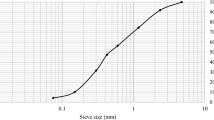
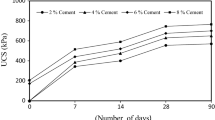
Abstract
One of the major challenges that countries all over the world are dealing with is their generated waste. Most of the research in the past few decades also focuses on the bulk utilization of this existing waste for different applications. This study focuses on the utilization of a part of municipal solid waste, i.e., MSW fines (particle size < 4.75 mm) reinforced with segregated fibers from the waste itself. The research investigates the influence of waste fiber content (FC) (0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, and 10%) on the dynamic parameters of MSW fines. The results revealed that the fiber inclusion remarkably influenced the shear strength parameters under monotonic loading and attained their optimum values when 8% of fiber content was applied. This study shows no significant improvements in dynamic shear modulus (G) of fiber-reinforced MSW fines under cyclic loading in the case of both unconsolidated undrained and consolidated undrained tests conducted on a cyclic triaxial test system. However, a significant improvement was noticed in the case of damping ratio (D) with FC. Further, a ru (excess pore water pressure ratio) model for fiber-reinforced MSW fines is suggested to predict the behavior of ru, which depends on two parameters, namely FC and γ (shear strain).











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data, models, and code generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
References
Adampira M, Derakhshandi M (2020) Influence of a layered liquefiable soil on seismic site response using physical modeling and numerical simulation. Eng Geol 266:105462. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENGGEO.2019.105462
Alidoust P, Keramati M, Shariatmadari N (2018) Laboratory studies on effect of fiber content on dynamic characteristics of municipal solid waste. Waste Manag 76:126–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WASMAN.2018.02.038
Altun S, Göktepe AB, Lav MA (2015) Liquefaction resistance of sand reinforced with geosynthetics. Geosynth Int 15:322–332. https://doi.org/10.1680/GEIN.2008.15.5.322
ASTM D3999 (2013) Standard test method for the determination of the modulus and damping properties of soils using the triaxial apparatus. West Conshohocken
ASTM D5311 (1992) Standard test method for load controlled cyclic triaxial strength of soil. United States, Philadelphia
Athanasopoulos G, Grizi A, Zekkos D et al (2008) Municipal solid waste as a reinforced soil: investigation using synthetic waste, pp 168–175. https://doi.org/10.1061/40970(309)21
Bhatnagar A, Kaczala F, Burlakovs J et al (2017) Hunting for valuables from landfills and assessing their market opportunities A case study with Kudjape landfill in Estonia. Waste Manag Res 35:627–635. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X17697816
Blair J, Mataraarachchi S (2021) A review of landfills, waste and the nearly forgotten nexus with climate change. Environments 8(8):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/ENVIRONMENTS8080073
Booker JR, Rahman MS, Seed HB (1976) GADFLEA: a computer program for the analysis of pore pressure generation and dissipation during cyclic or earthquake loading. Unknown
Parrodi JCH, Höllen D, Pomberger R (2018) Characterization of fine fractions from landfill mining: a review of previous investigations. Detritus 2:46–62.
Chakrabortty P, Roshan AR, Das A (2020) Evaluation of dynamic properties of partially saturated sands using cyclic triaxial tests. Indian Geotech J 50:948–962. https://doi.org/10.1007/S40098-020-00433-3
Chattaraj R, Sengupta A (2017) Dynamic properties of fly ash. J Mater Civ Eng 29:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0001712
Chen M, Shen SL, Arulrajah A et al (2015) Laboratory evaluation on the effectiveness of polypropylene fibers on the strength of fiber-reinforced and cement-stabilized Shanghai soft clay. Geotext Geomembr 43:515–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GEOTEXMEM.2015.05.004
Cossu R (1995) Preliminary study for a landfill mining project in Sardinia. In: Proceedings, Sardinia’95, 5th international landfill symposium. Caglari, pp 841–850
Das A, Chakrabortty P (2021) Large strain dynamic characteristics of quaternary alluvium sand with emphasis on empirical pore water pressure generation model. Eur J Environ Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2021.1916605
Debnath P, Dey AK (2017) Bearing capacity of geogrid reinforced sand over encased stone columns in soft clay. Geotext Geomembr 45:653–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GEOTEXMEM.2017.08.006
Degregorio VB, Member A (1990) Loading systems, sample preparation, and liquefaction. J Geotech Eng 116:805–821. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1990)116:5(805)
Dobry R (1987) Dynamic properties and seismic response of soft clay deposits. In: International symposium of geotechnical engineering of soft soils. Sociedad Mexicana de Mecanica de suelos, pp 51–86
Eskisar T, Altun S, Karakan E (2015) Assessment of liquefaction behavior of Izmir sand reinforced with randomly distributed fibers. In: 6th international conference on earthquake geotechnical engineering. Christchurch, New Zealand
Eskisar T, Karakan E, Altun S (2016) Effects of fibre reinforcement on liquefaction behaviour of poorly graded sands. Procedia Eng 161:538–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROENG.2016.08.688
Fatahi B, Fatahi B, Le TM, Khabbaz H (2015) Small-strain properties of soft clay treated with fibre and cement. Geosynth Int 20:286–300. https://doi.org/10.1680/GEIN.13.00018
Ghadr S (2020) Effect of grain size on undrained anisotropic behaviour of sand–fibre composite. Transp Geotech 22:100323. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TRGEO.2020.100323
Green RA, Green RA, Mitchell JK, Polito CP (2000) An energy-based excess pore pressure generation model for cohesionless soils. In: Proceedings of the John Booker memorial symposium. A.A. Balkema Publishers, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, pp 1–9
Haeri SM, Noorzad R, Oskoorouchi AM (2000) Effect of geotextile reinforcement on the mechanical behavior of sand. Geotext Geomembr 18:385–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0266-1144(00)00005-4
Hamidi A, Hooresfand M (2013) Effect of fiber reinforcement on triaxial shear behavior of cement treated sand. Geotext Geomembr 36:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GEOTEXMEM.2012.10.005
Havanagi Vasant G, Sinha A, Parvathi GS, Satish C (2017) Municipal solid waste in road embankment construction: a case study Article. J Indian Roads Congr 2:79–90
Idriss IM, Dobry R, Singh RD (1978) Nonlinear behavior of soft clays during cyclic loading. J Geotech Eng Div 104:1427–1447. https://doi.org/10.1061/AJGEB6.0000727
Jakka RS, Datta M, Ramana GV (2010) Liquefaction behaviour of loose and compacted pond ash. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 30:580–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOILDYN.2010.01.015
Kaartinen T, Sormunen K, Rintala J (2013) Case study on sampling, processing and characterization of landfilled municipal solid waste in the view of landfill mining. J Clean Prod 55:56–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2013.02.036
Kavazanjian Jr ED, Matasovic NE BR (1999) Large-diameter static and cyclic laboratory testing of municipal solid waste. In: Proceedings Sardinia, pp 437–444
Keramati M, Shariatmadari N, Sabbaghi M, Sadegh Abedin M (2018) Effect of confining stress and loading frequency on dynamic behavior of municipal solid waste in Kahrizak landfill. Int J Environ Sci Technol 15:1257–1264. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13762-017-1465-1/TABLES/3
Kilis EK, Üniversitesi A, Sezer A et al (2017) Dynamic behavior of a clayey sand reinforced with polypropylene fiber. In: Spec issue 3rd Int Conf Comput Exp Sci Eng (ICCESEN 2016) ACTA Phys Pol A, vol 132, pp 674–678. https://doi.org/10.12693/APhysPolA.132.674
Kokusho T (2013) Liquefaction potential evaluations: energy-based method versus stress-based method. Can Geotech J 50:1088–1099. https://doi.org/10.1139/CGJ-2012-0456/ASSET/IMAGES/CGJ-2012-0456IEQ56.GIF
Krishnaswamy NR, Thomas Isaac N (1994) Liquefaction potential of reinforced sand. Geotext Geomembr 13:23–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/0266-1144(94)90055-8
Krishnaswamy NR, Thomas Isaac N (1995) Liquefaction analysis of saturated reinforced granular soils. J Geotech Eng 121:645–651. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1995)121:9(645)
Krook J, Svensson N, Eklund M (2012) Landfill mining: a critical review of two decades of research. Waste Manag 32:513–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WASMAN.2011.10.015
Kumar A, Gupta D (2016) Behavior of cement-stabilized fiber-reinforced pond ash, rice husk ash–soil mixtures. Geotext Geomembr 44:466–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GEOTEXMEM.2015.07.010
Luo J, Miao L, Wang Z, Shi W (2015) Modified cam-clay model with dynamic shear modulus under cyclic loads. J Vibroeng 17:112–124
Maher MH, Woods RD (1990) Dynamic response of sand reinforced with randomly distributed fibers. J Geotech Eng 116:1116–1131. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1990)116:7(1116)
Maheshwari BK, Singh HP, Saran S (2013) Closure to “Effects of reinforcement on liquefaction resistance of Solani sand. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 139:1634–1635. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000935
Mönkäre TJ, Palmroth MRT, Rintala JA (2016) Characterization of fine fraction mined from two Finnish landfills. Waste Manag 47:34–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WASMAN.2015.02.034
Noorany I, Uzdavines M (1989) Dynamic behavior of saturated sand reinforced with geosynthetic fabrics. In: Geosynthetics’ 89 Conf., pp 385–396
Park HI, Lee SR, Do NY (2002) Evaluation of decomposition effect on long-term settlement prediction for fresh municipal solid waste landfills. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 128:107–118. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2002)128:2(107)
Prechthai T, Padmasri M, Visvanathan C (2008) Quality assessment of mined MSW from an open dumpsite for recycling potential. Resour Conserv Recycl 53:70–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RESCONREC.2008.09.002
Prevost JH (1985) A simple plasticity theory for frictional cohesionless soils. Int J Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 4:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/0261-7277(85)90030-0
Punthutaecha K, Puppala AJ, Vanapalli SK, Inyang H (2006) Volume change behaviors of expansive soils stabilized with recycled ashes and fibers. J Mater Civ Eng 18:295–306. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(2006)18:2(295)
Quaghebeur M, Laenen B, Geysen D et al (2013) Characterization of landfilled materials: screening of the enhanced landfill mining potential. J Clean Prod 55:72–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2012.06.012
Ram AK, Mohanty S (2021) Experimental investigation on dynamic behavior of silt-rich fly ash using cyclic triaxial and bender element tests. Innov Infrastruct Solut 6:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/S41062-021-00582-1
Ramaiah BJ, Ramana GV, Bansal BK (2016) Field and large scale laboratory studies on dynamic properties of emplaced municipal solid waste from two dump sites at Delhi, India. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 90:340–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOILDYN.2016.09.001
Ramaiah BJ, Ramana GV, Kavazanjian E et al (2016) Empirical model for shear wave velocity of municipal solid waste in situ. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 142:06015012. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001389
Ramaiah BJ, Ramana G V., Kavazanjian E, Bansal BK (2016) Dynamic properties of municipal solid waste from a dump site in Delhi, India. In: Geo-Chicago; Sustainable geoenvironmental systems, geotechnical special publication, vol 271, pp 121–130
Rawat P, Mohanty S (2021) Experimental investigation on MSW fine mixed with fibers: fiber reinforced waste. J Hazard Toxic Radioact Waste 25:04021009. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HZ.2153-5515.0000609
Rawat P, Mohanty S (2022) Parametric study on dynamic characterization of municipal solid waste fine fractions for geotechnical purpose. J Hazard Toxic Radioact Waste 26:04021047. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HZ.2153-5515.0000659
Seed HB, Martin PP, Lysmer J (1975) The generation and dissipation of pore water pressures during soil liquefaction
Skempton AW (2015) The pore-pressure coefficients A and B. Geotechnique 4:143–147. https://doi.org/10.1680/GEOT.1954.4.4.143
Somani M, Datta M, Ramana G, Sreekrishnan TR (2018) Investigations on fine fraction of aged municipal solid waste recovered through landfill mining: case study of three dumpsites from India. Waste Manag Res 36:744–755. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X18782393
Tang CS, Shi B, Zhao LZ (2010) Interfacial shear strength of fiber reinforced soil. Geotext Geomembr 28:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GEOTEXMEM.2009.10.001
Tielemans Y, Laevers P (2010) Closing the circle, an enhanced landfill mining case. In: 1st international symposium on enhanced landfill mining. Houthalen-Helchteren, Belgium
Towhata I, Kawano Y, Yonai Y et al (2004) Laboratory tests on dynamic properties of municipal wastes. In: 11th conference in soil dynamics and earthquake engineering and the 3rd international conference on earthquake geotechnical engineering, pp 688–693
Ulmans L (2011) Landfill mining: a multi-actor approach on policy preparation. In: Proceedings Sardinia 2011, thirteenth international waste management and landfill symposium. S. Margherita di Pula, Cagliari, Italy
Vijayasri T, Patra N, Raychowdhury P (2016) Cyclic behavior and liquefaction potential of renusagar pond ash reinforced with geotextiles. J Mater Civ Eng 28:04016125. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0001633
Wanka S, Münnich K, Fricke K (2017) Landfill mining—wet mechanical treatment of fine MSW with a wet jigger. Waste Manag 59:316–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WASMAN.2016.10.050
Wolfsberger T, Nispel J, Sarc R et al (2015) Landfill mining: development of a theoretical method for a preliminary estimate of the raw material potential of landfill sites. Waste Manag Res 33:671–680. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X15590473
Ye B, Cheng ZR, Liu C et al (2017) Liquefaction resistance of sand reinforced with randomly distributed polypropylene fibres. Geosynth Int 24:625–636. https://doi.org/10.1680/JGEIN.17.00029/ASSET/IMAGES/SMALL/JGEIN.17.00029-F16.GIF
Yetimoglu T, Salbas O (2003) A study on shear strength of sands reinforced with randomly distributed discrete fibers. Geotext Geomembr 21:103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0266-1144(03)00003-7
Yoo C, Abbas Q (2020) Laboratory investigation of the behavior of a geosynthetic encased stone column in sand under cyclic loading. Geotext Geomembr 48:431–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GEOTEXMEM.2020.02.002
Zekkos D, Bray JD, Riemer MF (2008) Shear modulus and material damping of municipal solid waste based on large-scale cyclic triaxial testing. Can Geotech J 45:45–58. https://doi.org/10.1139/T07-069/ASSET/IMAGES/T07-069T5H.GIF
Zekkos D, Grizi A, Athanasopoulos G (2013) Experimental investigation of the effect of fibrous reinforcement on shear resistance of soil-waste mixtures. Geotech Test J. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20120190
Zekkos D, Kavazanjian E Jr, Bray J et al (2010) Physical characterization of municipal solid waste for geotechnical purposes. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 136:1231–1241. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000326
Zekkos D, Matasovic N, El-Sherbiny R et al (2010) Dynamic properties of municipal solid waste. In: Dynamic properties of municipal solid waste. In Geotechnical characterization, field measurement, and laboratory testing of municipal solid waste, pp 112–134
Zhang J, Yang Z, Yang Q et al (2021) Pore water pressure model for sands reinforced with randomly distributed fibers based on cyclic triaxial tests. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 148:106812. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOILDYN.2021.106812
Zhao Y, Song L, Huang R et al (2007) Recycling of aged refuse from a closed landfill. Waste Manag Res 25:130–138. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X07074053
Funding
The authors declare no specific funding for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rawat, P., Mohanty, S. Study on cyclic strength and pore water pressure response of fiber-reinforced municipal solid waste (MSW) fines. Acta Geotech. 18, 4389–4403 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-023-01818-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-023-01818-3