Abstract
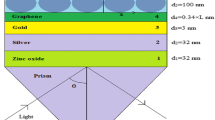
In this theoretical study, the effect of semiconductor on sensitivity of a graphene-based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor has been presented. Different semiconductors such as silicon (Si), germanium (Ge) and wurtzite III-V nitrides (AlN, GaN and InN) have been placed in between active silver (Ag) metal and graphene layer. Our simulation result shows that addition of semiconductor layer enhances the sensitivity by a factor of 3.76, 2.19, 3.82, 3.94 and 4.17 respectively for Si, Ge, InN, GaN and AlN. Also, we have examined the field enhancement factor due to above semiconductors and found maximum field intensity enhancement for the case of AlN. The analysis shows that best performance is achieved for red He-Ne laser light when optimized thicknesses of silver, AlN and graphene layer are 55, 14 and 0.34 nm (monolayer of graphene), respectively. More specifically, AlN would be a better choice for biosensing application in SPR biosensor.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nylander C, Liedberg CB, Lind T (1982) Gas detection by means of surface plasmons resonance. Sensors Actuators 3:79–88
Liedberg B, Nylander C, Lundstrom I (1995) Biosensing with surface plasmon resonance—how it all started. Biosens Bioelectron 10:i–ix
Homola J, Yee SS, Gauglitz G (1999) Surface plasmon resonance sensors: review. Sensors Actuators B Chem 54(1-2):3–15
Homola J (2003) Present and future of surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Anal Bioanal Chem 377(3):528–539
Van Regenmortel MH, Altschuh D, Chatellier J, Christensen L, Rauffer-Bruyere N, Richalet-Secordel P, Witz J, Zeder-Lutz G (1998) Measurement of antigen-antibody interactions with biosensors. J Mol Recognit 11:163–167
Johnsson B, Lofas S, Lindquist G (1991) Immobilization of proteins to a carboxymethyldextran-modified gold surface for biospecific interaction analysis in surface plasmon resonance sensors. Anal Biochem 198(2):268–277
Thiel AJ, Frutos AG, Jordan CE, Corn RM, Smith LM (1997) In situ surface plasmon resonance imaging detection of DNA hybridization to oligonucleotide arrays on gold surfaces. Anal Chem 69(24):4948–4956
Zalevsky Z, Abdulhalim I (2014) Integrated nanophotonic devices. Elsevier. pp. 221
Jorgenson RC, Yee SS (1993) A fiber-optic chemical sensor based on surface plasmon resonance. Sensors Actuators B Chem 12:213–220
Srivastava SK, Verma R, Gupta BD (2011) Surface plasmon resonance based fiber optic sensor for the detection of low water content in ethanol. Sensors Actuators B Chem 153:194–198
Choi SH, Kim YL, Byun KM (2011) Graphene-on-silver substrates for sensitive surface plasmon resonance imaging biosensors. Opt Express 19(2):458–466
Wu L, Chu HS, Koh WS, Li EP (2010) Highly sensitive graphene biosensors based on surface plasmon resonance. Opt Express 18(14):14395–14400
Zhu XM, Lin PH, Ao P, Sorensen LB (2002) Surface treatments for surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Sensors Actuators B Chem 84(2-3):106–112
Szunerits S, Maalouli N, Wijaya E, Vilcot JP, Boukherroub R (2013) Recent advances in the development of graphene-based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) interfaces. Anal Bioanal Chem 405(5):1435–1443
Song B, Li D, Qi WP, Elstner M, Fan CH, Fang HP (2010) Graphene on Au(111): a highly conductive material with excellent adsorption properties for high-resolution bio/nanodetection and identification. ChemPhysChem 11(3):585–589
Verma R, Gupta BD, Jha R (2011) Sensitivity enhancement of a surface plasmon resonance based biomolecules sensor using graphene and silicon layers. Sensors Actuators B Chem 160(1):623–631
Kai-Qun KL, Lai-Ming W, Dou-Guo Z, Rong-Sheng Z, Pei W, Yong-Hua L, Hai M (2007) Temperature effects on prism-based surface plasmon resonance sensor. Chin Phys Lett 24(11):3081
Jewett SA, Makowski MS, Andrews B, Manfra MJ, Ivanisevic A (2012) Gallium nitride is biocompatible and non-toxic before and after functionalization with peptides. Actabiomaterialia 8(2):728–733
Maier SA (2007) Plasmonics: fundamentals and applications. Springer
Raether H (1988) Surface plasmons on smooth and rough surfaces and on gratings. Springer, Berlin
Hansen WN (1968) Electric fields produced by the propagation of plane coherent electromagnetic radiation in a stratified medium. JOSA 58(3):380–388
Born M, Wolf E (1964) Principles of optics: electromagnetic theory of propagation, interference and diffraction of light. Pergamon Press, Oxford
Zhan T, Shi X, Dai Y, Liu X, Zi J (2013) Transfer matrix method for optics in graphene layers. J Phys Condens Matter 25(21):215301
Mohanty G, Sahoo BK, Akhtar J (2014) Comparative analysis for reflectivity of graphene based SPR biosensor. Opt Quant Electron 1–8
SCHOTT optical glass data sheets 2012-12-04
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6:4370–4379
Bruna M, Borini S (2009) Optical constants of graphene layers in the visible range. Appl Phys Lett 94:031901
Aspnes DE, Studna AA (1983) Dielectric functions and optical parameters of Si, Ge, GaP, GaAs, GaSb, InP, InAs, and InSb from 1.5 to 6.0 eV. Phys Rev B 27:985–1009
Pastrnak J, Roskovcova L (1966) Refraction index measurements on AlN single crystals. Phys Status Solidi 14:K5–K8
Barker AS Jr, Ilegems M (1973) Infrared lattice vibrations and free-electron dispersion in GaN. Phys Rev B 7:743–750
Zubrilov A, Levinshtein ME, Rumyantsev SL, Shur MS (2001) Properties of advanced semiconductor materials GaN, AlN, InN, BN, SiC, SiGe. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, pp 49–66
Hale GM, Querry MR (1973) Optical constants of water in the 200-nm to 200-μm wavelength region. Appl Opt 12:555–563
Ong BH, Yuan X, Tjin SC (2006) Bimetallic silver-gold film waveguide surface plasmon resonance sensor. In Integrated Optoelectronic Devices (pp. 61230B-61230B). International Society for Optics and Photonics
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by N.I.T Raipur under M.H.R.D Fellowship Scheme, Govt. of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohanty, G., Akhtar, J. & Sahoo, B.K. Effect of Semiconductor on Sensitivity of a Graphene-Based Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor. Plasmonics 11, 189–196 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0033-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0033-0