Abstract
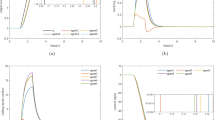
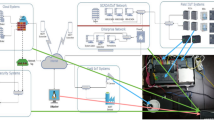
This study investigates the reliable control design for a class of interconnected nonlinear systems subjected to actuator faults, disturbances, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. DoS attacks are carried out in both sensor and controller channels. An integrated event-observer-based security sliding mode fault-tolerant control approach is presented to defend against DoS attacks and compensate for faults and disturbances. To be more specific, the fuzzy logic system (FLS) theory is used to approximate the unknown nonlinear component first. Using the output measurement and sensor channel triggered output information, an FLS aided nonlinear estimator is put forward, in which the faults and disturbances are reconstructed. Then, to achieve the trajectory tracking purpose in the presence of DoS attacks, actuator faults, and disturbances, an adaptive sliding mode manifold is established, based on which an event-driven mechanism is established and a reliable controller is designed. In the controller scheme, the fault compensation and disturbance rejection mechanisms are also included synchronously. The tracking ability is analyzed using the Lyapunov method and the FLS theory, followed by applications to an interconnected power network system and an interconnected inverted pendulum system to demonstrate the applicability of the proposed method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keller J Y, Chabir K, Sauter D. Input reconstruction for networked control systems subject to deception attacks and data losses on control signals. Int J Syst Sci, 2016, 47: 814–820
Ye D, Diao N N, Zhao X G. Fault-tolerant controller design for general polynomial-fuzzy-model-based systems. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst, 2018, 26: 1046–1051
Tong S, Huo B, Li Y. Observer-based adaptive decentralized fuzzy fault-tolerant control of nonlinear large-scale systems with actuator failures. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst, 2014, 22: 1–15
Guo B, Chen Y. Event-triggered robust adaptive sliding mode fault-tolerant control for nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans Ind Inf, 2020, 16: 6982–6992
Xiao S, Han Q L, Ge X, et al. Secure distributed finite-time filtering for positive systems over sensor networks under deception attacks. IEEE Trans Cybern, 2020, 50: 1220–1229
Chabukswar R, Mo Y, Sinopoli B. Detecting integrity attacks on SCADA systems. IFAC Proc Vol, 2011, 44: 11239–11244
Li X, Wen C, Chen C. Resilient cooperative control for networked Lagrangian systems against DoS attacks. IEEE Trans Cybern, 2022, 52: 836–848
Chen C C, Xu S S D, Liang Y W. Study of nonlinear integral sliding mode fault-tolerant control. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron, 2016, 21: 1160–1168
Li Y X, Yang G H. Fuzzy adaptive output feedback fault-tolerant tracking control of a class of uncertain nonlinear systems with nonaffine nonlinear faults. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst, 2016, 24: 223–234
Shen Q, Yue C, Goh C H, et al. Active fault-tolerant control system design for spacecraft attitude maneuvers with actuator saturation and faults. IEEE Trans Ind Electron, 2019, 66: 3763–3772
Jing Y H, Yang G H. Fuzzy adaptive fault-tolerant control for uncertain nonlinear systems with unknown dead-zone and unmodeled dynamics. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst, 2019, 27: 2265–2278
Wu C, Liu J, Xiong Y, et al. Observer-based adaptive fault-tolerant tracking control of nonlinear nonstrict-feedback systems. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst, 2018, 29: 3022–3033
Van M, Ge S S. Adaptive fuzzy integral sliding-mode control for robust fault-tolerant control of robot manipulators with disturbance observer. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst, 2021, 29: 1284–1296
Zhang L, Yang G H. Observer-based adaptive decentralized fault-tolerant control of nonlinear large-scale systems with sensor and actuator faults. IEEE Trans Ind Electron, 2019, 66: 8019–8029
Hu S, Yue D, Han Q L, et al. Observer-based event-triggered control for networked linear systems subject to denial-of-service attacks. IEEE Trans Cybern, 2020, 50: 1952–1964
Ma R, Shi P, Wu L. Dissipativity-based sliding-mode control of cyber-physical systems under denial-of-service attacks. IEEE Trans Cybern, 2021, 51: 2306–2318
Wu C, Wu L, Liu J, et al. Active defense-based resilient sliding mode control under denial-of-service attacks. IEEE Trans Inform Forensic Secur, 2020, 15: 237–249
de Persis C, Tesi P. Input-to-state stabilizing control under denial-of-service. IEEE Trans Automat Contr, 2015, 60: 2930–2944
Jiang X, Mu X, Hu Z. Decentralized adaptive fuzzy tracking control for a class of nonlinear uncertain interconnected systems with multiple faults and denial-of-service attack. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst, 2021, 29: 3130–3141
An L, Yang G H. Decentralized adaptive fuzzy secure control for nonlinear uncertain interconnected systems against intermittent DoS attacks. IEEE Trans Cybern, 2019, 49: 827–838
Shao X, Ye D. Fuzzy adaptive event-triggered secure control for stochastic nonlinear high-order MASs subject to DoS attacks and actuator faults. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst, 2021, 29: 3812–3821
Zhang C H, Yang G H. Event-triggered global finite-time control for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans Automat Contr, 2020, 65: 1340–1347
Wang A, Liu L, Qiu J, et al. Event-triggered robust adaptive fuzzy control for a class of nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst, 2019, 27: 1648–1658
Li J, Yang Z, Mu X, et al. Passivity-based event-triggered fault tolerant control for nonlinear networked control system with actuator failures and DoS jamming attacks. J Franklin Institute, 2020, 357: 9288–9307
Tang Y, Zhang D, Shi P, et al. Event-based formation control for nonlinear multiagent systems under DoS attacks. IEEE Trans Automat Contr, 2021, 66: 452–459
Pan H, Chang X, Zhang D. Event-triggered adaptive control for uncertain constrained nonlinear systems with its application. IEEE Trans Ind Inf, 2020, 16: 3818–3827
Li Y M, Tong S C. Prescribed performance adaptive fuzzy output-feedback dynamic surface control for nonlinear large-scale systems with time delays. Inf Sci, 2015, 292: 125–142
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Scientific and Technical Programs of Sichuan Province of China (Grant No. 2021YJ0092) and National Key Research and Development of China (Grant No. 2018YFB1307401).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, B., Dian, S. & Zhao, T. Active event-driven reliable defense control for interconnected nonlinear systems under actuator faults and denial-of-service attacks. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 65, 162205 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-021-3397-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-021-3397-2