Abstract
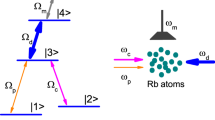
We report an experimental study of magnetic-field-sensitive multi-wave interference, realized in a three-wave RF-atom system. In the F = 1 hyperfine level of the 87Rb 52S1/2 ground state, Ramsey fringes were observed via the spin-selective Raman detection. A decrease in the fringe contrast was observed with increasing free evolution time. The maximum evolution time for observable fringe contrasts was investigated at different atom temperatures, under free-falling and trapped conditions. As the main interest of the Ramsey method, the improvement in magnetic field resolution is observed with an increase of evolution time T up to 3 ms and with the measurement resolution reaching 0.85 nT. This study paves the way for precision magnetic field measurements based on cold atoms.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. F. Ramsey, A molecular beam resonance method with separated oscillating fields, Phys. Rev. 78(6), 695 (1950)
T. P. Heavner, E. A. Donley, F. Levi, G. Costanzo, T. E. Parker, J. H. Shirley, N. Ashby, S. Barlow, and S. R. Jefferts, First accuracy evaluation of NIST-F2, Metrologia 51(3), 174 (2014)
J. Guena, M. Abgrall, D. Rovera, P. Laurent, B. Chupin, M. Lours, G. Santarelli, P. Rosenbusch, M. E. Tobar, Ruoxin Li, K. Gibble, A. Clairon, and S. Bize, Progress in atomic fountains at LNE-SYRTE, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 59(3), 391 (2012)
V. Gerginov, N. Nemitz, S. Weyers, R. Schröder, D. Griebsch, and R. Wynands, Uncertainty evaluation of the caesium fountain clock PTB-CSF2, Metrologia 47(1), 65 (2010)
M. Sadgrove, Y. Eto, S. Sekine, H. Suzuki, and T. Hirano, Ramsey interferometry using the Zeeman sublevels in a spin-2 Bose gas, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 82(9), 094002 (2013)
L. Chen, K. Zhang, Y. Xu, Q. Luo, W. Xu, M. Zhou, and Z. Hu, Multi-wave atom interferometer based on Doppler-insensitive Raman transition, Opt. Express 28(6), 8463 (2020)
Petrovic, I. Herrera, P. Lombardi, F. Schäfer, and F. S. Cataliotti, A multi-state interferometer on an atom chip, New J. Phys. 15(4), 043002 (2013)
M. Robert-de-Saint-Vincent, J. P. Brantut, C. J. Bordé, A. Aspect, T. Bourdel, and P. Bouyer, A quantum trampoline for ultra-cold atoms, Europhys. Lett. 89(1), 10002 (2010)
M. Gustavsson, E. Haller, M. J. Mark, J. G. Danzl, R. Hart, A. J. Daley, and H. C. Nägerl, Interference of interacting matter waves, New J. Phys. 12(6), 065029 (2010)
M. K. Zhou, K. Zhang, X. C. Duan, Y. Ke, C. G. Shao, and Z. K. Hu, Atomic multiwave interferometer for Aharonov–Casher-phase measurements, Phys. Rev. A 93(2), 023641 (2016)
G. Di Domenico, H. Saudan, G. Bison, P. Knowles, and A. Weis, Sensitivity of double-resonance alignment magnetometers, Phys. Rev. A 76(2), 023407 (2007)
S. Knappe, P. D. D. Schwindt, V. Gerginov, V. Shah, L. Liew, J. Moreland, H. G. Robinson, L. Hollberg, and J. Kitching, Microfabricated atomic clocks and magnetometers, J. Opt. A 8(7), S318 (2006)
P. D. D. Schwindt, S. Knappe, V. Shah, L. Hollberg, J. Kitching, L. A. Liew, and J. Moreland, Chip-scale atomic magnetometer, Appl. Phys. Lett. 85(26), 6409 (2004)
J. Li, W. Quan, B. Zhou, Z. Wang, J. Lu, Z. Hu, G. Liu, and J. Fang, SERF atomic magnetometer–recent advances and applications: A review, IEEE Sens. J. 18(20), 8198 (2018)
D. Budker and M. Romalis, Optical magnetometry, Nat. Phys. 3(4), 227 (2007)
M. W. Mitchell and S. P. Alvarez, Quantum limits to the energy resolution of magnetic field sensors, Rev. Mod. Phys. 92(2), 021001 (2020)
W. Zhao, W. Qian, D. Lv, and R. Wei, Improvement of average magnetic field measurement based on magnetic-field-sensitive Ramsey fringes, Opt. Lett. 47(8), 2073 (2022)
W. Wang, R. Dong, R. Wei, J. Lin, F. Zou, T. Chen, and Y. Wang, Measuring magnetic field vector by stimulated Raman transitions, Appl. Phys. Lett. 108(12), 122401 (2016)
C. Shi, R. Wei, Z. Zhou, D. Lv, T. Li, and Y. Wang, Magnetic field measurement on 87Rb atomic fountain clock, Chin. Opt. Lett. 8, 549 (2010)
A. Peters, K. Y. Chung, and S. Chu, High-precision gravity measurements using atom interferometry, Metrologia 38(1), 25 (2001)
Z. K. Hu, B. L. Sun, X. C. Duan, M. K. Zhou, L. L. Chen, S. Zhan, Q. Z. Zhang, and J. Luo, Demonstration of an ultrahigh-sensitivity atom-interferometry absolute gravimeter, Phys. Rev. A 88(4), 043610 (2013)
Z. Y. Wang, T. Chen, X. L. Wang, Z. Zhang, Y. F. Xu, and Q. Lin, A precision analysis and determination of the technical requirements of an atom interferometer for gravity measurement, Front. Phys. China 4(2), 174 (2009)
J. Wang, L. Zhou, R. B. Li, M. Liu, and M. S. Zhan, Cold atom interferometers and their applications in precision measurements, Front. Phys. China 4(2), 179 (2009)
R. Gautier, M. Guessoum, L. A. Sidorenkov, Q. Bouton, A. Landragin, and R. Geiger, Accurate measurement of the Sagnac effect for matter waves, Sci. Adv. 8(23), eabn8009 (2022)
W. J. Xu, L. Cheng, J. Liu, C. Zhang, K. Zhang, Y. Cheng, Z. Gao, L. S. Cao, X. C. Duan, M. K. Zhou, and Z. K. Hu, Effects of wave-front tilt and air density fluctuations in a sensitive atom interferometry gyroscope, Opt. Express 28(8), 12189 (2020)
Z. W. Yao, S. B. Lu, R. B. Li, J. Luo, J. Wang, and M. S. Zhan, Calibration of atomic trajectories in a large-area dual-atom-interferometer gyroscope, Phys. Rev. A 97(1), 013620 (2018)
X. Alauze, A. Bonnin, C. Solaro, and F. P. D. Santos, A trapped ultracold atom force sensor with a µm-scale spatial resolution, New J. Phys. 20(8), 083014 (2018)
R. Bennett and D. H. J. O’Dell, Revealing short-range non-Newtonian gravity through Casimir–Polder shielding, New J. Phys. 21(3), 033032 (2019)
P. Wolf, P. Lemonde, A. Lambrecht, S. Bize, A. Landragin, and A. Clairon, From optical lattice clocks to the measurement of forces in the Casimir regime, Phys. Rev. A 75(6), 063608 (2007)
S. Dimopoulos and A. A. Geraci, Probing submicron forces by interferometry of Bose–Einstein condensed atoms, Phys. Rev. D 68(12), 124021 (2003)
X. B. Deng, Y. Y. Xu, X. C. Duan, and Z. K. Hu, Precisely mapping the absolute magnetic field in vacuum by an optical ramsey atom interferometer, Phys. Rev. Appl. 15(5), 054062 (2021)
H. Zhang, X. Ren, W. Yan, Y. Cheng, H. Zhou, Z. Gao, Q. Luo, M. Zhou, and Z. Hu, Effects related to the temperature of atoms in an atom interferometry gravimeter based on ultra-cold atoms, Opt. Express 29(19), 30007 (2021)
W. Yan, X. Ren, M. Zhou, and Z. Hu, Precision magnetic field sensing with dual multi-wave atom interferometer, Sensors (Basel) 23(1), 173 (2022)
F. Reinhard, Design and construction of an atomic clock on an atom chip, Thesis, Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris VI, 2009
Y. Eto, M. Sadgrove, S. Hasegawa, H. Saito, and T. Hirano, Control of spin current in a Bose gas by periodic application of n pulses, Phys. Rev. A 90(1), 013626 (2014)
M. Fattori, C. D’Errico, G. Roati, M. Zaccanti, M. Jona-Lasinio, M. Modugno, M. Inguscio, and G. Modugno, Atom interferometry with a weakly interacting Bose–Einstein condensate, Phys. Rev. Lett. 100(8), 080405 (2008)
M. Fattori, T. Koch, S. Goetz, A. Griesmaier, S. Hensler, J. Stuhler, and T. Pfau, Demagnetization cooling of a gas, Nat. Phys. 2(11), 765 (2006)
S. Hensler, A. Greiner, J. Stuhler, and T. Pfau, Depolarisation cooling of an atomic cloud, Europhys. Lett. 71(6), 918 (2005)
A. Widera, F. Gerbier, S. Fölling, T. Gericke, O. Mandel, and I. Bloch, Precision measurement of spin-dependent interaction strengths for spin-1 and spin-2 87Rb atoms, New J. Phys. 8(8), 152 (2006)
H. Schmaljohann, M. Erhard, J. Kronjäger, M. Kottke, S. van Staa, L. Cacciapuoti, J. J. Arlt, K. Bongs, and K. Sengstock, Dynamics of F = 2 Spinor Bose–Einstein condensates, Phys. Rev. Lett. 92(4), 040402 (2004)
T. Kuwamoto, K. Araki, T. Eno, and T. Hirano, Magnetic field dependence of the dynamics of 87Rb spin-2 Bose–Einstein condensates, Phys. Rev. A 69(6), 063604 (2004)
X. T. Xu, Z. Y. Wang, R. H. Jiao, C. R. Yi, W. Sun, and S. Chen, Ultra-low noise magnetic field for quantum gases, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 90(5), 054708 (2019)
B. Merkel, K. Thirumalai, J. E. Tarlton, V. M. Schäfer, C. J. Ballance, T. P. Harty, and D. M. Lucas, Magnetic field stabilization system for atomic physics experiments, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 90(4), 044702 (2019)
F. Riehle, Frequency Standards: Basics and Applications, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2004
H. C. J. Gan, G. Maslennikov, K. W. Tseng, T. R. Tan, R. Kaewuam, K. J. Arnold, D. Matsukevich, and M. D. Barrett, Oscillating-magnetic-field effects in high-precision metrology, Phys. Rev. A 98(3), 032514 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2020YFC2200200), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants Nos. 12004128, 12104174, and 12274163), and Open Fund of Wuhan, Gravitation and Solid Earth Tides, National Observation and Research Station (Grants Nos. WHYWZ202211 and WHYWZ202104). We thank Dr. Xiaochun Duan and Dr. Jean-Michel Le Floch for the enlightening talk about this work. Codes and data are available upon request from the authors. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, W., Ren, X., Xu, W. et al. Magnetic-field-sensitive multi-wave interference. Front. Phys. 18, 52306 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-023-1300-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-023-1300-8