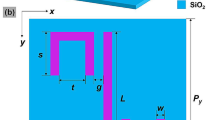
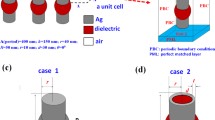
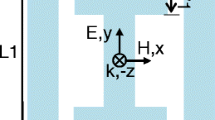
Abstract
We theoretically demonstrate and investigate plasmonically induced reflectance (PIR) in a new planar metamaterial with two completely different approaches. Here, we not only show that broken symmetry is a general strategy to create electromagnetically induced reflectance (EIR)-like effect but also demonstrate that the nanoplasmonic EIR can be realized even without broken symmetry via the excitation of the higher-order plasmonic modes in the same designed planar metamaterial. In nanophotonics, plasmonic structures enable large field strengths within small mode volumes. Therefore, combining EIR with nanoplasmonics would open up the way toward ultracompact sensors with extremely high sensitivity. In the second approach of creating the PIR of our proposed nanostructure, the restrictions on size are partially relaxed, making fabrication much easier. Their interactions and coupling between plasmonic modes are investigated in detail by analyzing field distributions and spectral responses. Also, we show that the PIR frequency position depended very sensitively on the dielectric surrounding. Furthermore, the narrow and fully modulated PIR features due to the extraordinary reduction of damping may serve for designing novel devices in the field of chemical and biomedical sensing.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu N, Weiss T, Mesch M, Langguth L, Eigenthaler, Hirscher M, Sonnichsen C, Giessen H (2010) Planar metamaterial analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency for plasmonic sensing. Nano Lett 10:1103–1107
Wu C, Khanikaev AB, Shvets G (2011) Broadband slow light metamaterial based on a double-continuum fano resonance. Phys Rev Lett 106:107403
Tassin P, Zhang L, Koschny T, Economou E, Soukoulis C (2009) Low-loss metamaterials based on classical electromagnetically induced transparency. Phys Rev Lett 102:053901
Papasimakis N, Fedotov V, Zheludev N, Prosvirnin S (2008) Metamaterial analog of electromagnetically induced transparency. Phys Rev Lett 101:253903
Liu N, Langguth L, Weiss T, Kastel J, Fleischhauer M, Pfau T, Giessen H (2009) Plasmonic analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency at the Drude damping limit. Nat Mater 8:758–762
Zhang S, Genov DA, Wang Y, Liu M, Zhang X (2008) Plasmon-induced transparency in metamaterials. Phys Rev Lett 101(4):047401
Lukyanchuck B, Zheludev NI, Maier SA, Halas NJ, Nordlander P, Giessen H, Chong CT (2010) The Fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials. Nat Mater 9:707–715
Kekatpure RD, Barnard E S, Cai W, Brongersma M L (2010) Phase-coupled plasmon-induced transparency. Phys Rev Lett 104:243902
Artar A, Yanik AA, Altug H (2011) Directional double Fano resonances in plasmonic hetero-oligomers. Nano Lett 11:3694–3700
Artar A, Yanik AA, Altug H (2011) Multispectral plasmon induced transparency in coupled meta-atoms. Nano Lett 11:1685–1689
Liu N, Hentschel M, Weiss T, Alivisatos AP, Giessen H (2011) Three-dimensional plasmon rulers. Science 332:1407–10
Sheikholeslami S, Garcia-Etxarri A, Dionne JA (2011) Controlling the interplay of electric and magnetic modes via Fano-like plasmon resonances. Nano Lett 11:3927–3934
Yannopapas V, Paspalakis E, Vitanov NV (2009) Electromagnetically induced transparency and slow light in an array of metallic nanoparticles. Phys Rev B 80:035104
Lu Y, Xu H, Rhee JY, Jang WH, Ham B S, Lee YP (2010) Magnetic plasmon resonance: underlying route to plasmonic electromagnetically induced transparency in metamaterial. Phys Rev B 82:195112
Jin X R, Lu YH, Zheng HY, Lee YP, Lee JY, Jang WH (2010) Plasmonic electromagnetically-induced transparency in symmetric structures. Opt Express 18:13396
Verellen N, Sonnefraud Y, Sobhani H, Hao F, Moshchalkov VV, Dorpe PV, Nordlander P, Maier SA (2009) Fano resonances in individual coherent plasmonic nanocavities. Nano Lett 9:1663–1667
Ham BS (2008) Observations of delayed all-optical routing in a slow-light regime. Phys Rev A 78:011808(R)
Novotny L (2007) Effective wavelength scaling for optical antennas. Phys Rev Lett 98:266802
Vafapour Z, Zakery A (2015) New regime of plasmonically induced transparency. Plasmonics. doi:10.1007/s11468-015-9992-4
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6:4370–4379
Ordal MA, et al. (1983) Optical properties of the metals Al, Co, Cu, Au, Fe, Pb, Ni, Pd, Pt, Ag, Ti, and W in the infrared and far infrared. Appl Opt 22:1099–1119
He XJ, Wang L, Wang JM, Tian XH, Jiang JX, Geng ZX (2013) Electromagnetically induced transparency in planar complementary metamaterial for refractive index sensing applications. J Phys D: Appl Phys 46(36):365302
Dong ZD, Liu H, Cao JX, Li T, Wang SM, Zhu SN, Zhang X (2010) Enhanced sensing performance by the plasmonic analog of electromagnetically induced transparency in active metamaterials. Appl Phys Lett 97:114101
Chen CY, Un I W, Tai NH, Yen TJ (2009) Asymmetric coupling between subradiant and superradiant plasmonic resonances and its enhanced sensing performance. Opt Express 17:15372
Weiss T, Granet G, Gippius NA, Tikhodeev SG, Giessen H (2009) Matched coordinates and adaptive spatial resolution in the fourier modal method. Opt Express 17 (10):8051–8061
Tikhodeev SG, Yablonskii AL, Muljarov EA, Gippius NA, Ishihara T (2002) Quasiguided modes and optical properties of photonic crystal slabs. Phys Rev B 66:045102
Stephen DG (2011) Introduction to the finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) method for electromagnetics. Synthesis Lect Comput Electromagn 6(1):1–250. doi:10.2200/S00316ED1V01Y201012CEM027
Han S, Singh R, Cong L, Yang H (2015) Engineering the fano resonance and electromagnetically induced transparency in near-fild coupled bright and dark metamaterial. J Phys D Appl Phys 48(3):035104
Burresi M, Oosten DV, Kampfrath T, Schoenmaker H, Heideman R, Leinse A, Kuipers L (2009) Probing the magnetic field of light at optical frequencies. Science 326:550
Cai W, Shalaev V (2010) Optical metamaterials fundamentals and application. Springer, London: Springer New York Dordrecht Heidelberg, pp 157
Pendry JB (2000) Negative refraction makes a perfect lens. Phys Rev Lett 85:3966–3969
Acknowledgment
Z. Vafapour would like to express her special thanks to Dr. M. R. Forouzeshfard for useful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vafapour, Z., Zakery, A. New Approach of Plasmonically Induced Reflectance in a Planar Metamaterial for Plasmonic Sensing Applications. Plasmonics 11, 609–618 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0077-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0077-1