Abstract
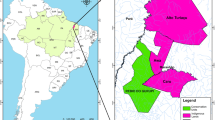
This study investigated oasis evolution and the changes of peripheral desert in the Sangong River Basin since the 1950s by rebuilding seven land cover maps derived from black-and-white aerial photographs (1958, 1968, and 1978), a color-infrared aerial photograph (1987), Landsat Thematic Mapper (TM) imagery (1998), Satellite Pour l’Observation de la Terre (SPOT) imagery (2004), and Landsat Operational Land Imager (OLI) imagery (2014). The results showed that: (1) Since 1950, the oasis consecutively expanded more than four times from an alluvial fan to an alluvial plain, causing the shrinkage of desert landscapes that were dominated by a Haloxylon ammodendron Bunge community (HBC) and a Tamarix chinensis Lour community (TLC). Furthermore, the primary (1958–1968) and final (2004–2014) stages were the most important periods, during which agricultural land experienced the most rapid expansion during the period 1958–1968, and the built-up area showed the most rapid expansion after the 2000s. (2) Two basic management modes, a “local mode” formed by the local governments and a “farm management mode” developed by Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps, together promoted oasis evolution under various land-use and landcover (LULC) stages. (3) The evolution of the modern oasis during the 1950s–2004 showed the general features of an arid oasis, while during the period of 2004–2014 it was characterized by a large-scale inter-basin water diversion or the import of new water sources. (4) The oasis expanded at the expense of desert vegetation, resulting in distinct variation in the structure of the desert plant community, which will make it more difficult to protect the desert ecosystem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen X, 2008. Land Use/Cover Change in Arid Areas in China. Beijing: Science Press, 29–30. (in Chinese)
Chen X, Luo G, 2008. Researches and progress of oasis ecology in arid areas. Arid Land Geography, 31(4): 487–495.(in Chinese)
Cheng W, Zhou C, Liu H et al., 2005. The oasis expansion and eco-environment change over the last 50 years in Manas River. Science China: Earth Sciences, 35(11): 1074–1086.(in Chinese)
Donker D K, Hasman A, Van Geijn H P, 1993. Interpretation of low kappa values. International Journal of Bio-Medical Computing, 33(1): 55–64.
Feng Y, Luo G, Lu L et al., 2011. Effects of land use change on landscape pattern of the Manas River watershed in Xinjiang, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 64(8): 2067–2077.
Foley J A, De Fries R, Asner G P et al., 2005. Global consequences of land use. Science, 309(5734): 570–574.
Gao P, Niu X, Wang B et al., 2015. Land use changes and its driving forces in hilly ecological restoration area based on gis and RS of northern China. Sci. Rep., 5: 11038ai].
Ge Q, Dai J, He N et al., 2008. Land use, land cover change and carbon cycle research of China over the past 300 years. Science China: Earth Sciences, 38(2): 197–220.(in Chinese)
Giles M F, 2002. Status of land cover classification accuracy assessment. Remote Sensing of Environment, 80: 185–201.
Huang C, Zhang M, Zou J et al., 2015. Changes in land use, climate and the environment during a period of rapid economic development in Jiangsu Province, China. Science of the Total Environment, 536: 173–181.
Janssen L L F, van der Wel F J M, 1994. Accuracy assessment of satellite derived land cover data: A review. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 60(4): 419–426.
Li B, Fang X, Ye Y et al., 2010. Accuracy assessment of global historical cropland datasets based on regional reconstructed historical data: A case study in Northeast China. Science China: Earth Sciences, 40(8): 1689–1699.(in Chinese)
Liao J, Wang T, Xue X, 2012. Oasis evolution in the Heihe River Basin during 1956–2010. Journal of Desert Research, 32(5): 1426–1441.(in Chinese)
Liu J, Deng X, 2009. Development of research method of LUCC spatio-temporal process. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(21): 3251–3258.(in Chinese)
Liu J, Jin T, Liu G et al., 2014. Analysis of land use /cover change from 2000 to 2010 and its driving forces in Manas River Basin, Xinjiang. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(12): 3211–3223.
Liu J, Kuang W, Zhang Z et al., 2014. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns and causes of land use changes in China since the late 1980s. Acta Geographica Sinica, 69(1): 1–11.(in Chinese)
Liu J, Shao Q, Yan X et al., 2011. An overview of the progress and research framework on the effects of land use change upon global climate. Advances in Earth Science, 26(10): 1015–1022.(in Chinese)
Liu X, Yang J, Yang Q, 2005. Analysis on the variations characteristics of air temperature, precipitation in the Sangong River Basin in the past 40 years. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 12(6): 54–57.(in Chinese)
Luo G, Amuti T, Zhu L et al., 2015. Dynamics of landscape patterns in an inland river delta of Central Asia based on a cellular automata-Markov model. Regional Environmental Change, 15(2): 277–289.
Luo G, Zhou C, Chen X, 2003. Process of land use/land cover change in the oasis of arid region. Acta Geographica Sinica, 58(1): 63–72.(in Chinese)
Luo G, Zhou C, Chen X, 2006. Landscape plaque stability study in the oasis of arid region: A case study of Sangong River watershed. Chinese Science Bulletin, 51(Suppl?): 73–80.
Luo G, Zhou C, Chen X et al., 2008. A methodology of characterizing status and trend of land changes in oases: A case study of Sangong River watershed, Xinjiang, China. Journal of Environment Management, 88(4): 775–783.
Luo Y, 2014. Long term effects of drip irrigation on soil salinization in arid area oasis. Science China: Earth Science, 44(8): 1679–1688.(in Chinese)
Lv G, Du X, Yang J et al., 2007. Community stability of deserts vegetation at Fukang oasis-desert ecotone. Arid Land Geography, 30(5): 660–665.(in Chinese)
Ma C, Ren Z, Li X, 2013. Land use change flow and its spatial agglomeration in the loess platform region. Acta Geographica Sinica, 68(2): 257–267.(in Chinese)
Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China (MLR, PRC). GB/T21010-2007 Classification of Land Use Status. (in Chinese)
Pascual J I, Lorente N, Song Z et al., 2003. Selectivity in vibrationally mediated single-molecule chemistry. Nature, 423(6939): 525–528.
Pontius R G, Shusas E, McEachern M, 2004. Detecting important categorical land changes while accounting for persistence. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 101(2/3): 251–268.
Saiko T A, Zonn I S, 2000. Irrigation expansion and dynamics of desertification in the circum-Aral region of Central Asia. Applied Geography, 20(4): 349–367.
Su L, Abudu S, Hudan T et al., 2011. Effects of under-mulch drip irrigation on soil salinity distribution and cotton yield in an arid region. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 48(4): 708–714.(in Chinese)
Sun L, Luo Y, 2013. Study on the evolution trends of soil salinity in cotton field under long-term drip irrigation. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 20(1): 186–192.(in Chinese)
Sun L, Luo Y, Yang C J et al., 2012. Salt Distribution and accumlation in soils different in rate of under-mulch drip irrigation with brackish water. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 49(3): 428–436.(in Chinese)
Sun P, Zhou H, Li Y et al., 2010. Trunk sap flow and water consumption of Haloxylon ammodedron growing in the Gurbantunggut Desert. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30(24): 6901–6909.(in Chinese)
Tang F, Chen X, Luo G et al., 2006. Two typical LUCC process and driving force analysis in the oasis of arid region: A case study of Sangong River watershed in north Tianshan Mountain. Science China: Earth Science, 36(Suppl. II): 58–67. (in Chinese)
Turner II B, 1994. Local faces, global flows: The role of land use and land cover in global environmental change. Land Degradation and Rehabilitation, 5(2): 71–78.
Wang J, Bai J, Luo G et al., 2015. Growth and water consumption characteristics of cotton in Manas Basin during recent 34 years. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 46(8): 83–89.(in Chinese)
Wang Z, Shi Q, Wang T et al., 2011. Spatial-temporal characteristics of vegetation cover change in mountainoasis-desert system of Xinjiang from 1982 to 2006. Journal of Natural Resources, 26(4): 609–618. (in Chinese)
Yan J, Chen X, Luo G et al., 2005. Response of the changes of shallow groundwater level and quality to LUCC driven by artificial factors: A case study in Sangong River Watershed in Xinjiang. Journal of Natural Resources, 20(2): 172–180.(in Chinese)
Yan J, Chen X, Luo G et al., 2006. Ground water level temporal and spatial variation in response t o the change of land cover in arid oasis region. Chinese Science Bulletin, 51(Suppl I): 42–48. (in Chinese)
Yang Y, Zheng D, Zhang X et al., 2013. The spatial coupling of land use changes and its environmental effects on Hotan oasis during 1980–2010. Acta Geographica Sinica, 68(6): 813–824.(in Chinese)
Ye Y, Fang X, Ren Y et al., 2009. Cropland cover change in Northeast China during the past 300 years. Science China: Earth Science, 39(3): 340–350.(in Chinese)
Zhao W, Liu H, 2006. Recent advances in desert vegetation response to groundwater table changes. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26(8): 2702–2708. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation: National Natural Science Foundation of China, No.U1303382; The National Basic Research Program of China, No.2014CB460603; The Project of State Key Laboratory of Desert and Oasis Ecology, No.Y471163
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Luo, G., Li, L. et al. An analysis of oasis evolution based on land use and land cover change: A case study in the Sangong River Basin on the northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains. J. Geogr. Sci. 27, 223–239 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-017-1373-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-017-1373-9