Abstract
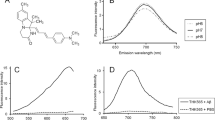
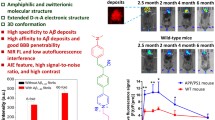
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive and age-related irreversible neurodegenerative disease. When AD occurs, the relevant amount of zinc ions in brain considerably changes. In this contribution, we have explored the possibility of in vivo rapid fluorescence imaging of AD through accurate targeting biomarker of zinc gluconate. By using the 3- and 6-month-old Alzheimer’s model mice (AD-1) as the experimental models, our observations demonstrate that zinc gluconate molecules could pass through the blood–brain barrier and then produce hippocampus region-specific accumulation of fluorescent zinc nanoclusters in vivo, thus allowing kinetically controlled selective imaging of AD by fluorescence bio-imaging.
摘要
阿尔兹海默症是一种与年龄相关的、不可逆转的神经退行性疾病。阿尔兹海默症患者大脑中的锌离子水平会发生明显变化。本文探索了一种基于葡萄糖酸锌的阿尔兹海默症快速荧光标记成像新方法。研究结果表明,葡萄糖酸锌可以通过阿尔兹海默症模型鼠的血脑屏障,富集于病变的海马区并实现对于阿尔兹海默症的精确标记与实时动态靶向荧光成像。


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Citron M (2002) Nat Neurosci 5:1055–1057
Ballard C, Gauthier S, Corbett A et al (2011) Lancet 377:1019–1031
Hardy J, Selkoe DJ (2002) Science 297:353–356
Tao L, Liviu A, Joseph Z et al (2014) Nature 507:448–454
Selkoe DJ (2001) Physiol Rev 81:741–766
Agren MA, Chvapil M, Franzen L (1991) J Surg Res 50:101–105
Powell SR (2000) J Nutr 130:1447S–1454S
Lansdown ABG, Mirastschijski U, Stubbs N et al (2007) Wound Rep Reg 15:2–16
Wang JL, Zhang G, Li QW et al (2013) Sci Rep 3:1157
Gao SP, Chen DH, Li QW et al (2014) Sci Rep 4:4384
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81325011), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2015AA020502, 2012AA022703) and the Major Science and Technology Project of Suzhou (ZXY2012028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, L., Zhao, C., Su, M. et al. In vivo rapid fluorescence imaging of Alzheimer’s disease through accurate target bio-marking of zinc gluconate. Sci. Bull. 60, 1465–1467 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-015-0851-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-015-0851-7