Abstract
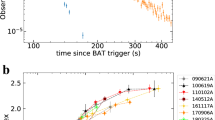
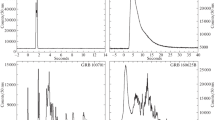
The mono-frequency peak luminosity and the corresponding photon energy of the time-integrated (L sp , E sp ) and peak time (L tp , E tp ) νf ν spectra were derived for a sample of 38 redshift-known Fermi GRBs by fitting the spectra with the Band function. It was found that E tp is generally consistent with E sp , and L tp is averagely three times larger than L sp . The slope of the L tp –E tp relation was consistent with that of the L sp –E sp relation. The photon indices in the peak time spectrum, particularly, the index of the low energy end was, were statistically larger than that in the time-integrated spectrum. These results indicate that L sp and E sp are dominated by L tp and E tp , respectively. The difference of the spectral indices between the time-integrated and peak time spectra may be because of the overlap effect of a series of time-resolved spectra within a GRB. Our simulations, which were based on the observed spectral evolution and correlation between the energy flux and the peak energy within individual GRBs support our speculations. The L tp –E tp relation may be less contaminated by the overlap effect, and it would may be an intrinsic feature of radiation physics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Piran T. Gamma-ray bursts and the fireball model. Phys Rep, 1999, 314: 575–667
Zhang B, Mészáros P. Gamma-ray bursts: Progress, problems and prospects. Int J Modern Phys A, 2004, 19: 2385–2472
Mészáros P. Gamma-ray bursts. Rep Prog Phys, 2006, 69: 2321–2259
Zhang B. Gamma-ray bursts in the swift era. Chin J Astron Astrophys, 2007, 7: 1–50
Gehrels N, Ramirez-Ruiz E, Fox D B. Gamma-ray bursts in the swift era. Annu Rev Astron Astrophys, 2009, 47: 567–617
Liang E. Gamma-ray bursts in the swift-fermi era: Confronting data with theory. Sci China-Phys Mech Astron, 2010, 53: 14–23
Band D, Matteson J, Ford L, et al. BATSE observations of gamma-ray burst spectra. I. Spectral diversity. Astrophys J, 1993, 413: 281–292
Amati L, Frontera F, Tavani M, et al. Intrinsic spectra and energetics of BeppoSAX gamma-ray bursts with known redshifts. Astron Astrophys, 2002, 390: 81–89
Liang E W, Dai Z G, Wu X F. The luminosity-E p relation within gamma-ray bursts and the implications for fireball models. Astrophys J, 2004, 606: L29–L32
Yonetoku D, Murakami T, Nakamura T, et al. Gamma-ray burst formation rate inferred from the spectral peak energy-peak luminosity relation. Astrophys J, 2004, 609: 935–951
Ghirlanda G, Ghisellini G, Lazzati D. The collimation-corrected gamma-ray burst energies correlate with the peak energy of their νF ν spectrum. Astrophys J, 2004, 616: 331–338
Liang E, Zhang B. Model-independent multivariable gamma-ray burst luminosity indicator and its possible cosmological implications. Astrophys J, 2005, 633: 611–623
Dong W, Liang E, Lu R. The flux-E p relation within GRB060218 in comparison with typical GRB pulses. Sci China-Phys Mech Astron, 2010, 53: 78–81
Zhang B, Mészáros P. An analysis of gamma-ray burst spectral break models. Astrophys J, 2002, 581: 1236–1247
Eichler D, Levinson A. An interpretation of the hνpeak–E iso correlation for gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys J, 2004, 614: L13–L16
Nava L, Ghisellini G, Ghirlanda G, et al. On the interpretation of spectral-energy correlations in long gamma-ray bursts. Astron Astrophys, 2006, 450: 471–481
Thompson C, Mészáros P, Rees M J. Thermalization in relativistic out-flows and the correlation between spectral hardness and apparent luminosity in gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys J, 2007, 666: 1012–1023
Abdo A A, Ackermann M, Arimoto M, et al. Fermi observations of high-energy gamma-ray emission from GRB 080916C. Science, 2009, 323: 1688–1693
Zhang B B, Zhang B, Liang E W, et al. A comprehensive analysis of Fermi gamma-ray burst data. I. Spectral components and the possible physical origins of LAT/GBM GRBs. Astrophys J, 2011, 730: 141
Lu R J, Wei J J, Liang E W, et al. A comprehensive analysis of Fermi gamma-ray burst data. II. E p evolution patterns and implications for the observed spectrum-luminosity relations. Astrophys J, 2012, 756: 112
Abdo A A, Ackermann M, Ajello M, et al. Fermi observations of GRB 090902B: A distinct spectral component in the prompt and delayed emission. Astrophys J, 2009, 706: L138–L144
Ryde F, Axelsson M, Zhang B B, et al. Identification and properties of the photospheric emission in GRB090902B. Astrophys J, 2010, 709: L172–L177
Ackermann M, Asano K, Atwood W B, et al. Fermi observations of GRB 090510: A short-hard gamma-ray burst with an additional, hard power-law component from 10 keV to GeV energies. Astrophys J, 2010, 716: 1178–1190
Liang E W, Dai Z G. The peak energy distribution of the νF ν spectra and the implications for the jet structure models of gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys J, 2004, 608: L9–L12
Lamb D Q, Ricker G R, Atteia J L, et al. Scientific highlights of the HETE-2 mission. New Astron Rev, 2004, 48: 423–430
Lv H, Liang E, Tong X. Spectral properties of Fermi/GBM gammaray bursts and the GeV emission detection rate with Fermi/LAT. Sci China-Phys Mech Astron, 2010, 53: 73–77
Sakamoto T, Lamb D Q, Graziani C, et al. High energy transient explorer 2 observations of the extremely soft X-ray flash XRF 020903. Astrophys J, 2004, 602: 875–885
Amati L, Frontera F, Guidorzi C. Extremely energetic Fermi gammaray bursts obey spectral energy correlations. Astron Astrophys, 2009, 508: 173–180
Meegan C, Lichti G, Bhat P N, et al. The fermi gamma-ray burst monitor. Astrophys J, 2009, 702: 791–804
Liang E, Kargatis V. Dependence of the spectral evolution of Γ-ray bursts on their photon fluence. Nature, 1996, 381: 49–51
Lu R J, Hou S J, Liang E W. The E p-flux correlation in the rising and decaying phases of gamma-ray burst pulses: evidence for viewing angle effect? Astrophys J, 2010, 720: 1146–1154
Zhang B, Lu R J, Liang EW, et al. GRB 110721A: Photosphere “death line” and the physical origin of the GRB band function. Astrophys J, 2012, 758: L34
Campana S, Mangano V, Blustin A J, et al. The association of GRB 060218 with a supernova and the evolution of the shock wave. Nature, 2006, 442: 1008–1010
Mészáros P, Rees M J. Steep slopes and preferred breaks in gamma-ray burst spectra: The role of photospheres and comptonization. Astrophys J, 2000, 530: 292–298
Pe’er A, Mészáros P, Rees M J. The observable effects of a photospheric component on GRB and XRF prompt emission spectrum. Astrophys J, 2006, 642: 995–1003
Toma K, Wu X F, Mészáros P. Photosphere-internal shock model of gamma-ray bursts: Case studies of Fermi/LAT bursts. Mon Not R Astron Soc, 2011, 415: 1663–1680
Meszaros P, Rees M J, Papathanassiou H. Spectral properties of blastwave models of gamma-ray burst sources. Astrophys J, 1994, 432: 181–193
Wang X Y, Li Z, Dai Z G, et al. GRB 080916C: On the radiation origin of the prompt emission from keV/MeV to GeV. Astrophys J, 2009, 698: L98–L102
Daigne F, Bošnjak Z, Dubus G. Reconciling observed gamma-ray burst prompt spectra with synchrotron radiation. Astron Astrophys, 2011, 526: A110
Zhao X H, Dai Z G, Liu T, et al. Inverse compton emission from the prompt optical emission region in gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys J, 2010, 708: 1357–1365
Rees M J, Mészáros P. Dissipative photosphere models of gamma-ray bursts and X-ray flashes. Astrophys J, 2005, 628: 847–852
Giannios D. Prompt GRB emission from gradual energy dissipation. Astron Astrophys, 2008, 480: 305–312
Beloborodov A M. Collisional mechanism for gamma-ray burst emission. Mon Not R Astron Soc, 2010, 407: 1033–1047
Pe'er A, Ryde F. A theory of multicolor blackbody emission from relativistically expanding plasmas. Astrophys J, 2011, 732: 49
Racusin J L, Karpov S V, Sokolowski M, et al. Broadband observations of the naked-eye Γ-ray burst GRB080319B. Nature, 2008, 455: 183–188
Kumar P, Panaitescu A. What did we learn from gamma-ray burst 080319B? Mon Not R Astron Soc, 2008, 391: L19–L23
Piran T, Sari R, Zou Y C. Observational limits on inverse compton processes in gamma-ray bursts. Mon Not R Astron Soc, 2009, 393: 1107–1113
Resmi L, Zhang B. Gamma-ray burst prompt emission variability in synchrotron and synchrotron self-compton light curves. Mon Not R Astron Soc, 2012, 426: 1385–1395
Fan Y Z, Wei D M, Zhang F W, et al. The photospheric radiation model for the prompt emission of gamma-ray bursts: Interpreting four observed correlations. Astrophys J, 2012, 755: L6
Zhang B, Pe’er A. Evidence of an initially magnetically dominated out-flow in GRB 080916C. Astrophys J, 2009, 700: L65–L68
Zhang B, Yan H. The internal-collision-induced magnetic reconnection and turbulence (ICMART) model of gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys J, 2011, 726: 90
Giannios D. The peak energy of dissipative gamma-ray burst photospheres. Mon Not R Astron Soc, 2012, 422: 3092–3098
Veres P, Zhang B B, Mészáros P. The extremely high peak energy of GRB 110721A in the context of a dissipative photosphere synchrotron emission model. Astrophys J, 2012, 761: L18
Vurm I, Lyubarsky Y, Piran T. On thermalization in gamma-ray burst jets and the peak energies of photospheric spectra. Astrophys J, 2013, 764: 143
Nemmen R S, Georganopoulos M, Guiriec S, et al. A universal scaling for the energetics of relativistic jets from black hole systems. Science, 2012, 338: 1445–1448
Zhang J, Liang EW, Sun X N, et al. Radiation mechanism and jet composition of gamma-ray bursts and GeV-TeV-selected radio-loud active galactic nuclei. Astrophys J, 2013, 774: L5
Wu Q, Zou Y C, Cao X, et al. A uniform correlation between synchrotron luminosity and doppler factor in gamma-ray bursts and blazars: A hint of similar intrinsic luminosities? Astrophys J, 2011, 740: L21
Wang J, Wei J Y. Gamma-ray burst afterglows as analogs of high-frequency-peaked BL Lac objects. Astrophys J, 2011, 726: L4
Wang F Y, Yi S X, Dai Z G. Similar radiation mechanism in gamma-ray bursts and blazars: Evidence from two luminosity correlations. arXiv: 1403.7857
Fossati G, Maraschi L, Celotti A, et al. A unifying view of the spectral energy distributions of blazars. Mon Not R Astron Soc, 1998, 299: 433–448
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lyu, F., Wang, Y., Liang, Y. et al. Comparison between the time-integrated spectrum and the peak time spectrum of gamma-ray bursts and possible implications. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 58, 1–8 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-014-5575-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-014-5575-1